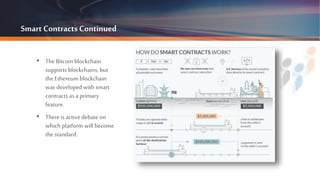
Blockchain is a decentralized, transparent database technology originally created for Bitcoin, enabling secure transactions without the need for intermediaries. It maintains a permanent ledger of transactions that cannot be altered once completed, fostering trust and anonymity among users. Governments are exploring various blockchain applications for transparency and efficiency in areas like financial management and identification verification.