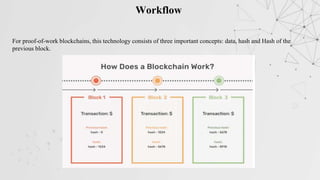
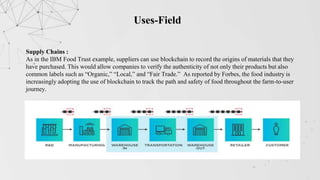
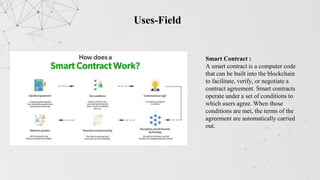
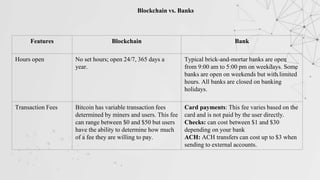
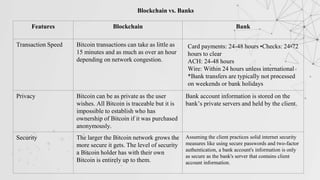
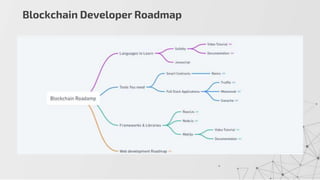
This document extensively discusses blockchain technology, highlighting its secure data storage, decentralization, and advantages over traditional banking. It covers various aspects such as the history of blockchain, its features like immutability and better security, as well as its applications across industries such as finance, healthcare, and supply chain. Furthermore, it emphasizes the growing demand for blockchain developers in the tech sector, suggesting a shift towards decentralized systems and improved online transactions.