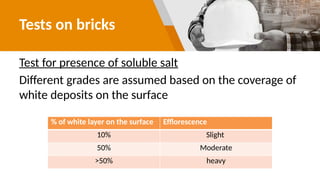
The document provides a comprehensive overview of bricks, including their composition, manufacturing process, classifications, and quality tests. It highlights the importance of bricks as a foundational building material, detailing different types of bricks and their specific uses in construction. Additionally, it outlines the qualities of good bricks and various tests conducted to ensure their standards.