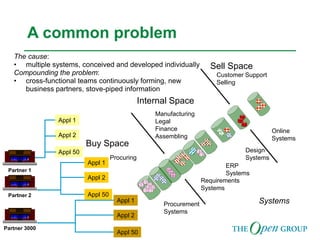
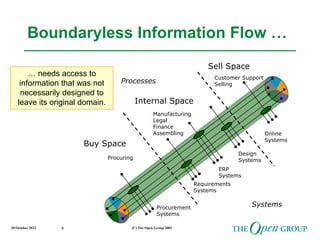
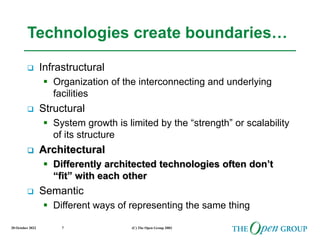
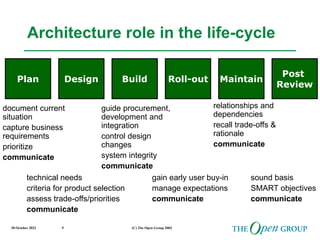
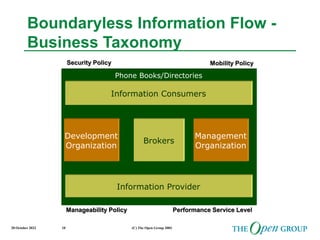
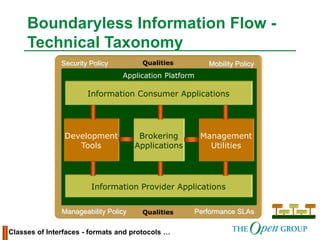
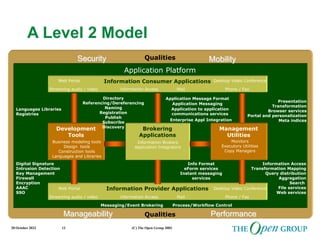
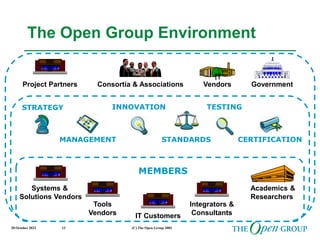
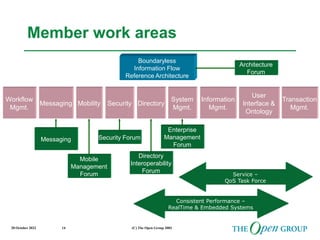
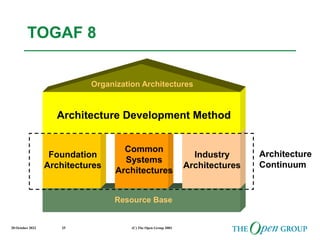
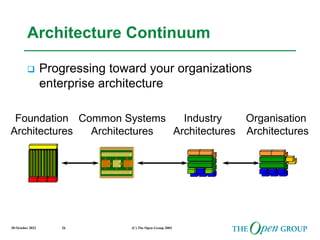
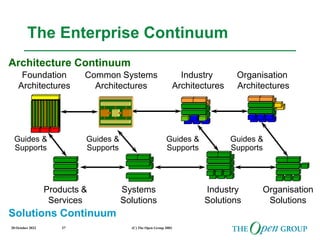
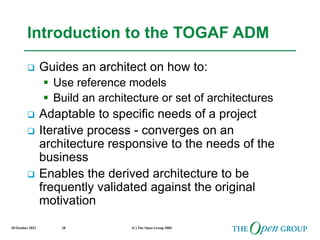
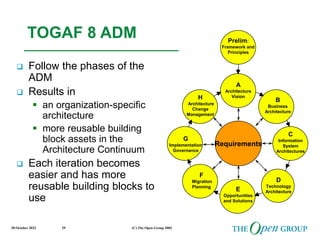
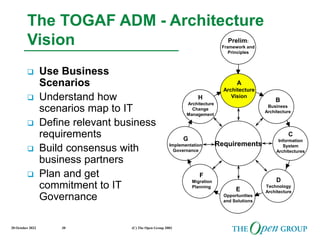
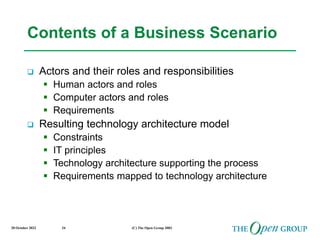
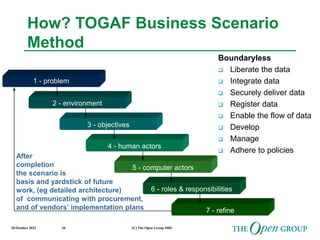
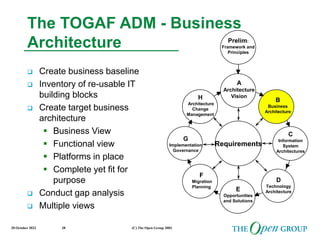
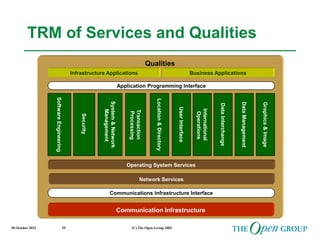
This document discusses the role of architecture in enabling boundaryless information flow. It describes how multiple individual systems have created boundaries that inhibit information sharing. The Open Group's vision is to achieve boundaryless information flow through global interoperability. The document outlines how architecture can guide various stages of the system development life cycle to help break down boundaries and ensure integration. It also provides an overview of The Open Group's architecture forum and framework.