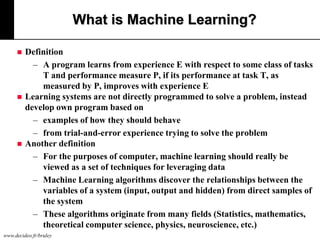
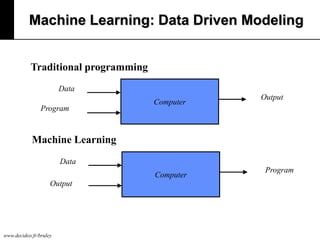
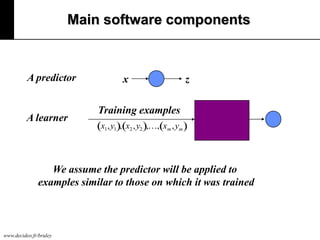
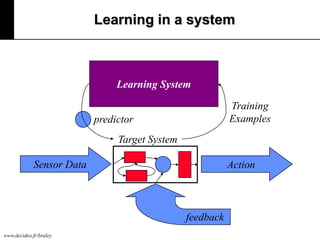
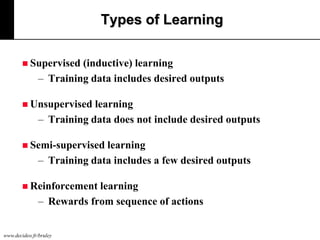
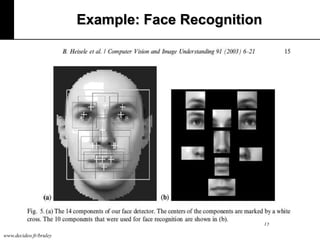
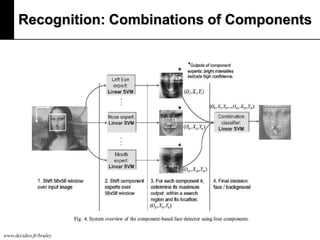
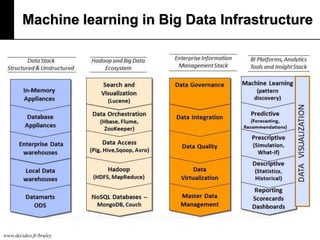
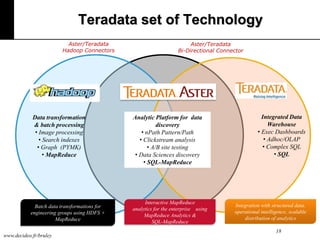
The document discusses machine learning, defining it as a program that learns from experience to improve its performance on tasks. It provides definitions of learning from various scholars and outlines different types of machine learning problems including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Key applications mentioned include vision, sound, text, and finance. The role of machine learning in big data infrastructure is also briefly discussed.