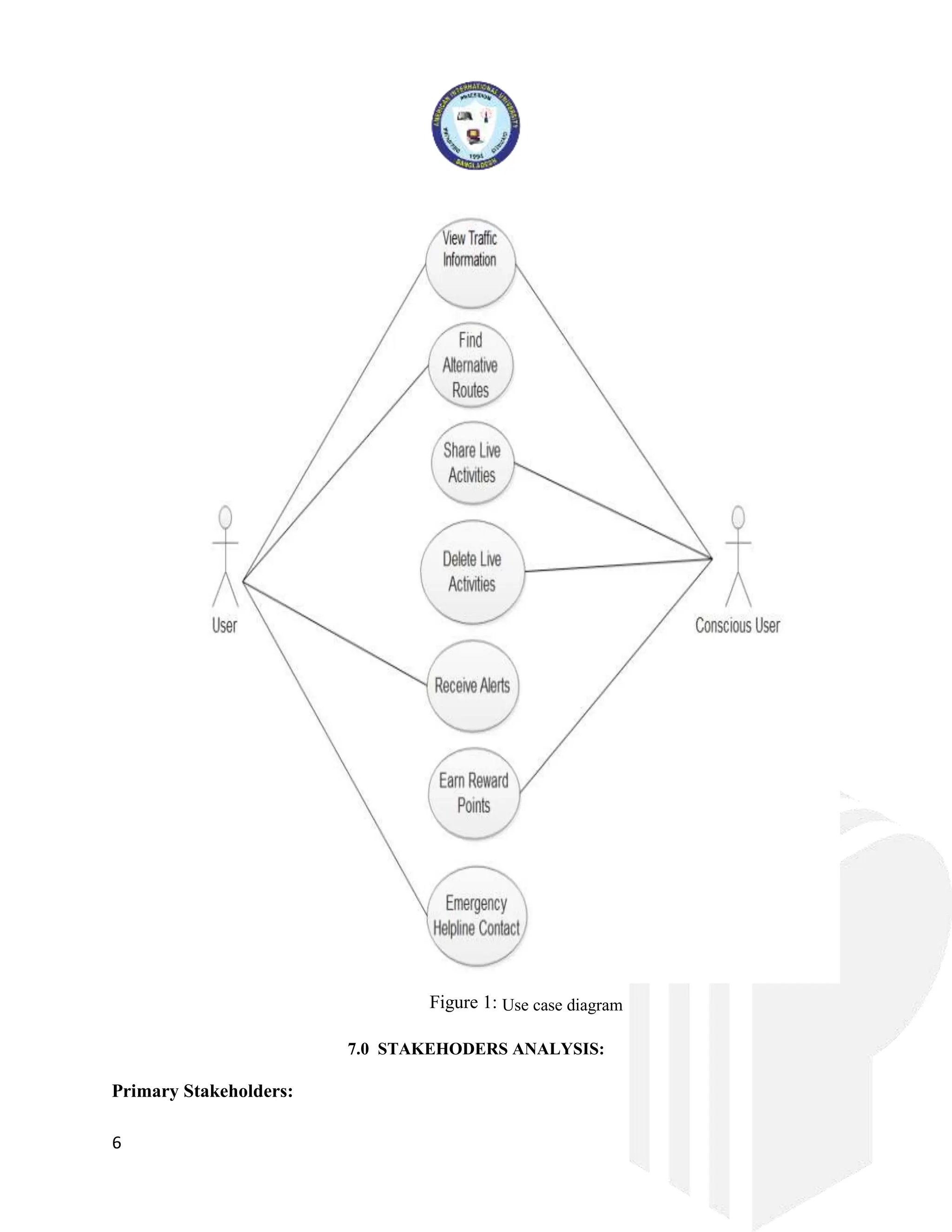
The document outlines a project for developing a traffic avoidance application aimed at improving urban transportation in Bangladesh by providing real-time traffic information and route suggestions. It details project management approaches, objectives, stakeholder analysis, milestones, and an agile development methodology. The application will allow users to avoid congestion, report road conditions, and enhance their travel experience through community-driven input and sophisticated algorithms.