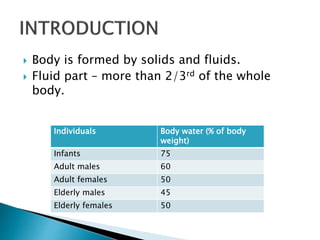
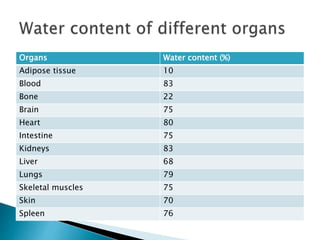
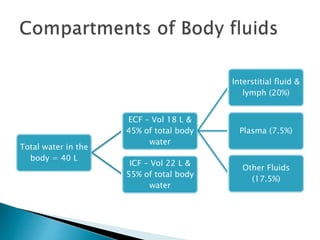
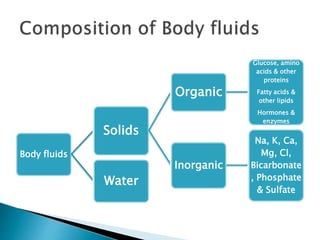
The document discusses the composition and significance of body fluids, highlighting that over two-thirds of the body is made up of fluids. It details the water content in various organs and outlines the roles of body water in homeostasis, transport mechanisms, metabolic reactions, tissue texture, and temperature regulation. The total body water is specified at 40 liters, with distinctions between extracellular and intracellular fluid volumes.