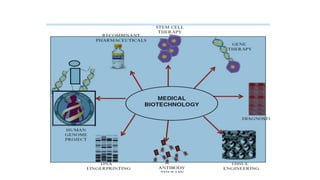
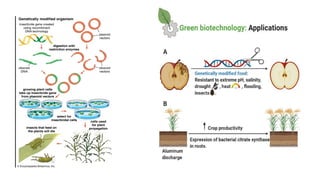
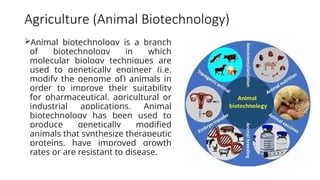
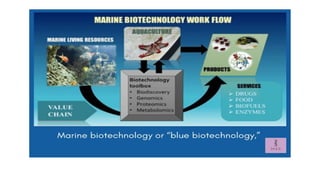
Biotechnology, a term first coined in 1919, integrates natural and engineering sciences to solve problems and develop products using living organisms. It has major applications across various fields, including healthcare, agriculture, environmental, industrial, marine, and food biotechnology, each utilizing techniques like genetic engineering and molecular breeding to address specific challenges. Key examples include the development of therapeutic proteins in healthcare, genetically modified crops in agriculture, and sustainable practices in environmental biotechnology.