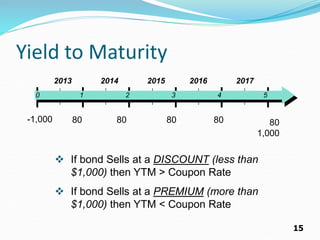
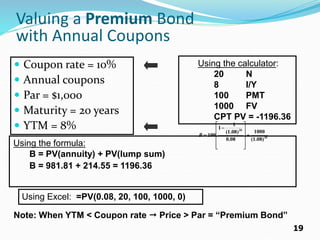
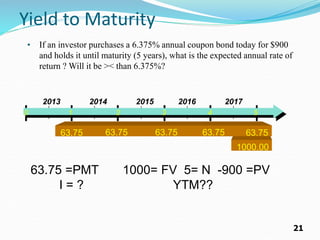
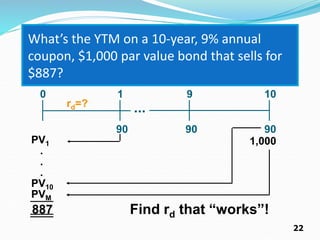
The document provides an overview of bonds, including their basic features such as par value, maturity date, yield to maturity, and coupon rate. It explains how to compute the value of bonds using present value calculations for both annual and semiannual payments, with examples illustrating bonds sold at a discount or premium. Key concepts discussed include bond valuation, cash flows, and the relationship between yield to maturity and coupon rates.










![14
Semiannual Bonds
Semiannual coupon = $70
Semiannual yield = 8%
Periods to maturity = 14
Bond value =
70[1 – 1/(1.08)14] / .08 + 1000
/ (1.08)14 = 917.56
2t
2t
2
YTM
1
F
2
YTM
2
YTM
1
1
-
1
2
C
Value
Bond
14
14
)
08
.
1
(
1000
08
.
0
)
08
.
1
(
1
1
70
B
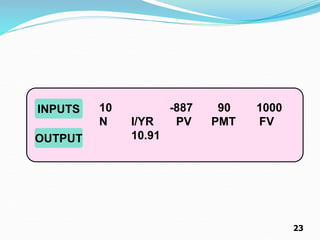
Using the calculator:
14 N
8 I/Y
70 PMT
1000 FV
CPT PV = -917.56
Using Excel: =PV(0.08, 14, 70, 1000, 0)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bondbasics-240614061248-a6676194/85/bond-importance-and-characteristics-pptx-14-320.jpg)