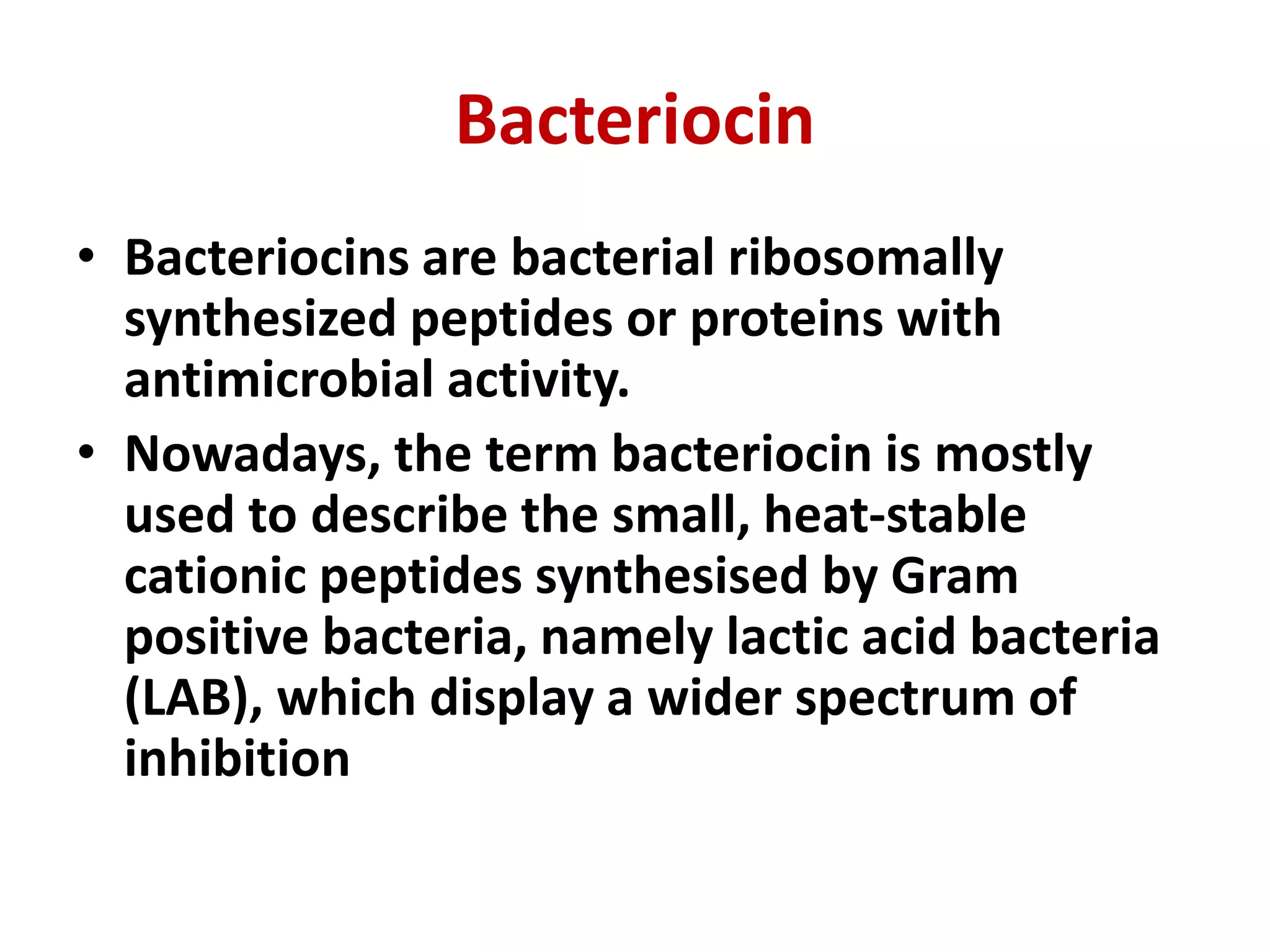
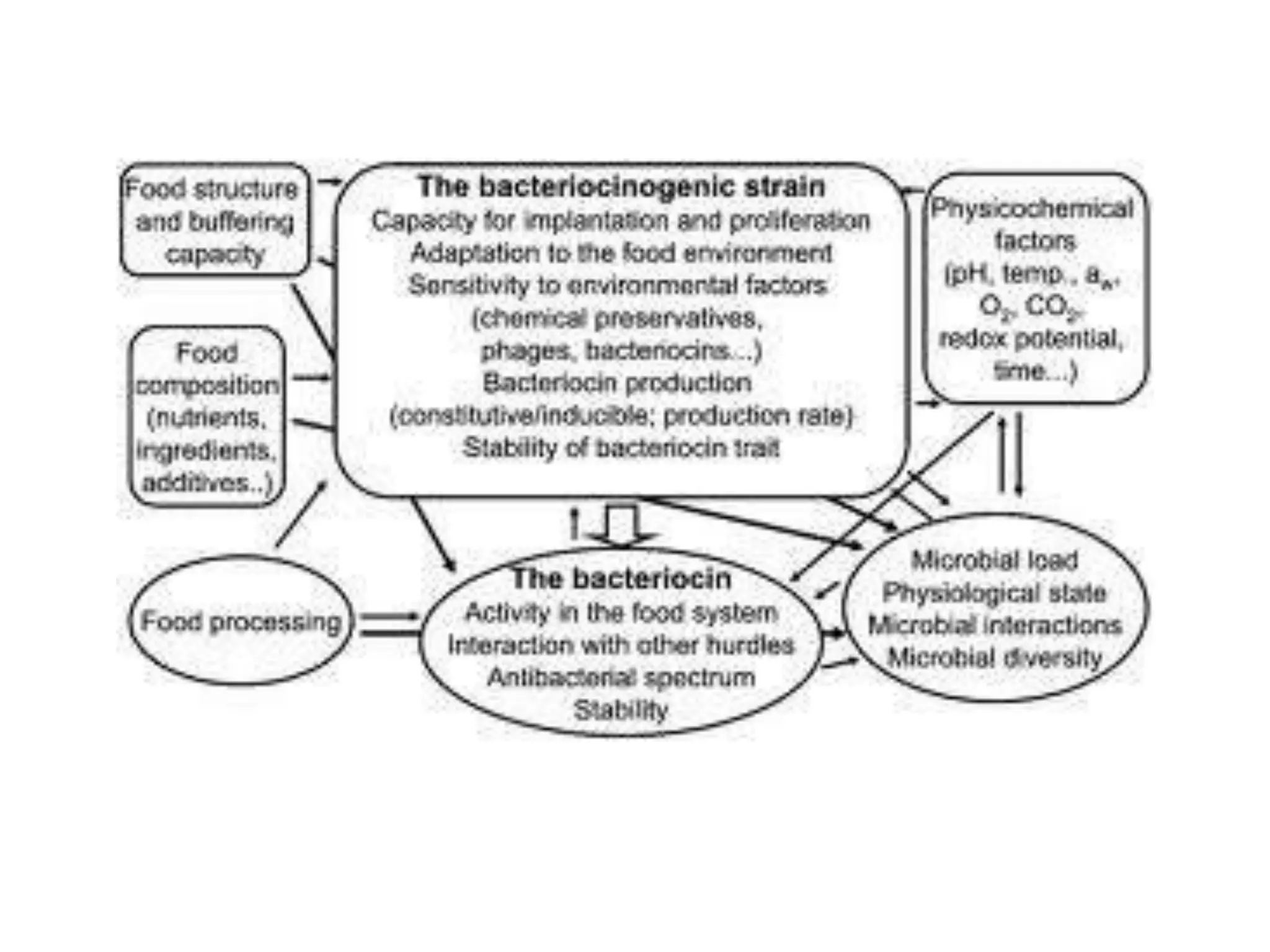
This document discusses biopreservation techniques for food processing and preservation, specifically focusing on sauerkraut and kimchi fermentation. It explains that biopreservation uses beneficial bacteria or their products to control spoilage and pathogens by competing for nutrients and producing antimicrobial compounds like lactic acid. For sauerkraut and kimchi, lactic acid bacteria are important as they ferment the cabbage or vegetables, lowering the pH through lactic acid production and extending shelf life. Key factors that affect fermentation include temperature, moisture, oxygen levels, salt content and pH.


![• These days LAB bacteriocins are used as an integral part of
hurdle technology. Using them in combination with other
preservative techniques can effectively control spoilage
bacteria and other pathogens, and can inhibit the
activities of a wide spectrum of organisms, including
inherently resistant Gram-negative bacteria."[1]
• In fish processing, biopreservation is achieved by adding
antimicrobials or by increasing the acidity of the fish
muscle. Most bacteria stop multiplying when the pH is
less than 4.5. Traditionally, acidity has been increased by
fermentation, marination or by directly adding acetic,
citric or lactic acid to food products. Other preservatives
include nitrites, sulphites, sorbates, benzoates and
essential oils](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biopreservation-130515085830-phpapp01/75/Biopreservation-5-2048.jpg)