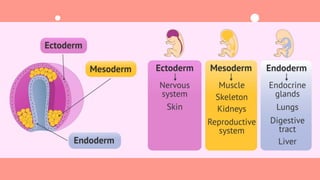
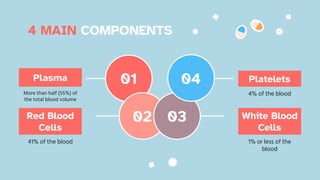
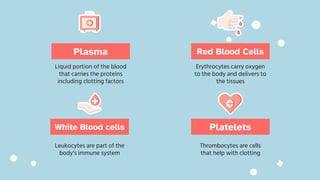
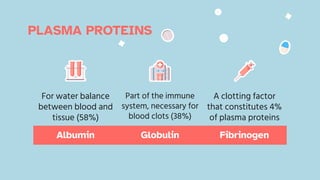
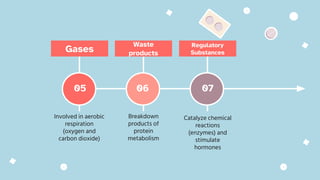
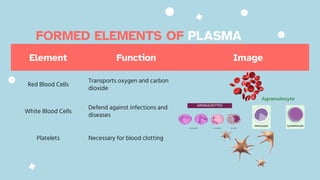
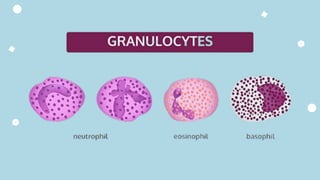
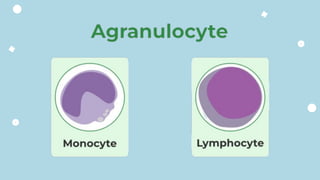
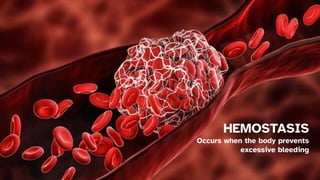
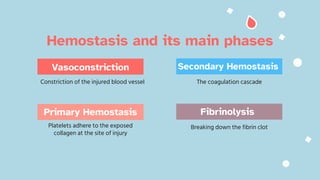
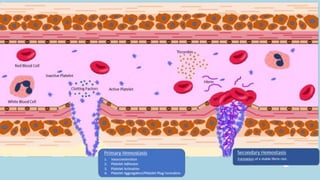
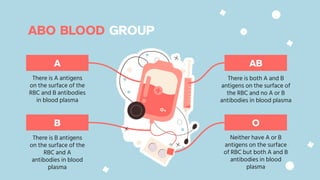
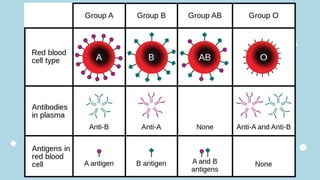
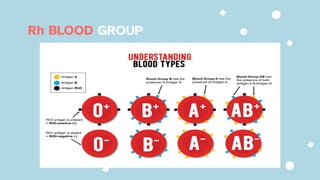
The document discusses the composition and functions of blood. Blood is composed of plasma and formed elements including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Plasma is the liquid portion of blood that transports nutrients, waste, hormones, and antibodies. It also contains water, proteins, ions, and gases. Red blood cells carry oxygen throughout the body. White blood cells help fight infections and diseases. Platelets are involved in blood clotting during hemostasis. The document also covers blood groups, transfusions, and blood typing.