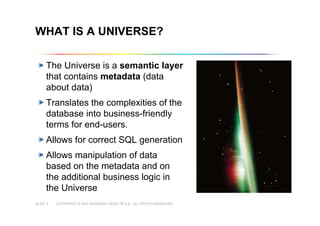
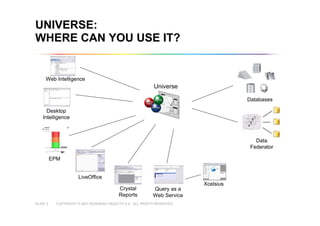
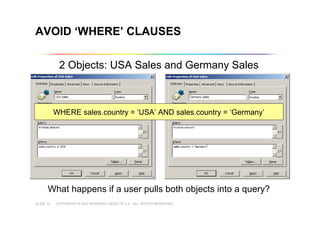
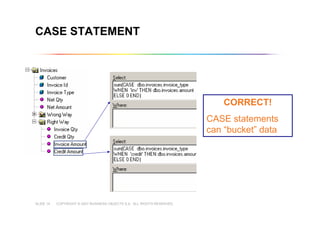
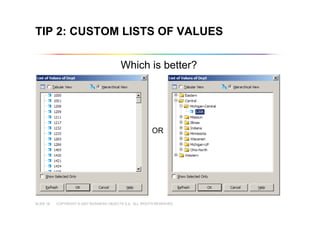
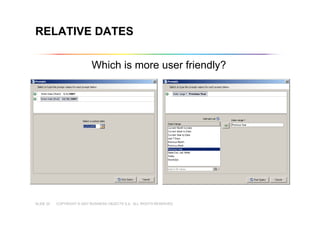
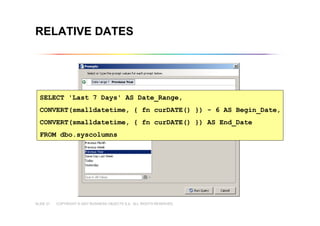
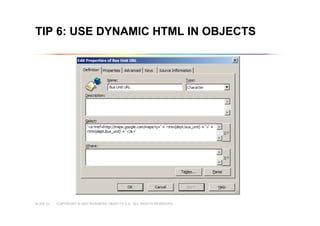
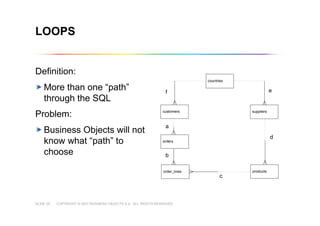
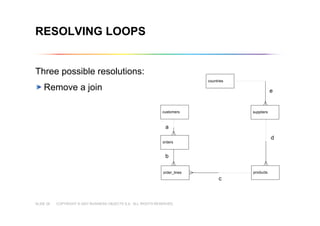
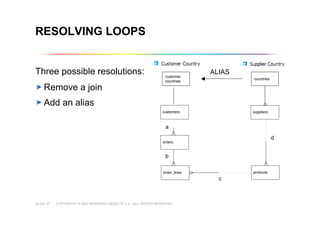
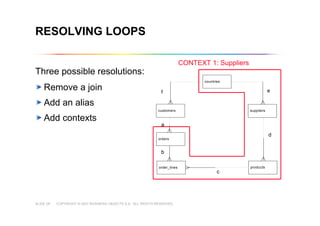
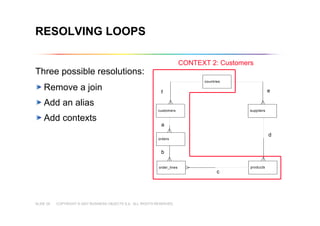
This document outlines best practices for building universes in Business Objects. It defines what a universe is, as a semantic layer that translates database structures into business terms. The agenda covers defining objects, advanced object creation tips like using case statements and custom lists of values, resolving loops in joins, and concludes by emphasizing taking time to build the universe correctly to simplify the user experience.