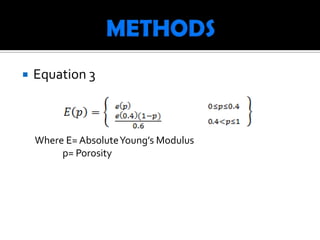
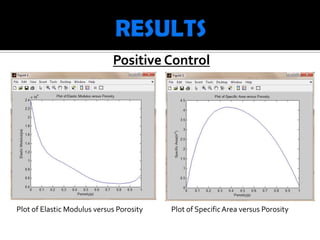
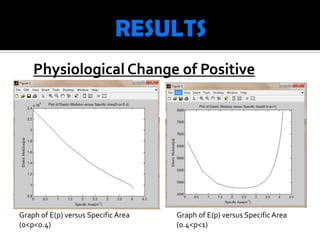
This document describes modeling the relationship between porosity and elastic modulus of bone. Equations 1-3 model elastic modulus as a function of porosity using Matlab and Excel. Plots show the relationship between elastic modulus and porosity, and specific surface area and porosity. The original model determines optimal porosity for maximum elastic modulus. The new model provides a more accurate way to analyze bone fractures and predict recovery by demonstrating how specific surface area affects elastic modulus. Results unexpectedly showed elastic modulus increasing with surface area above 2.6m-1 for porosity over 0.4.