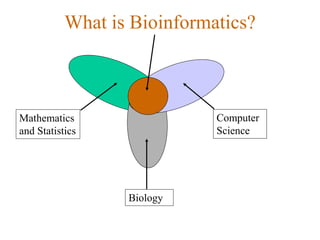
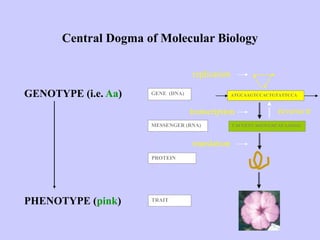
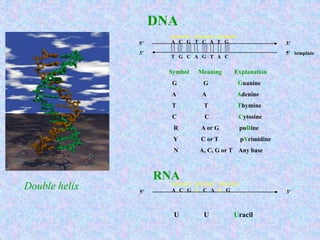
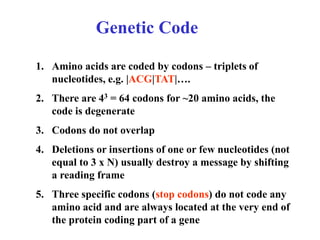
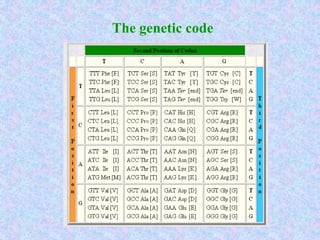
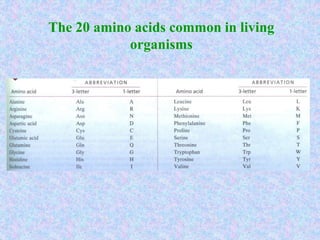
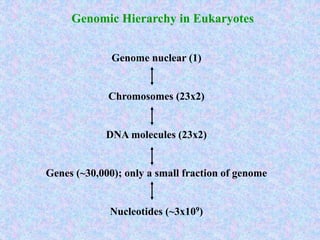
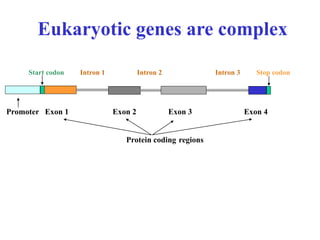
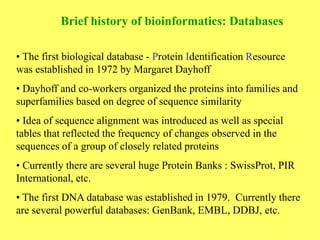
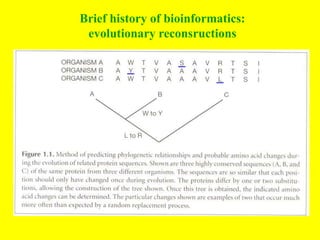
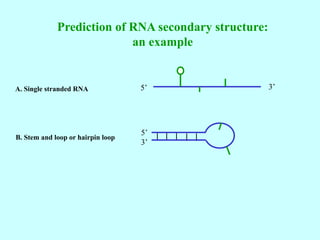
Bioinformatics involves gathering, storing, analyzing, and spreading vast amounts of biological data using computers and statistics. It draws from biology, computer science, and mathematics. Key areas include molecular biology, genetics, biotechnology, medicine, agriculture, and ecology. Bioinformatics addresses problems like data collection, sequence alignment, and prediction/classification. It has grown exponentially with investments and plays a role in many fields. The central dogma of molecular biology describes how genetic information flows from DNA to RNA to protein. Genomes contain genes made of DNA that code for RNA and proteins through the genetic code. A brief history outlined early biological databases and methods like sequence alignment and analysis.