Recommended
PPTX
PPT
brute force ppt lsdgldslgkdsglsdghsdghsdgsg
PPT
BCA Chapter 5 The Greedy Method Notes.ppt
PPT
PPTX
data structure and algorithm (Advanced algorithm Stretegies)
PPT
DAA_Module2 Brute Force and Exhaustive Search FINAL.ppt
PPTX
lecture 1(Fundamental of algorithms).pptx
PPTX
PPT
Design and Analysis of Algorithm Brute Force 1.ppt
PPTX
Chap4TheDesignandAnalysisOfAlgorithm.pptx
PPTX
Design of Algorithms Using Brute Force Approach Advance Algo Anum Rehman.pptx
PPT
introduction design and analysis algorithm
PPTX
Module 2 Design Analysis and Algorithms
PPT
PPT
divide and conquer ppt in Design and Analysis of Algorithms
PPTX
AoA Lec Design of algorithm spresentation
PPTX
Data structures and algo hhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhh
PPTX
PPTX
TRAVELING SALESMAN PROBLEM, Divide and Conquer
PPTX
PPTX
Algorithms : Introduction and Analysis
PPT
Design and analysis of algorithm in Computer Science
PPT
daa notes for students in jmtu018.03.02.ppt
PPTX
PDF
Anlysis and design of algorithms part 1
PDF
whhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhheek 8 Cc.pdf
PPT
PPTX
Design and Analysis of Algorithm for II year Computer science and Engineering...
PPT
the memory system computer arcchitecture
PDF
memory hierarchy in computer architecture
More Related Content
PPTX
PPT
brute force ppt lsdgldslgkdsglsdghsdghsdgsg
PPT
BCA Chapter 5 The Greedy Method Notes.ppt
PPT
PPTX
data structure and algorithm (Advanced algorithm Stretegies)
PPT
DAA_Module2 Brute Force and Exhaustive Search FINAL.ppt
PPTX
lecture 1(Fundamental of algorithms).pptx
PPTX
Similar to brute force methods and its uses........
PPT
Design and Analysis of Algorithm Brute Force 1.ppt
PPTX
Chap4TheDesignandAnalysisOfAlgorithm.pptx
PPTX
Design of Algorithms Using Brute Force Approach Advance Algo Anum Rehman.pptx
PPT
introduction design and analysis algorithm
PPTX
Module 2 Design Analysis and Algorithms
PPT
PPT
divide and conquer ppt in Design and Analysis of Algorithms
PPTX
AoA Lec Design of algorithm spresentation
PPTX
Data structures and algo hhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhh
PPTX
PPTX
TRAVELING SALESMAN PROBLEM, Divide and Conquer
PPTX
PPTX
Algorithms : Introduction and Analysis
PPT
Design and analysis of algorithm in Computer Science
PPT
daa notes for students in jmtu018.03.02.ppt
PPTX
PDF
Anlysis and design of algorithms part 1
PDF
whhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhheek 8 Cc.pdf
PPT
PPTX
Design and Analysis of Algorithm for II year Computer science and Engineering...
More from suganyapownaiya
PPT
the memory system computer arcchitecture
PDF
memory hierarchy in computer architecture
PDF
Arithmetic for computers and its types..
PDF
Nervous System concepts using image processing and deep learning
PPTX
fundamentals of gis concepts and its methods
PPT
object oriented modeling concepts.......
Recently uploaded
PPTX
Presentation-WPS Office.pptx afgouvhyhgfccf
PDF
Soil Compressibility (Elastic Settlement).pdf
PPTX
Designing Work for Humans, Not Machines: Human-Centered Maintenance Excellence
PDF
Shear Strength of Soil/Mohr Coulomb Failure Criteria-1.pdf
PPTX
This Bearing Didn’t Fail Suddenly — How Vibration Data Predicts Failure Month...
PDF
Decision-Support-Systems-and-Decision-Making-Processes.pdf
PDF
Rajesh Prasad- Brief Profile with educational, professional highlights
PDF
engineering management chapter 5 ppt presentation
PDF
Computer Network Lab Manual ssit -kavya r.pdf or Computer Network Lab Manual ...
PPT
Cloud computing-1.ppt presentation preview
PPTX
ME3592 - Metrology and Measurements - Unit - 1 - Lecture Notes
PDF
(en/zhTW) Heterogeneous System Architecture: Design & Performance
PDF
Shear Strength of Soil (Direct shear test).pdf
PDF
Ericsson 6230 Training Module Document.pdf
PPTX
GET 211- Computing and Software Engineering (1).pptx
PPTX
Introduction to AI and Applications Module-4.pptx
PPTX
Basic Volume Mass Relationship and unit weight as function of volumetric wate...
PDF
Applications of AI in Civil Engineering - Dr. Rohan Dasgupta
PPT
Integer , Goal and Non linear Programming Model
PDF
Plasticity and Structure of Soil/Atterberg Limits.pdf
brute force methods and its uses........ 1. 2. 3-2
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
Brute Force
Brute Force
A straightforward approach, usually based directly on the
A straightforward approach, usually based directly on the
problem’s statement and definitions of the concepts involved
problem’s statement and definitions of the concepts involved
Examples:
Examples:
1.
1. Computing
Computing a
an
n
(
(a
a > 0,
> 0, n
n a nonnegative integer)
a nonnegative integer)
2.
2. Computing
Computing n
n!
!
3.
3. Multiplying two matrices
Multiplying two matrices
4.
4. Searching for a key of a given value in a list
Searching for a key of a given value in a list
3. 3-3
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
Brute-Force Sorting Algorithm
Brute-Force Sorting Algorithm
Selection Sort
Selection Sort Scan the array to find its smallest element and
Scan the array to find its smallest element and
swap it with the first element. Then, starting with the second
swap it with the first element. Then, starting with the second
element, scan the elements to the right of it to find the
element, scan the elements to the right of it to find the
smallest among them and swap it with the second elements.
smallest among them and swap it with the second elements.
Generally, on pass
Generally, on pass i
i (0
(0
i
i
n-
n-2), find the smallest element in
2), find the smallest element in
A
A[
[i..n-
i..n-1] and swap it with
1] and swap it with A
A[
[i
i]:
]:
A
A[0]
[0]
. . .
. . .
A
A[
[i
i-1] |
-1] | A
A[
[i
i], . . . ,
], . . . , A
A[
[min
min], . . .,
], . . ., A
A[
[n
n-
-
1]
1]
in their final positions
in their final positions
Example: 7 3 2 5
Example: 7 3 2 5
4. 3-4
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
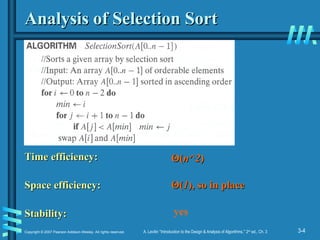
Analysis of Selection Sort
Analysis of Selection Sort
Time efficiency:
Time efficiency:
Space efficiency:
Space efficiency:
Stability:
Stability:
Θ
Θ(
(n^2
n^2)
)
Θ
Θ(
(1
1), so in place
), so in place
yes
5. 3-5
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
Brute-Force String Matching
Brute-Force String Matching
pattern
pattern: a string of
: a string of m
m characters to search for
characters to search for
text
text: a (longer) string of
: a (longer) string of n
n characters to search in
characters to search in
problem: find a substring in the text that matches the pattern
problem: find a substring in the text that matches the pattern
Brute-force algorithm
Brute-force algorithm
Step 1 Align pattern at beginning of text
Step 1 Align pattern at beginning of text
Step 2 Moving from left to right, compare each character of
Step 2 Moving from left to right, compare each character of
pattern to the corresponding character in text until
pattern to the corresponding character in text until
– all characters are found to match (successful search); or
all characters are found to match (successful search); or
– a mismatch is detected
a mismatch is detected
Step 3 While pattern is not found and the text is not yet
Step 3 While pattern is not found and the text is not yet
exhausted, realign pattern one position to the right and
exhausted, realign pattern one position to the right and
repeat Step 2
repeat Step 2
6. 3-6
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
Examples of Brute-Force String Matching
Examples of Brute-Force String Matching
1.
1. Pattern:
Pattern: 001011
001011
Text:
Text: 10010101101001100101111010
10010101101001100101111010
2.
2. Pattern:
Pattern: happy
happy
Text:
Text: It is never too late to have a happy
It is never too late to have a happy
childhood.
childhood.
7. 3-7
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
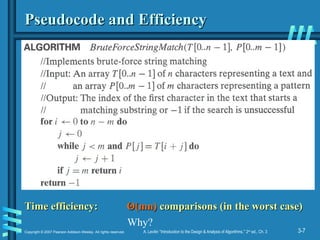
Pseudocode and Efficiency
Pseudocode and Efficiency
Time efficiency:
Time efficiency: Θ
Θ(mn)
(mn) comparisons (in the worst case)
comparisons (in the worst case)
Why?
8. 3-8
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
Brute-Force Polynomial Evaluation
Brute-Force Polynomial Evaluation
Problem: Find the value of polynomial
Problem: Find the value of polynomial
p
p(
(x
x) =
) = a
an
nx
xn
n
+
+ a
an
n-1
-1x
xn
n-1
-1
+… +
+… + a
a1
1x
x1
1
+
+ a
a0
0
at a point
at a point x
x =
= x
x0
0
Brute-force algorithm
Brute-force algorithm
Efficiency:
Efficiency:
p
p
0.0
0.0
for
for i
i
n
n downto
downto 0
0 do
do
power
power
1
1
for
for j
j
1
1 to
to i
i do
do //compute
//compute x
xi
i
power
power
power
power
x
x
p
p
p
p +
+ a
a[
[i
i]
]
power
power
return
return p
p
0
0
i
i
n
n i
i = Θ
Θ(n^2) multiplications
(n^2) multiplications
9. 3-9
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
Polynomial Evaluation: Improvement
Polynomial Evaluation: Improvement
We can do better by evaluating from right to left:
We can do better by evaluating from right to left:
Better brute-force algorithm
Better brute-force algorithm
Efficiency:
Efficiency:
Horner’s Rule is another linear time method.
Horner’s Rule is another linear time method.
p
p
a
a[0]
[0]
power
power
1
1
for
for i
i
1
1 to
to n
n do
do
power
power
power
power
x
x
p
p
p
p +
+ a
a[
[i
i]
]
power
power
return
return p
p
Θ
Θ(
(n)
n) multiplications
multiplications
10. 3-10
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
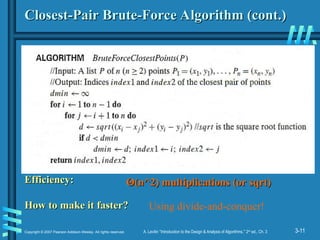
Closest-Pair Problem
Closest-Pair Problem
Find the two closest points in a set of
Find the two closest points in a set of n
n points (in the two-
points (in the two-
dimensional Cartesian plane).
dimensional Cartesian plane).
Brute-force algorithm
Brute-force algorithm
Compute the distance between every pair of distinct points
Compute the distance between every pair of distinct points
and return the indexes of the points for which the distance
and return the indexes of the points for which the distance
is the smallest.
is the smallest.
11. 3-11
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
Closest-Pair Brute-Force Algorithm (cont.)
Closest-Pair Brute-Force Algorithm (cont.)
Efficiency:
Efficiency:
How to make it faster?
How to make it faster?
Θ
Θ(n^2) multiplications (or sqrt)
(n^2) multiplications (or sqrt)
Using divide-and-conquer!
12. 3-12
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
Brute-Force Strengths and Weaknesses
Brute-Force Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths
Strengths
• wide applicability
wide applicability
• simplicity
simplicity
• yields reasonable algorithms for some important
yields reasonable algorithms for some important
problems
problems
(e.g., matrix multiplication, sorting, searching, string
(e.g., matrix multiplication, sorting, searching, string
matching)
matching)
Weaknesses
Weaknesses
• rarely yields efficient algorithms
rarely yields efficient algorithms
• some brute-force algorithms are unacceptably slow
some brute-force algorithms are unacceptably slow
• not as constructive as some other design techniques
not as constructive as some other design techniques
13. 3-13
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
Exhaustive Search
Exhaustive Search
A brute force solution to a problem involving search for an
A brute force solution to a problem involving search for an
element with a special property, usually among
element with a special property, usually among
combinatorial objects such as permutations, combinations, or
combinatorial objects such as permutations, combinations, or
subsets of a set.
subsets of a set.
Method:
Method:
• generate a list of all potential solutions to the problem in a
generate a list of all potential solutions to the problem in a
systematic manner (see algorithms in Sec. 5.4)
systematic manner (see algorithms in Sec. 5.4)
• evaluate potential solutions one by one, disqualifying
evaluate potential solutions one by one, disqualifying
infeasible ones and, for an optimization problem, keeping
infeasible ones and, for an optimization problem, keeping
track of the best one found so far
track of the best one found so far
• when search ends, announce the solution(s) found
when search ends, announce the solution(s) found
14. 3-14
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
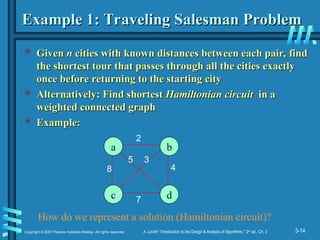
Example 1: Traveling Salesman Problem
Example 1: Traveling Salesman Problem
Given
Given n
n cities with known distances between each pair, find
cities with known distances between each pair, find
the shortest tour that passes through all the cities exactly
the shortest tour that passes through all the cities exactly
once before returning to the starting city
once before returning to the starting city
Alternatively: Find shortest
Alternatively: Find shortest Hamiltonian circuit
Hamiltonian circuit in a
in a
weighted connected graph
weighted connected graph
Example:
Example:
a b
c d
8
2
7
5 3
4
How do we represent a solution (Hamiltonian circuit)?
15. 3-15
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
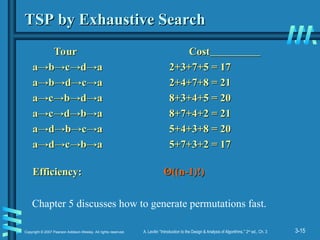
TSP by Exhaustive Search
TSP by Exhaustive Search
Tour Cost
Tour Cost
a→
a→b
b→
→c
c→
→d
d→
→a 2+3+7+5 = 17
a 2+3+7+5 = 17
a→
a→b
b→
→d
d→
→c
c→
→a 2+4+7+8 = 21
a 2+4+7+8 = 21
a→
a→c
c→
→b
b→
→d
d→
→a 8+3+4+5 = 20
a 8+3+4+5 = 20
a→
a→c
c→
→d
d→
→b
b→
→a 8+7+4+2 = 21
a 8+7+4+2 = 21
a→
a→d
d→
→b
b→
→c
c→
→a 5+4+3+8 = 20
a 5+4+3+8 = 20
a→
a→d
d→
→c
c→
→b
b→
→a 5+7+3+2 = 17
a 5+7+3+2 = 17
Efficiency:
Efficiency: Θ
Θ((n-1)!)
((n-1)!)
Chapter 5 discusses how to generate permutations fast.
16. 3-16
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
Example 2: Knapsack Problem
Example 2: Knapsack Problem
Given
Given n
n items:
items:
• weights:
weights: w
w1
1 w
w2
2 … w
… wn
n
• values:
values: v
v1
1 v
v2
2 … v
… vn
n
• a knapsack of capacity
a knapsack of capacity W
W
Find most valuable subset of the items that fit into the knapsack
Find most valuable subset of the items that fit into the knapsack
Example: Knapsack capacity W=16
Example: Knapsack capacity W=16
item weight value
item weight value
1
1 2 $20
2 $20
2
2 5 $30
5 $30
3
3 10 $50
10 $50
4
4 5 $10
5 $10
17. 3-17
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
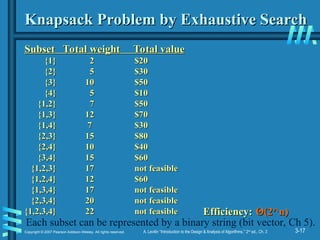
Knapsack Problem by Exhaustive Search
Knapsack Problem by Exhaustive Search
Subset
Subset Total weight
Total weight Total value
Total value
{1} 2 $20
{1} 2 $20
{2} 5 $30
{2} 5 $30
{3} 10 $50
{3} 10 $50
{4} 5 $10
{4} 5 $10
{1,2} 7 $50
{1,2} 7 $50
{1,3} 12 $70
{1,3} 12 $70
{1,4} 7 $30
{1,4} 7 $30
{2,3} 15 $80
{2,3} 15 $80
{2,4} 10 $40
{2,4} 10 $40
{3,4} 15 $60
{3,4} 15 $60
{1,2,3} 17 not feasible
{1,2,3} 17 not feasible
{1,2,4} 12 $60
{1,2,4} 12 $60
{1,3,4} 17 not feasible
{1,3,4} 17 not feasible
{2,3,4} 20 not feasible
{2,3,4} 20 not feasible
{1,2,3,4} 22 not feasible
{1,2,3,4} 22 not feasible Efficiency:
Efficiency: Θ
Θ(2^n)
(2^n)
Each subset can be represented by a binary string (bit vector, Ch 5).
18. 3-18
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
Example 3: The Assignment Problem
Example 3: The Assignment Problem
There are
There are n
n people who need to be assigned to
people who need to be assigned to n
n jobs, one
jobs, one
person per job. The cost of assigning person
person per job. The cost of assigning person i
i to job
to job j
j is C[
is C[i
i,
,j
j].
].
Find an assignment that minimizes the total cost.
Find an assignment that minimizes the total cost.
Job 0 Job 1 Job 2 Job 3
Job 0 Job 1 Job 2 Job 3
Person 0 9
Person 0 9 2 7 8
2 7 8
Person 1 6 4 3 7
Person 1 6 4 3 7
Person 2 5 8 1 8
Person 2 5 8 1 8
Person 3 7 6 9 4
Person 3 7 6 9 4
Algorithmic Plan:
Algorithmic Plan: Generate all legitimate assignments, compute
Generate all legitimate assignments, compute
their costs, and select the cheapest one.
their costs, and select the cheapest one.
How many assignments are there?
How many assignments are there?
Pose the problem as one about a cost matrix:
Pose the problem as one about a cost matrix:
n!
cycle cover
in a graph
19. 3-19
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
9 2 7 8
9 2 7 8
6 4 3 7
6 4 3 7
5 8 1 8
5 8 1 8
7 6 9 4
7 6 9 4
Assignment
Assignment (col.#s)
(col.#s) Total Cost
Total Cost
1, 2, 3, 4
1, 2, 3, 4 9+4+1+4=18
9+4+1+4=18
1, 2, 4, 3
1, 2, 4, 3 9+4+8+9=30
9+4+8+9=30
1, 3, 2, 4
1, 3, 2, 4 9+3+8+4=24
9+3+8+4=24
1, 3, 4, 2
1, 3, 4, 2 9+3+8+6=26
9+3+8+6=26
1, 4, 2, 3
1, 4, 2, 3 9+7+8+9=33
9+7+8+9=33
1, 4, 3, 2
1, 4, 3, 2 9+7+1+6=23
9+7+1+6=23
etc.
etc.
(For this particular instance, the optimal assignment can be found by
(For this particular instance, the optimal assignment can be found by
exploiting the specific features of the number given. It is: )
exploiting the specific features of the number given. It is: )
Assignment Problem by Exhaustive Search
Assignment Problem by Exhaustive Search
C =
C =
2,1,3,4
20. 3-20
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
Final Comments on Exhaustive Search
Final Comments on Exhaustive Search
Exhaustive-search algorithms run in a realistic amount of
Exhaustive-search algorithms run in a realistic amount of
time
time only on very small instances
only on very small instances
In some cases, there are much better alternatives!
In some cases, there are much better alternatives!
• Euler circuits
Euler circuits
• shortest paths
shortest paths
• minimum spanning tree
minimum spanning tree
• assignment problem
assignment problem
In many cases, exhaustive search or its variation is the only
In many cases, exhaustive search or its variation is the only
known way to get exact solution
known way to get exact solution
The Hungarian method
runs in O(n^3) time.
Editor's Notes #10 Draw example.
#11 The basic operation of the algorithm is computing the Euclidean distance between two points.
The square root is a complex operation who’s result is often irrational, therefore the results
can be found only approximately. Computing such operations are not trivial. One can avoid
computing square roots by comparing distance squares instead.


![3-3
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
Brute-Force Sorting Algorithm
Brute-Force Sorting Algorithm
Selection Sort
Selection Sort Scan the array to find its smallest element and
Scan the array to find its smallest element and
swap it with the first element. Then, starting with the second
swap it with the first element. Then, starting with the second
element, scan the elements to the right of it to find the
element, scan the elements to the right of it to find the
smallest among them and swap it with the second elements.
smallest among them and swap it with the second elements.
Generally, on pass
Generally, on pass i
i (0
(0
i
i
n-
n-2), find the smallest element in
2), find the smallest element in
A
A[
[i..n-
i..n-1] and swap it with
1] and swap it with A
A[
[i
i]:
]:
A
A[0]
[0]
. . .
. . .
A
A[
[i
i-1] |
-1] | A
A[
[i
i], . . . ,
], . . . , A
A[
[min
min], . . .,
], . . ., A
A[
[n
n-
-
1]
1]
in their final positions
in their final positions
Example: 7 3 2 5
Example: 7 3 2 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bruteforce1-251229173405-8c1528ff/85/brute-force-methods-and-its-uses-3-320.jpg)


![3-8
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
Brute-Force Polynomial Evaluation
Brute-Force Polynomial Evaluation
Problem: Find the value of polynomial
Problem: Find the value of polynomial
p
p(
(x
x) =
) = a
an
nx
xn
n
+
+ a
an
n-1
-1x
xn
n-1
-1
+… +
+… + a
a1
1x
x1
1
+
+ a
a0
0
at a point
at a point x
x =
= x
x0
0
Brute-force algorithm
Brute-force algorithm
Efficiency:
Efficiency:
p
p
0.0
0.0
for
for i
i
n
n downto
downto 0
0 do
do
power
power
1
1
for
for j
j
1
1 to
to i
i do
do //compute
//compute x
xi
i
power
power
power
power
x
x
p
p
p
p +
+ a
a[
[i
i]
]
power
power
return
return p
p
0
0
i
i
n
n i
i = Θ
Θ(n^2) multiplications
(n^2) multiplications](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bruteforce1-251229173405-8c1528ff/85/brute-force-methods-and-its-uses-8-320.jpg)
![3-9
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
Polynomial Evaluation: Improvement
Polynomial Evaluation: Improvement
We can do better by evaluating from right to left:
We can do better by evaluating from right to left:
Better brute-force algorithm
Better brute-force algorithm
Efficiency:
Efficiency:
Horner’s Rule is another linear time method.
Horner’s Rule is another linear time method.
p
p
a
a[0]
[0]
power
power
1
1
for
for i
i
1
1 to
to n
n do
do
power
power
power
power
x
x
p
p
p
p +
+ a
a[
[i
i]
]
power
power
return
return p
p
Θ
Θ(
(n)
n) multiplications
multiplications](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bruteforce1-251229173405-8c1528ff/85/brute-force-methods-and-its-uses-9-320.jpg)




![3-18
Copyright © 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin “Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms,” 2nd
ed., Ch. 3
Example 3: The Assignment Problem
Example 3: The Assignment Problem
There are
There are n
n people who need to be assigned to
people who need to be assigned to n
n jobs, one
jobs, one
person per job. The cost of assigning person
person per job. The cost of assigning person i
i to job
to job j
j is C[
is C[i
i,
,j
j].
].
Find an assignment that minimizes the total cost.
Find an assignment that minimizes the total cost.
Job 0 Job 1 Job 2 Job 3
Job 0 Job 1 Job 2 Job 3
Person 0 9
Person 0 9 2 7 8
2 7 8
Person 1 6 4 3 7
Person 1 6 4 3 7
Person 2 5 8 1 8
Person 2 5 8 1 8
Person 3 7 6 9 4
Person 3 7 6 9 4
Algorithmic Plan:
Algorithmic Plan: Generate all legitimate assignments, compute
Generate all legitimate assignments, compute
their costs, and select the cheapest one.
their costs, and select the cheapest one.
How many assignments are there?
How many assignments are there?
Pose the problem as one about a cost matrix:
Pose the problem as one about a cost matrix:
n!
cycle cover
in a graph](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bruteforce1-251229173405-8c1528ff/85/brute-force-methods-and-its-uses-18-320.jpg)

