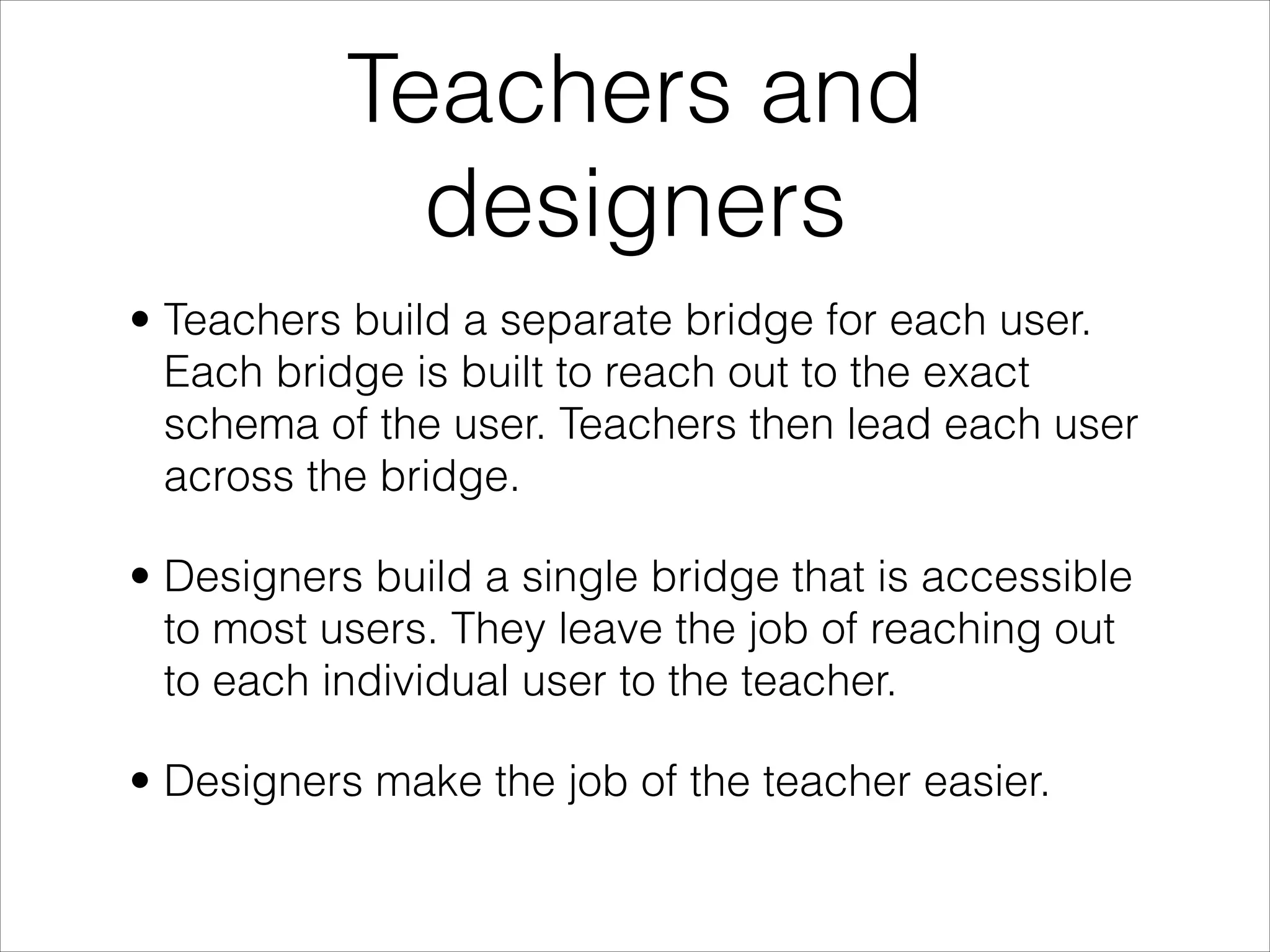
The document discusses the role of analogies in learning, emphasizing that they allow individuals to understand new concepts by connecting them to familiar ideas. It outlines the limitations of analogies and the need for them to be tailored to the learner's existing knowledge, comparing them to bridges that must be custom-built for effective use. It also differentiates the roles of teachers and designers in constructing these analogies, with teachers focusing on individual users and designers aiming to create accessible analogies for broader audiences.