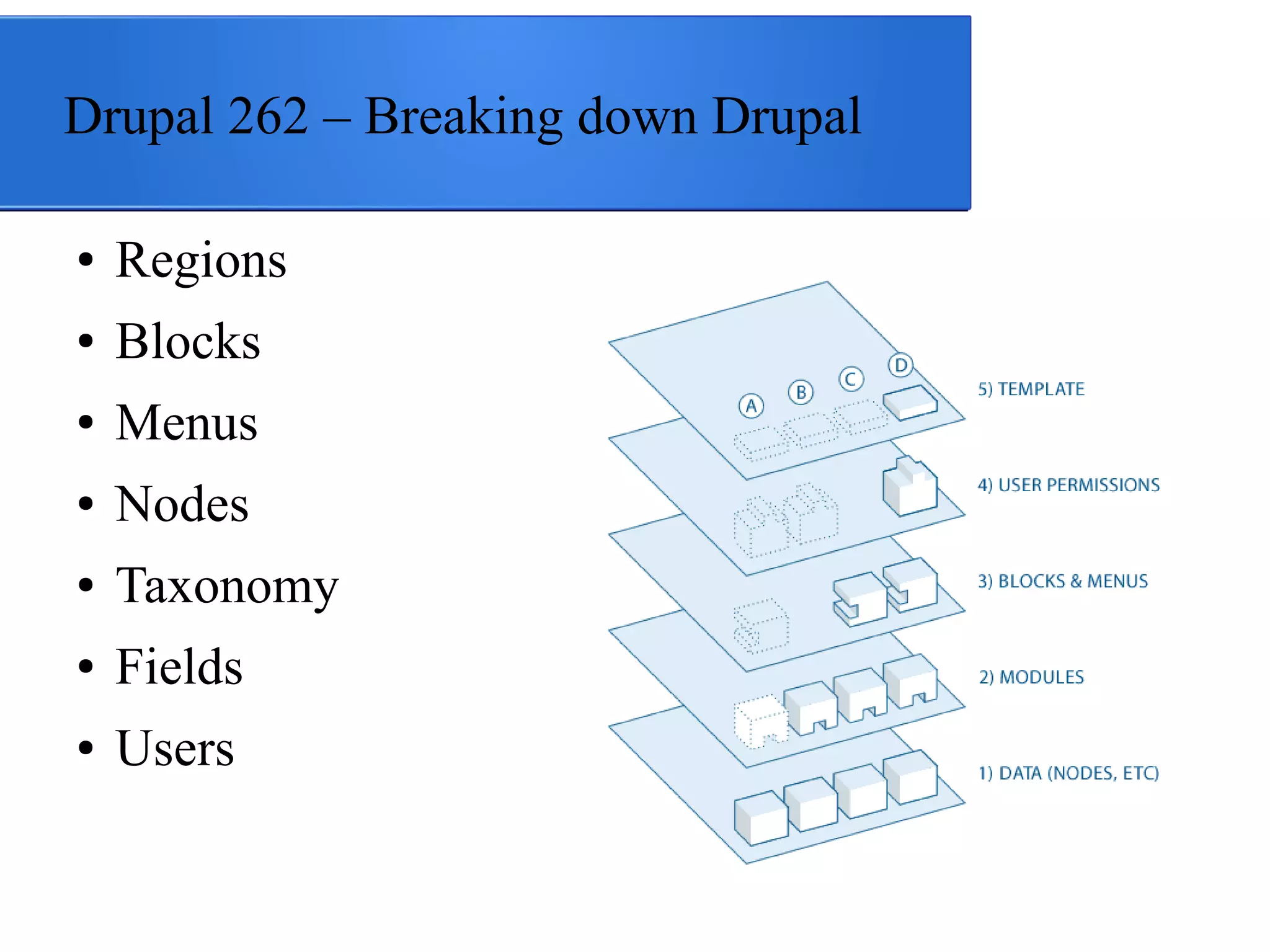
The document outlines the structure and components of Drupal, highlighting key elements such as regions, blocks, menus, nodes, taxonomy, fields, and users. It explains that regions act like an outline for content organization, while blocks and menus facilitate navigation and content display. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of nodes as content endpoints and the role of taxonomy and fields in extending content customization.