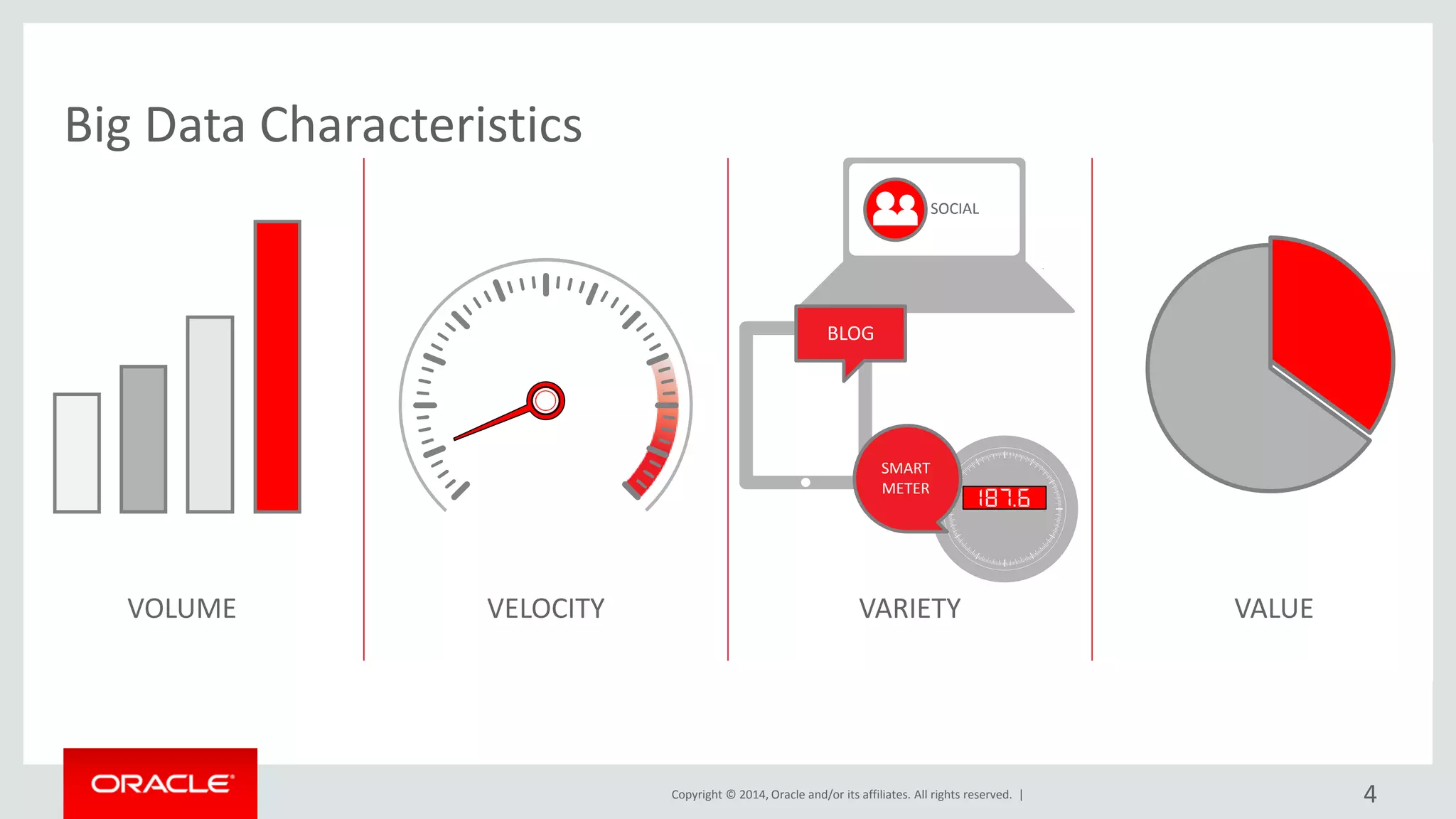
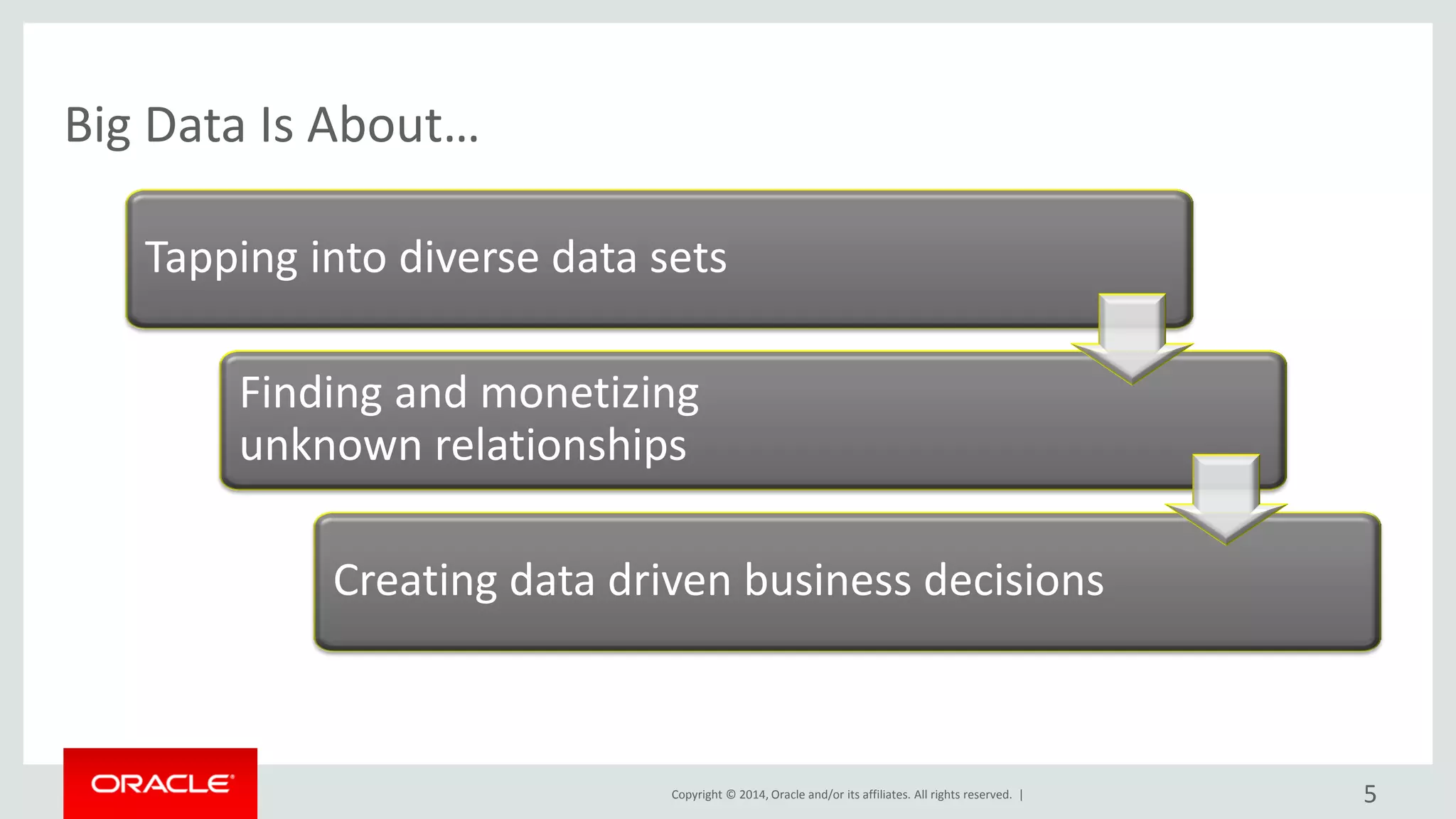
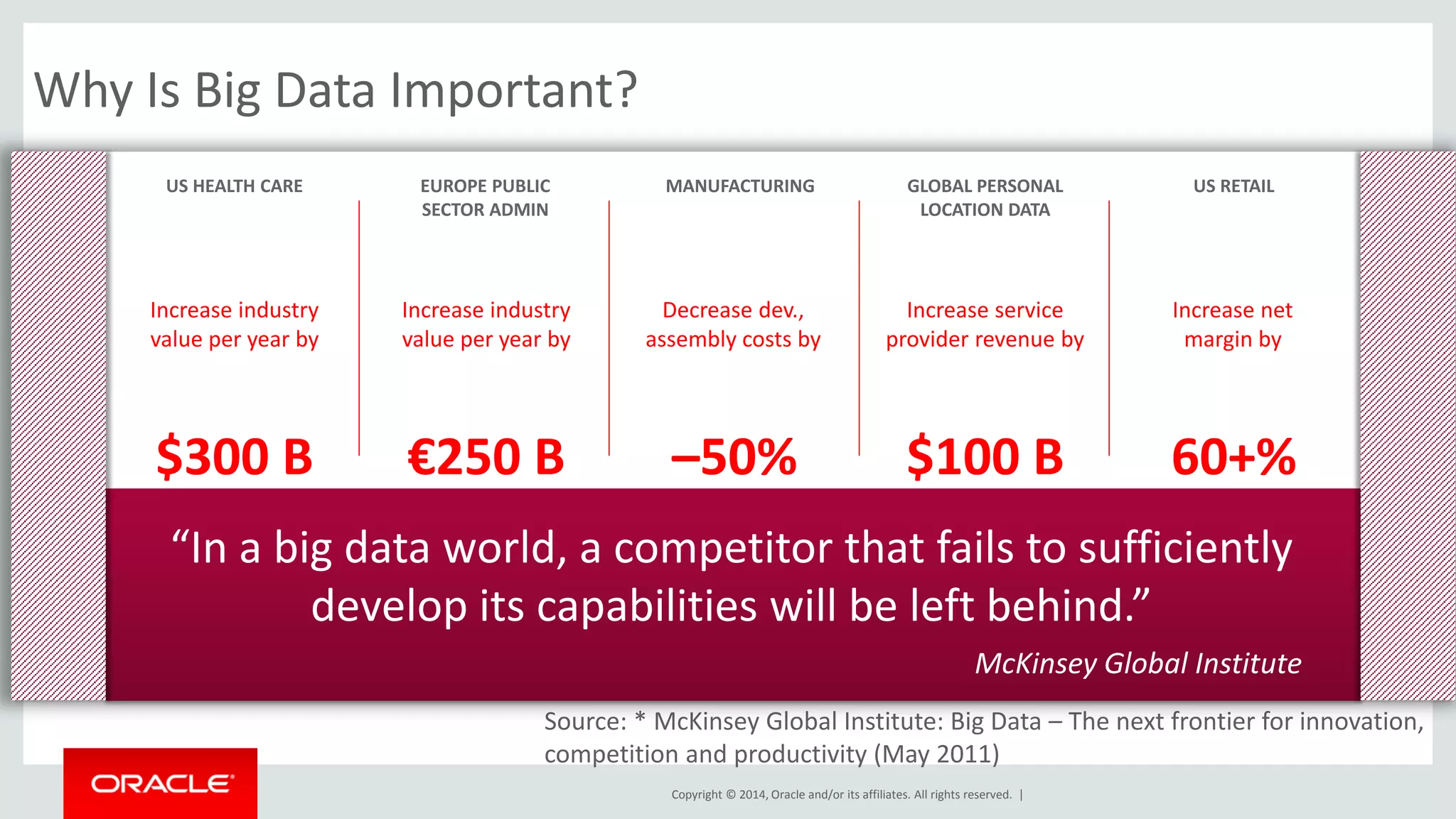
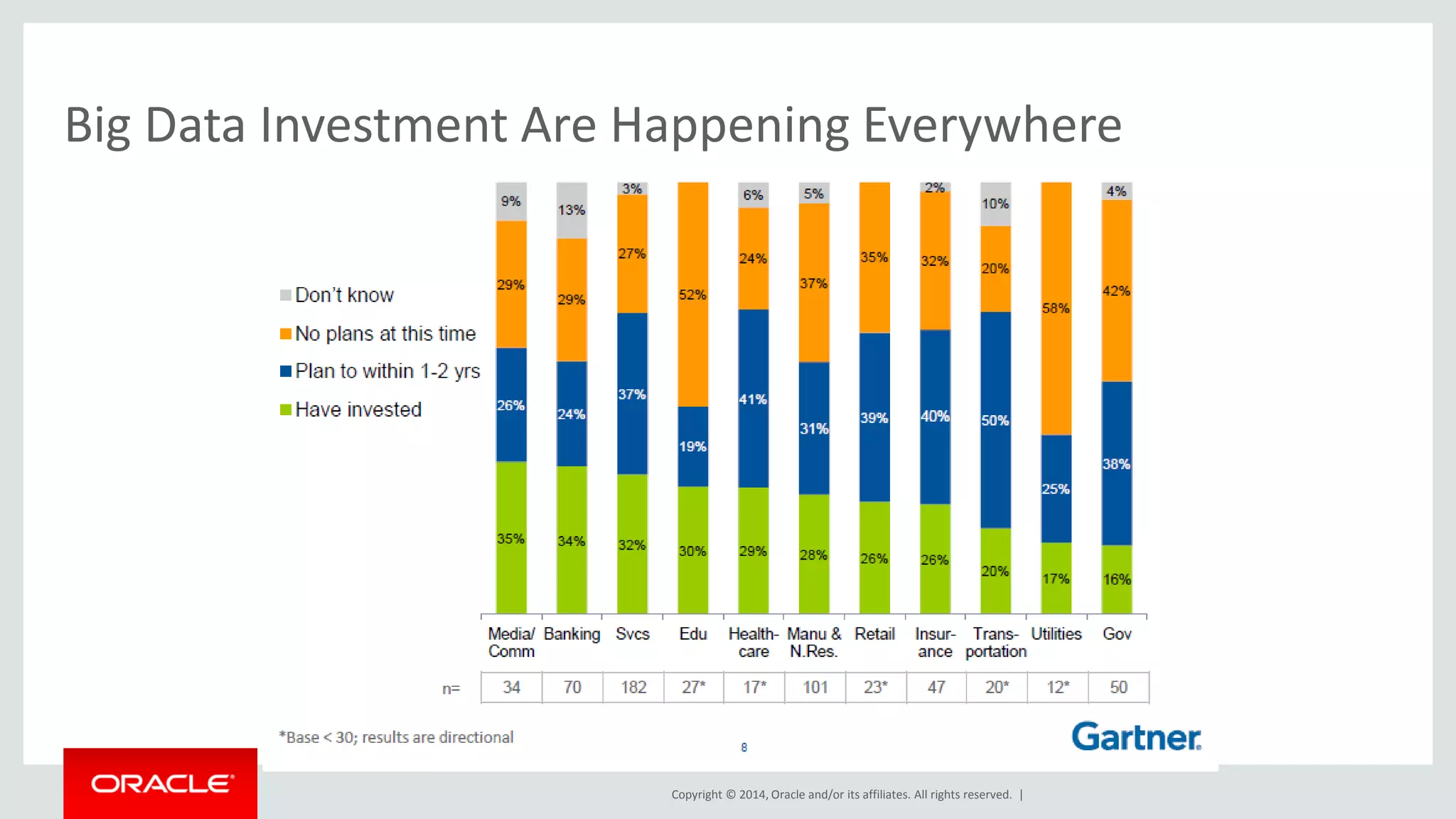
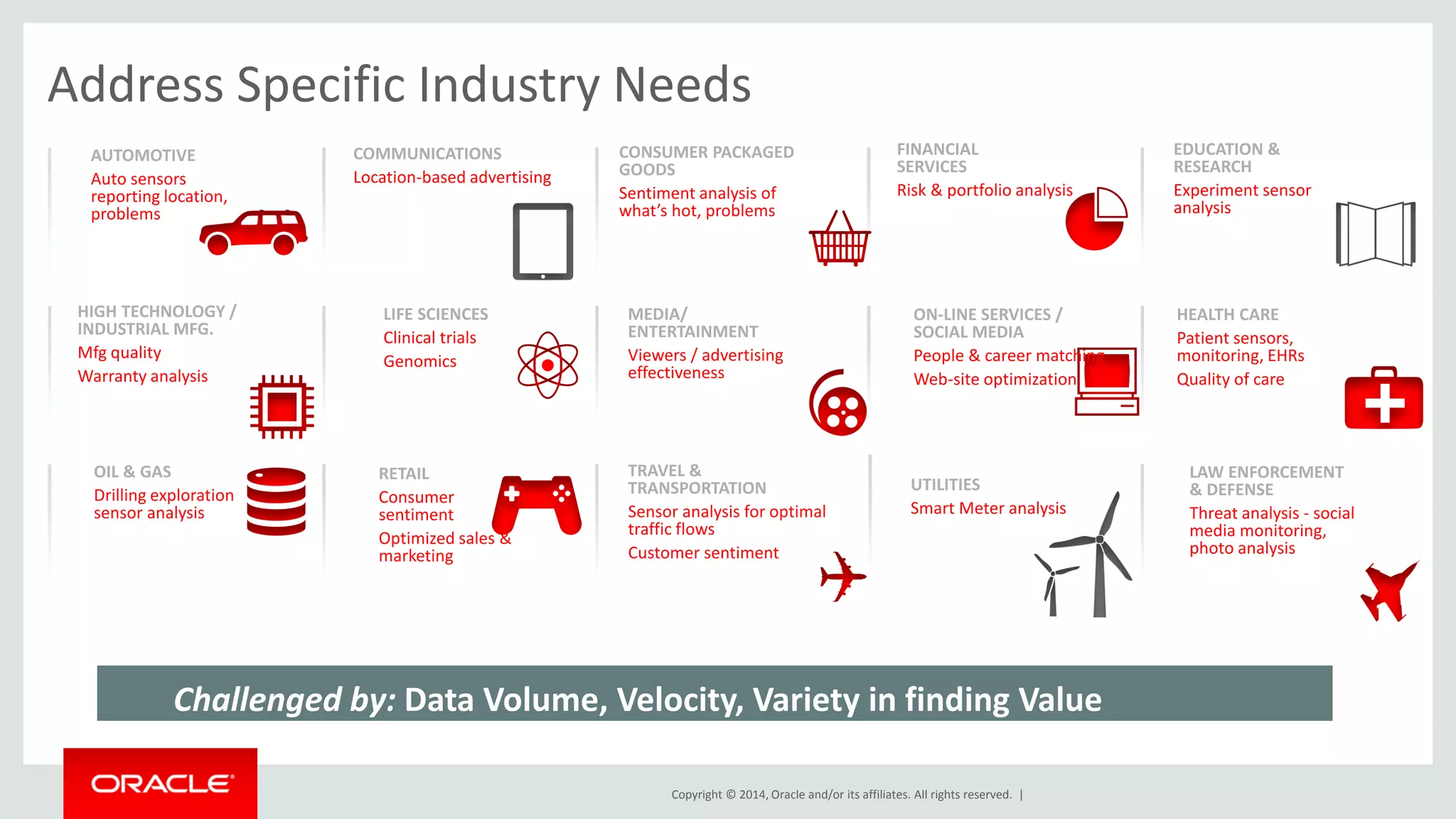
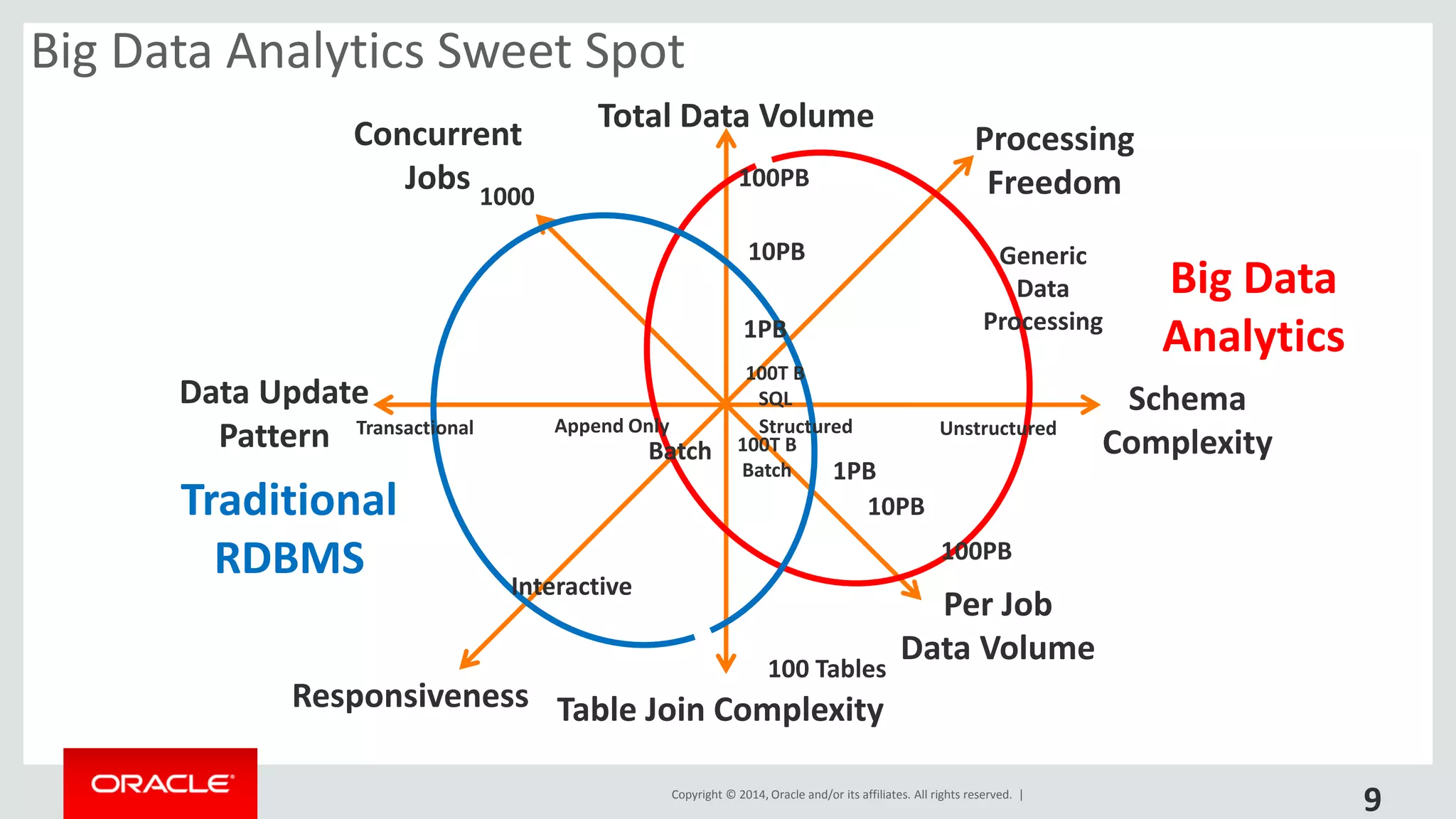
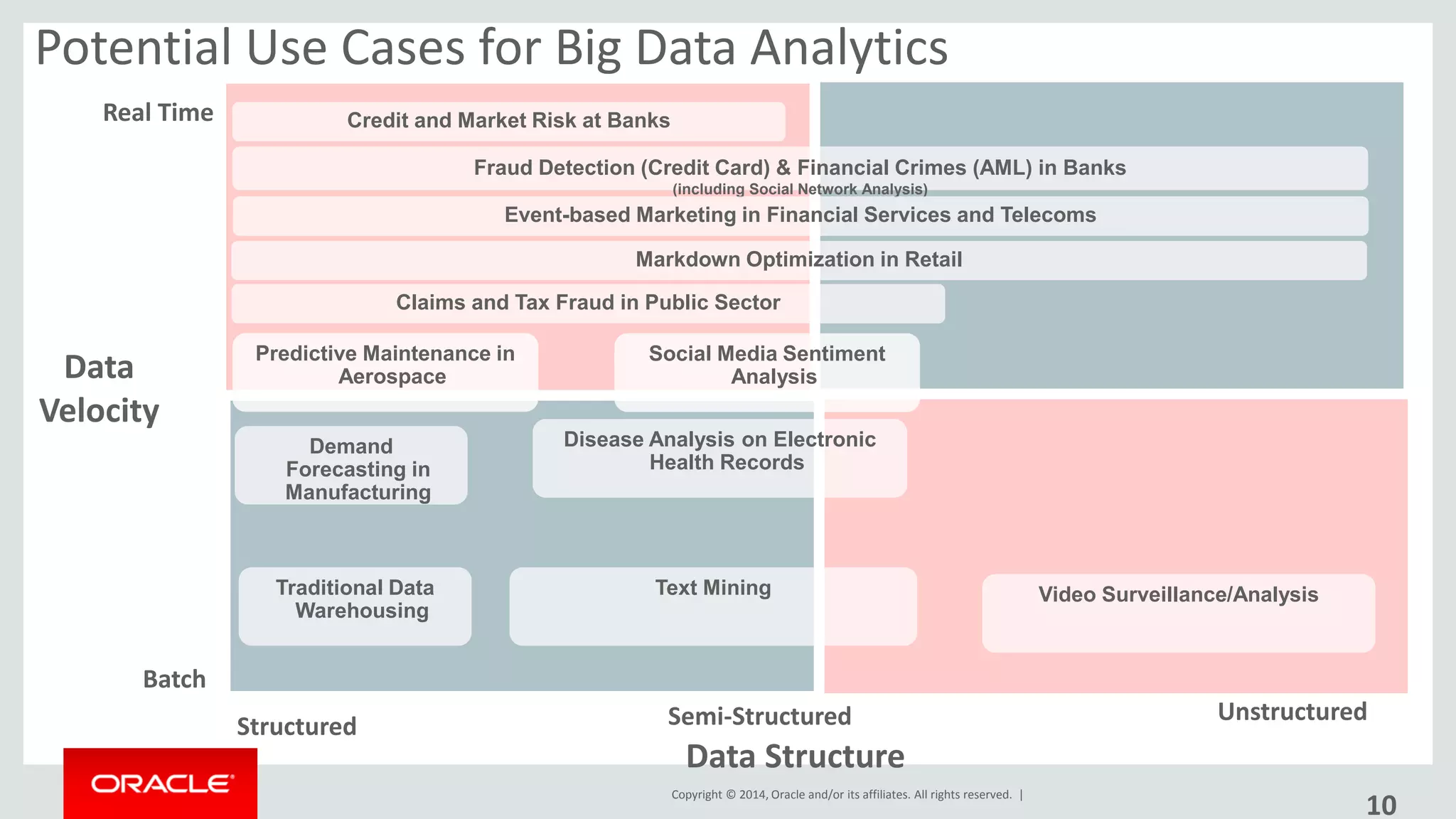
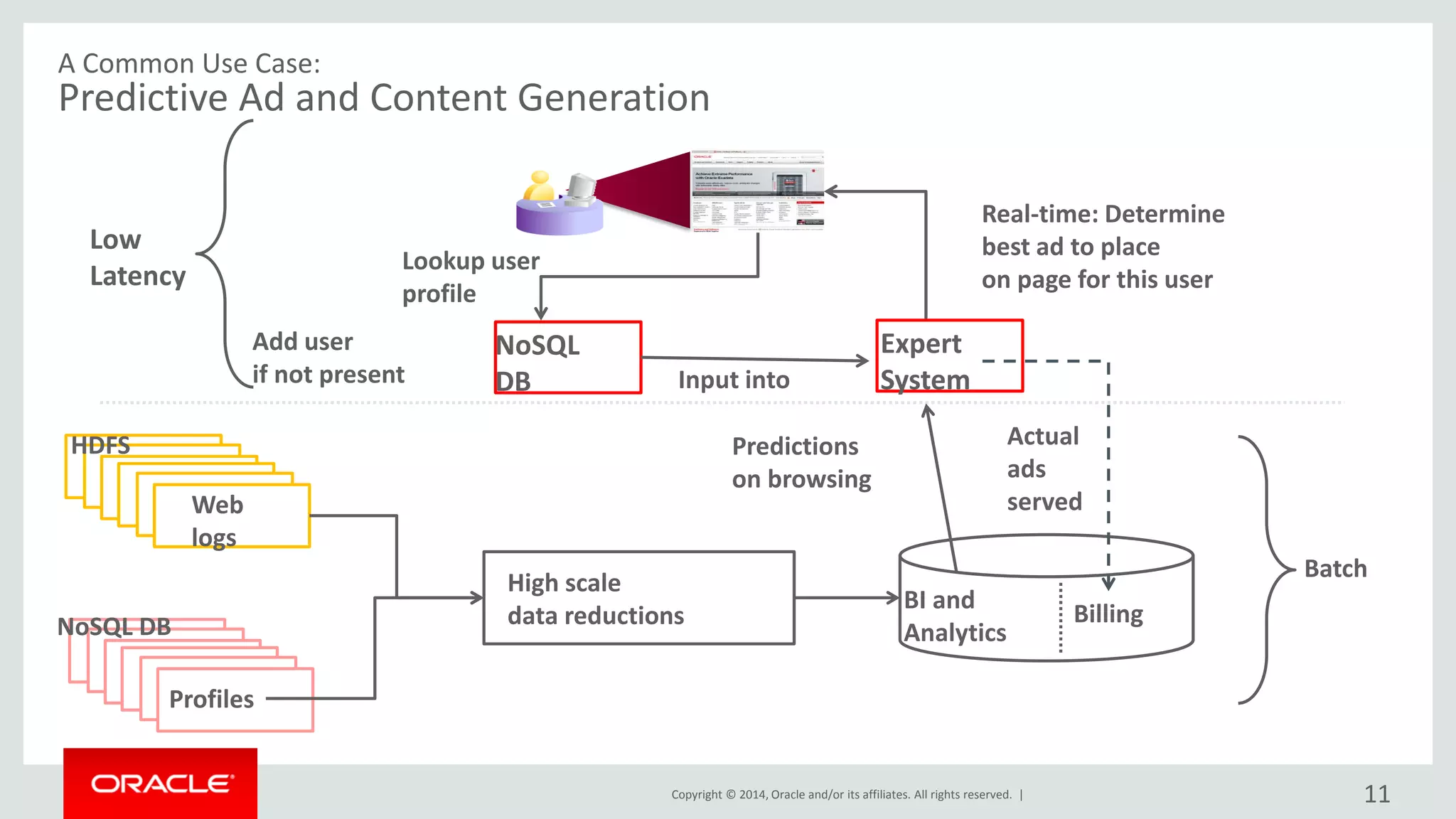
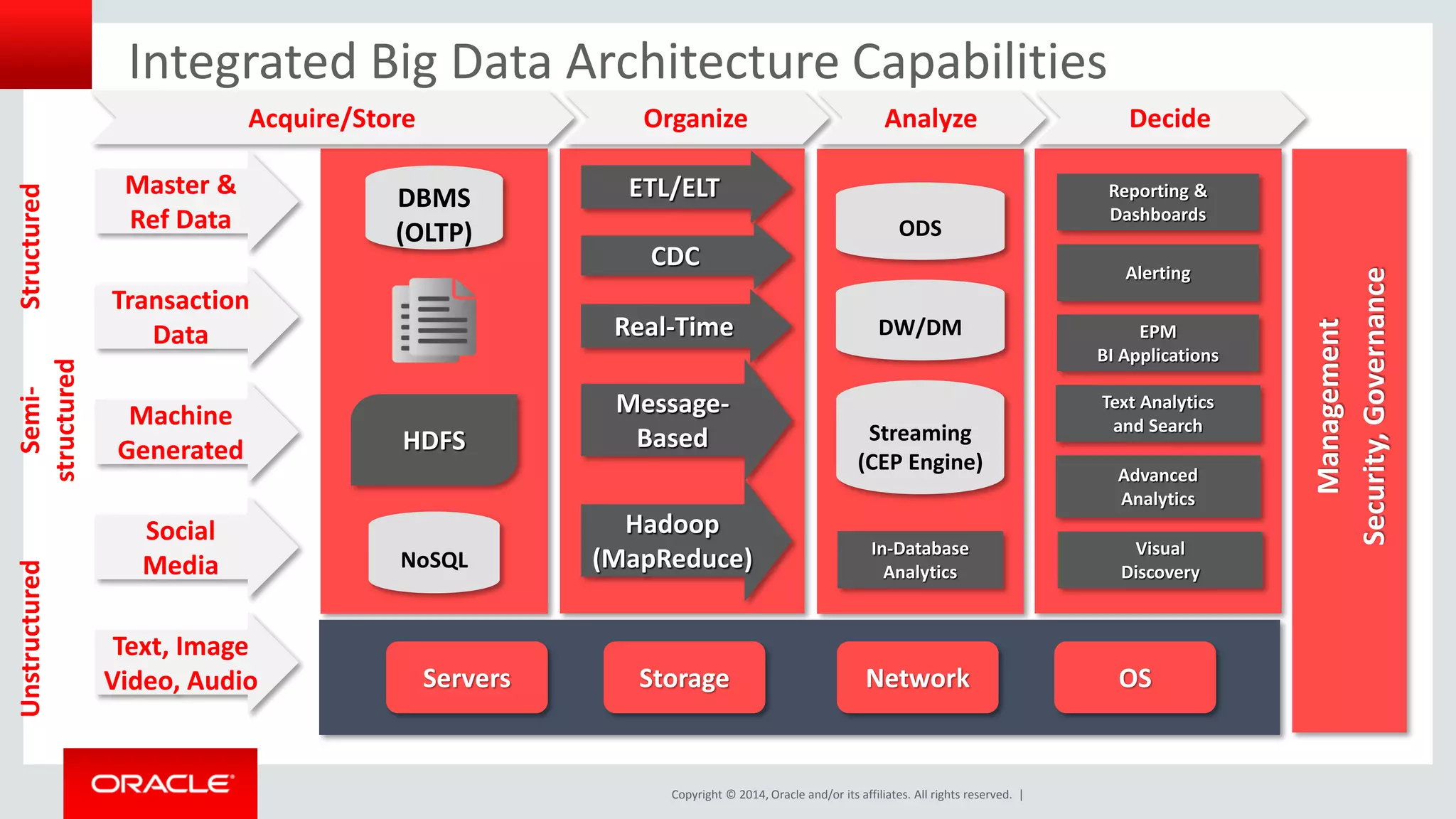
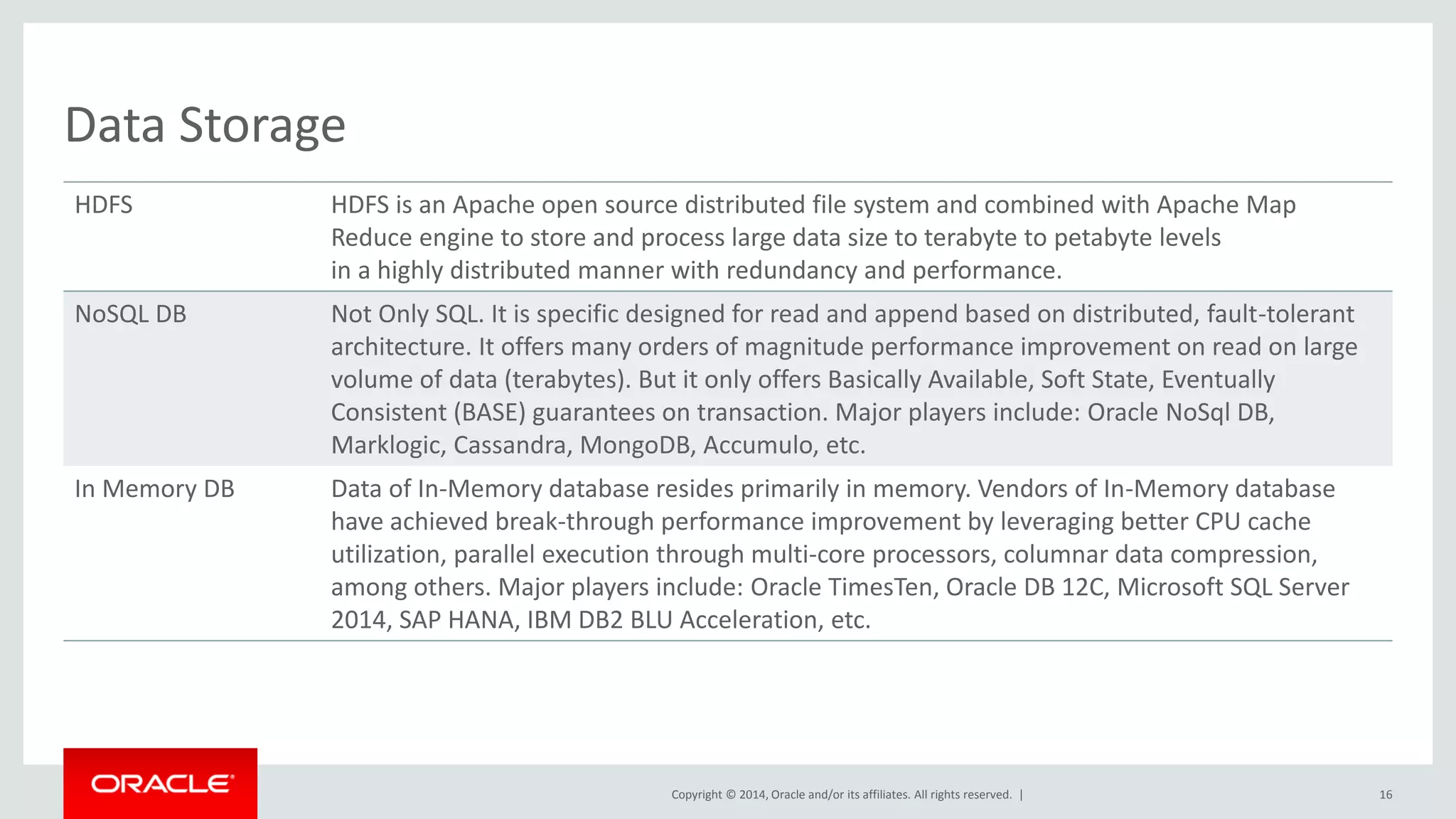
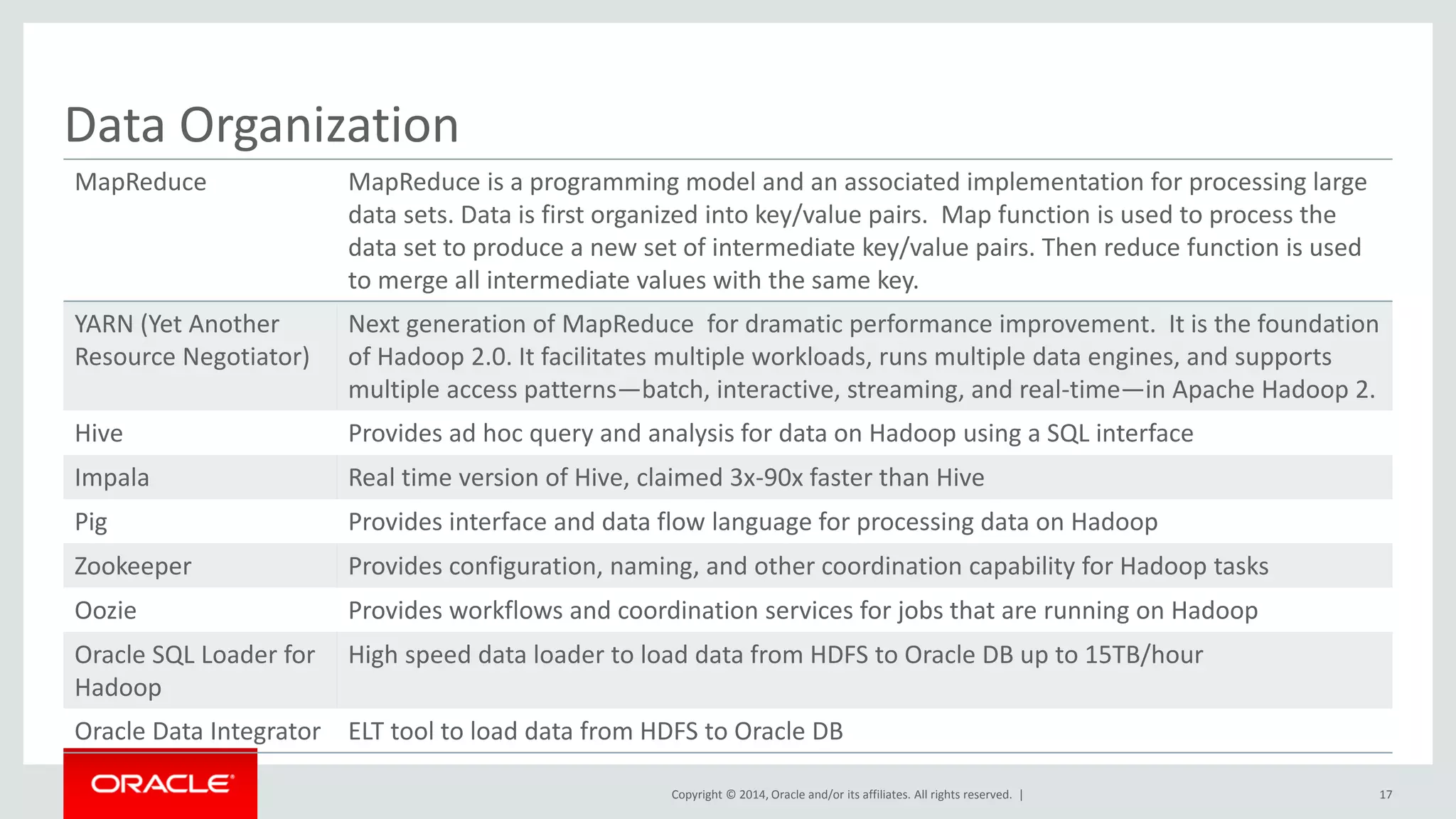
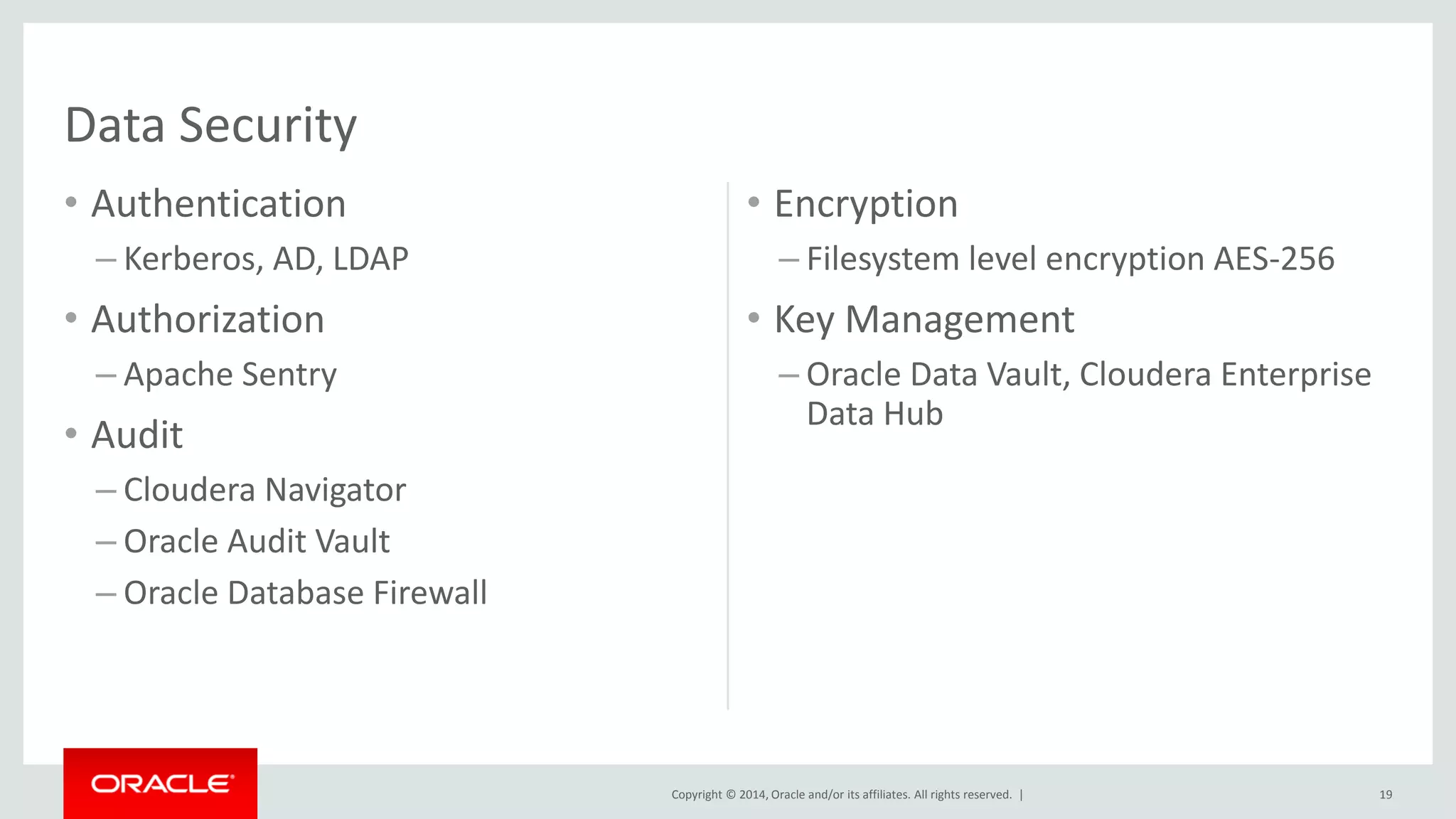
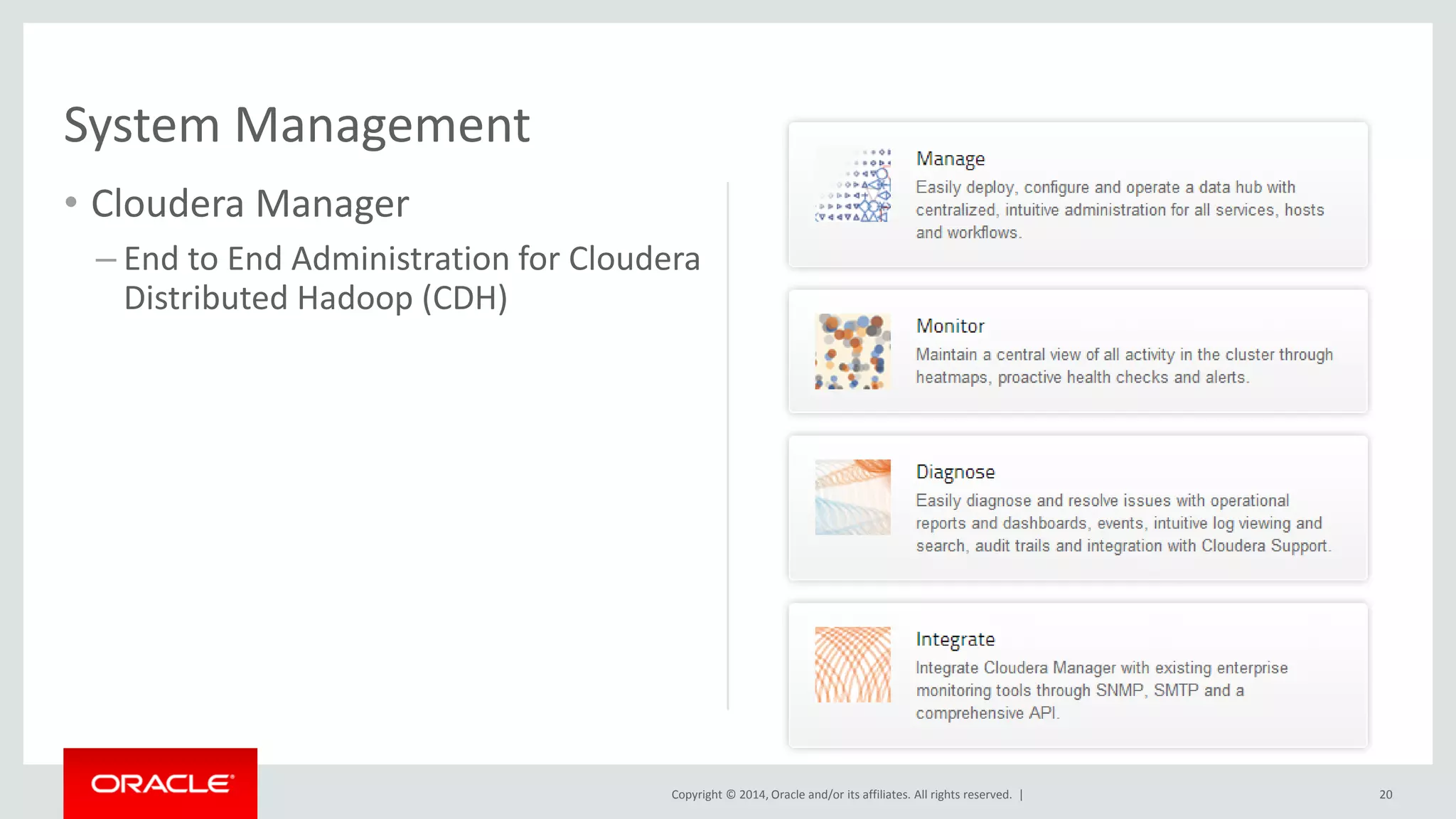
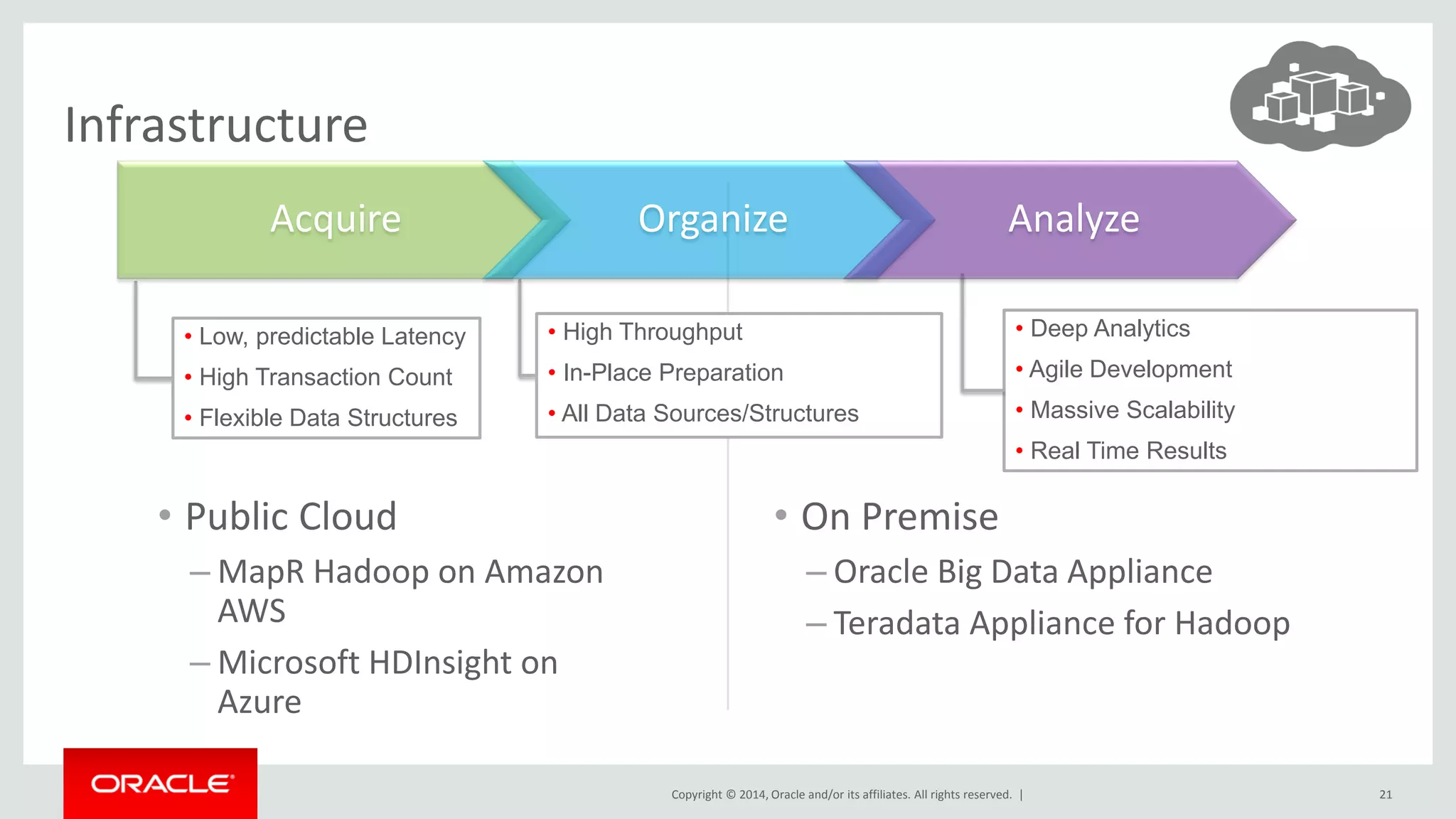
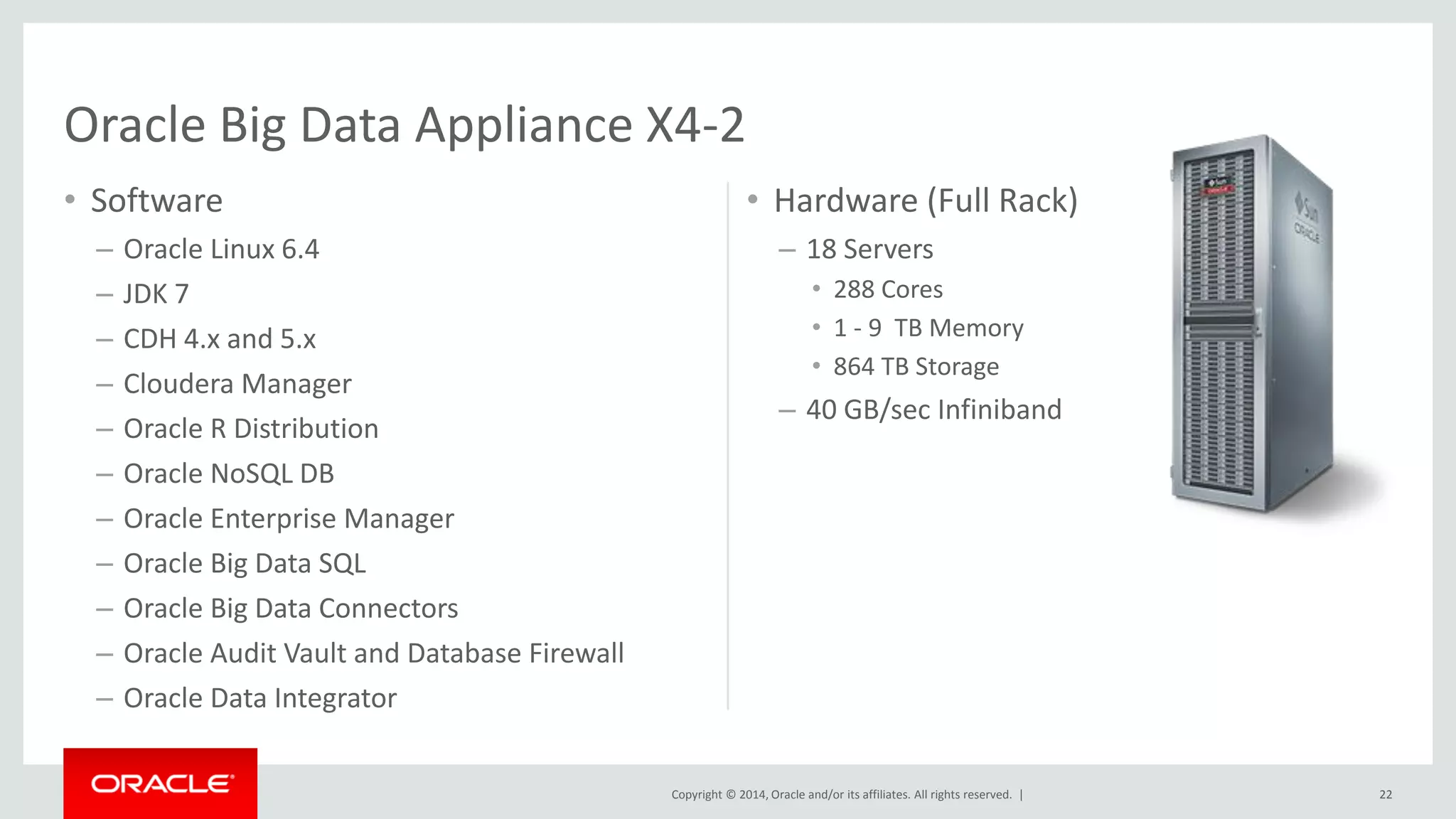
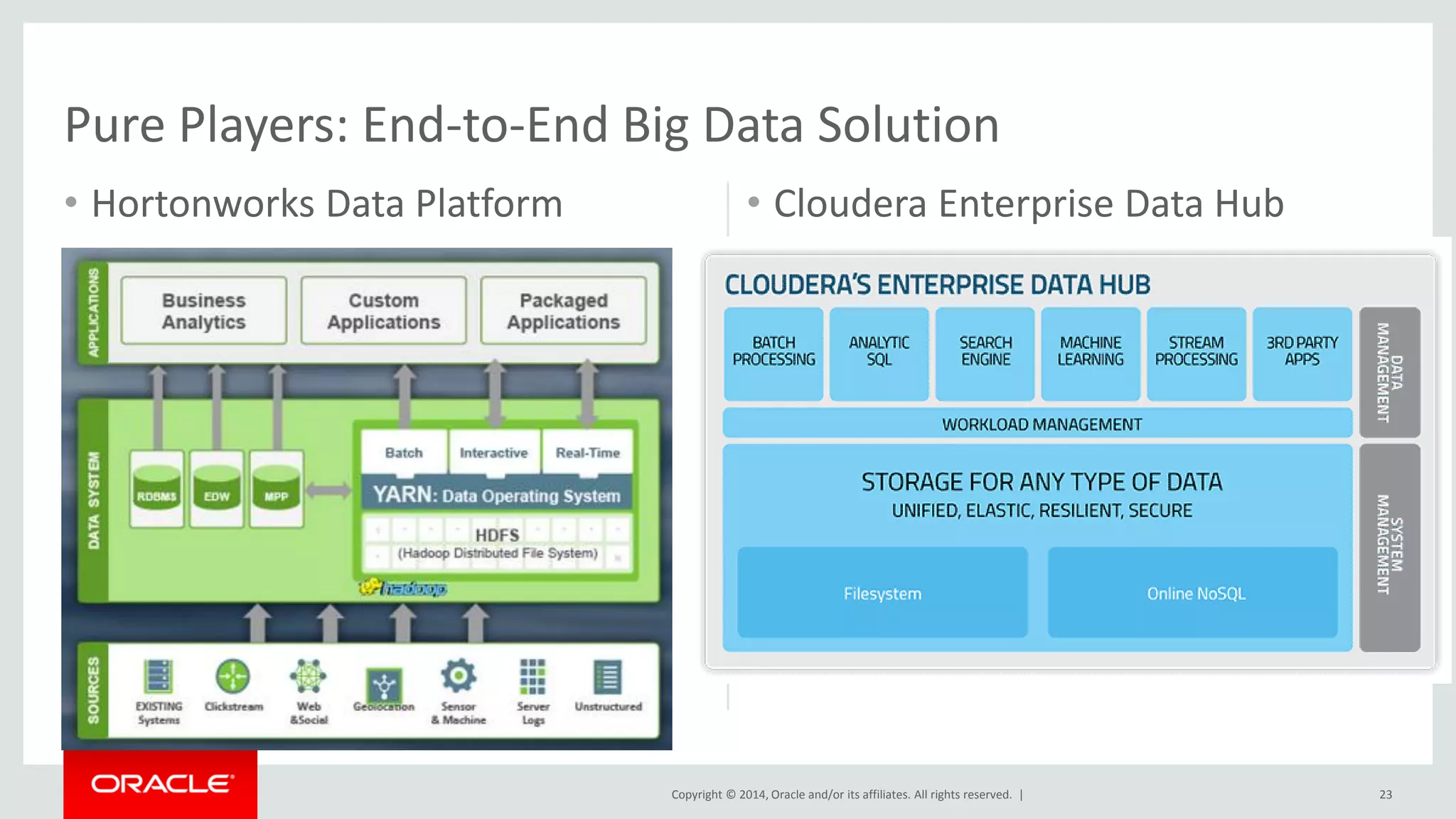
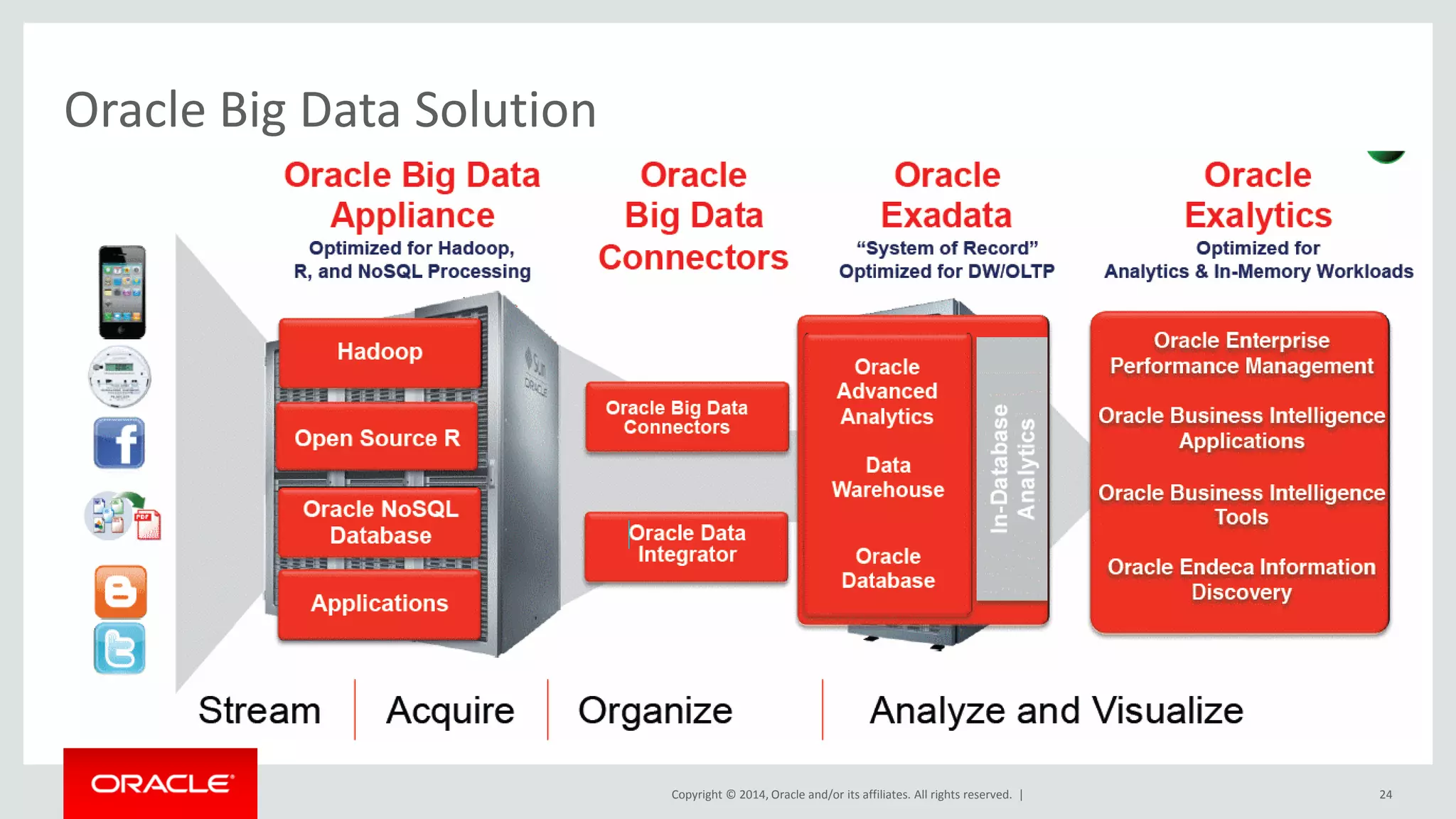
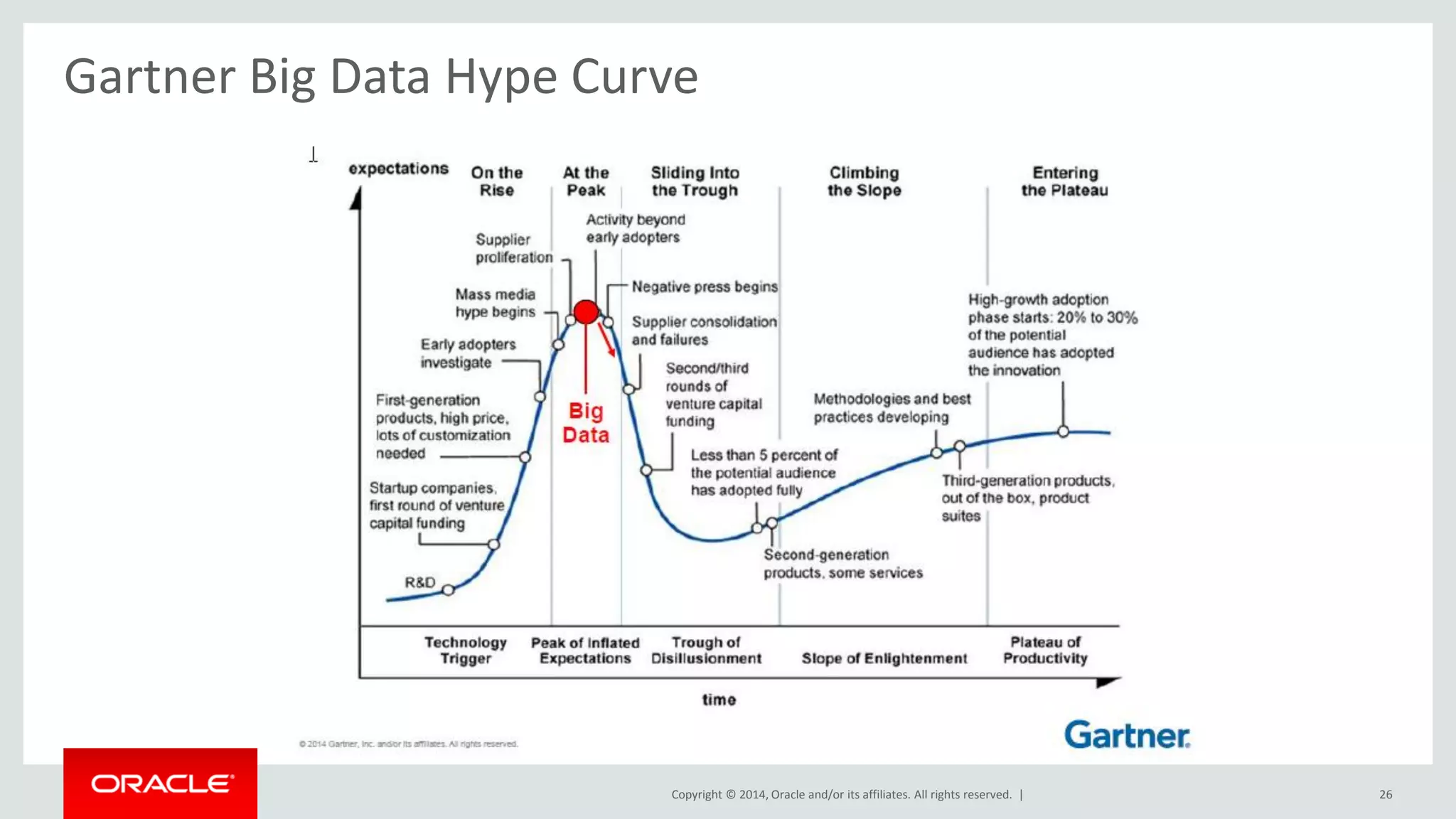
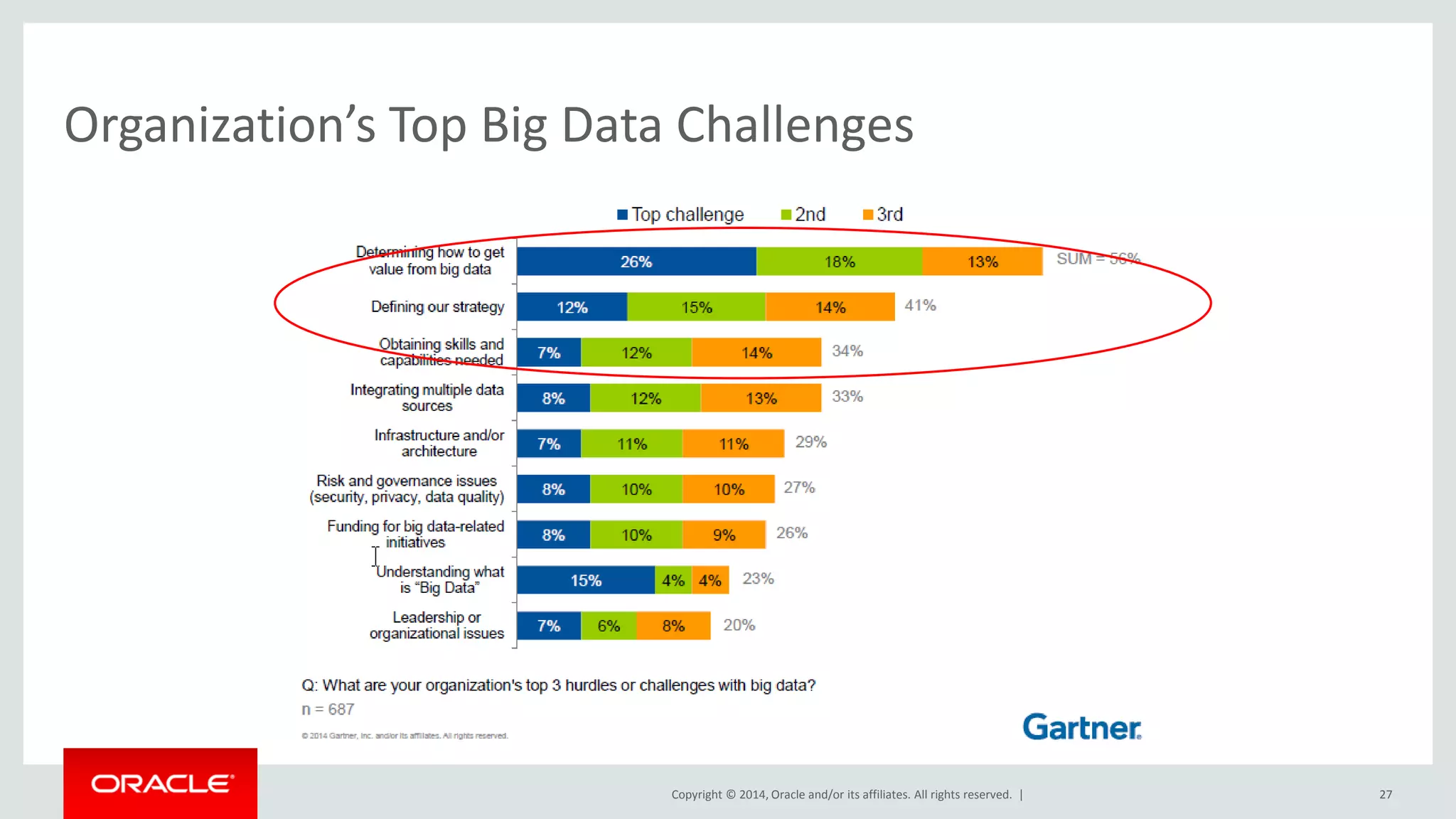
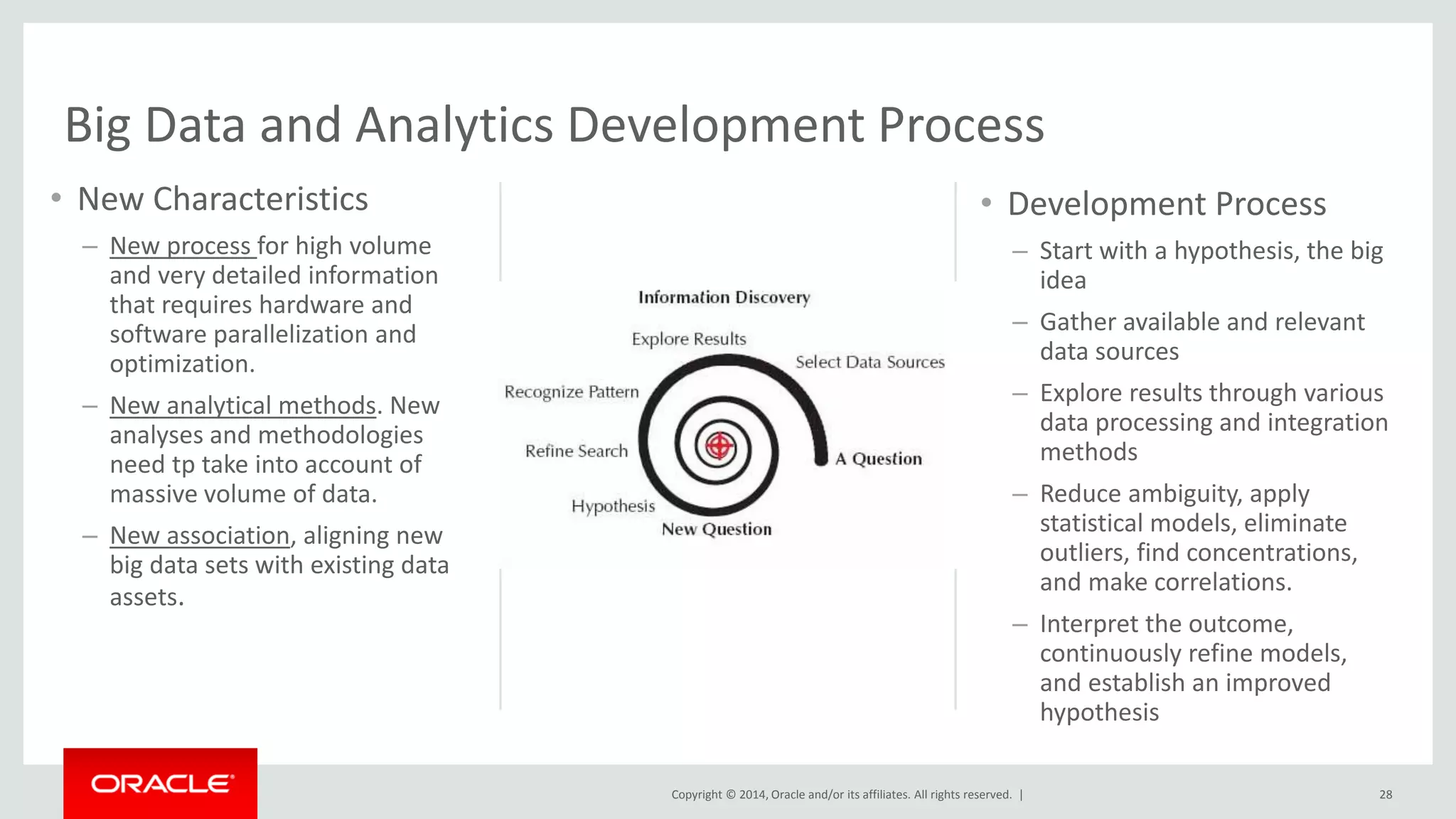
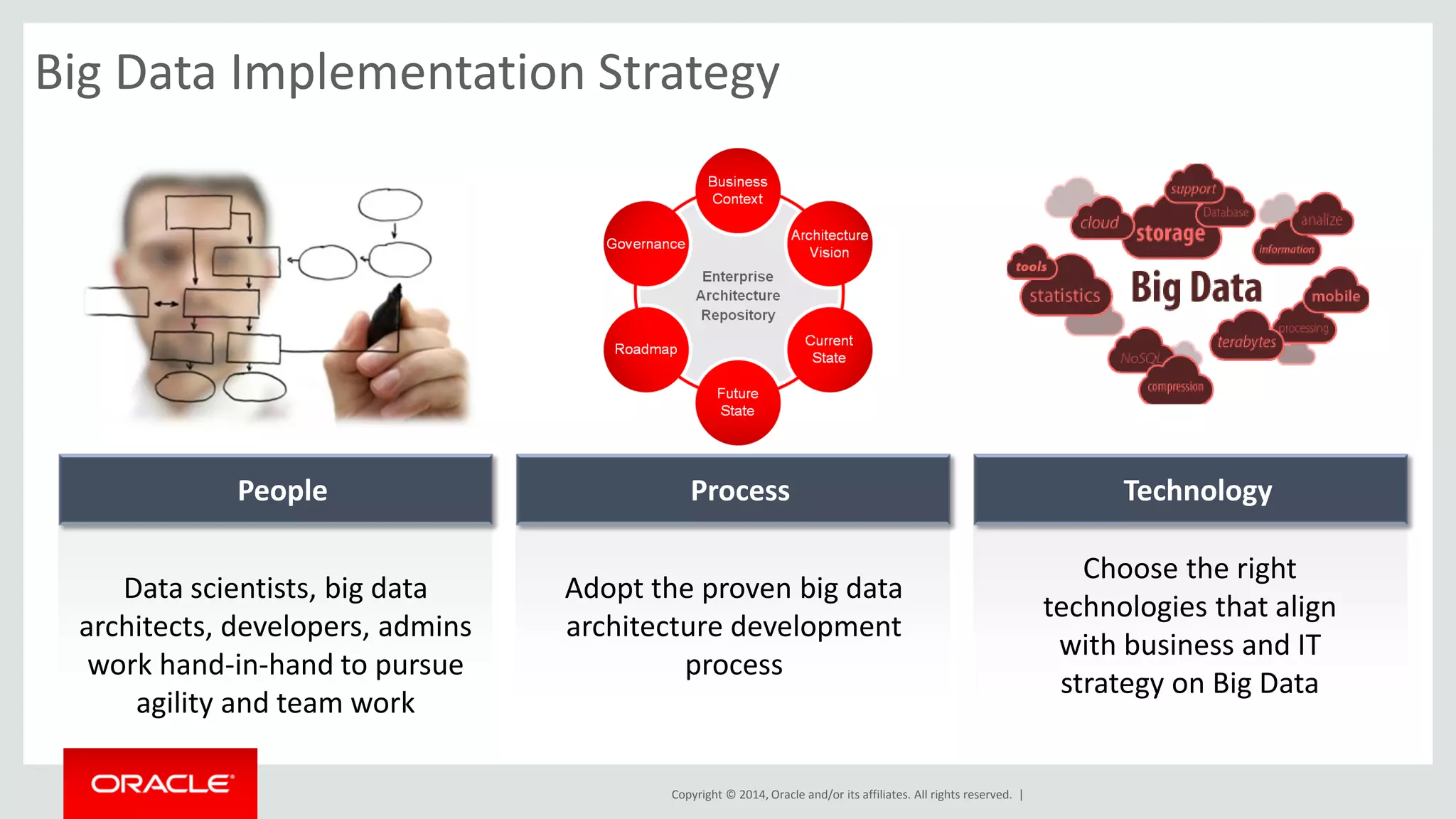
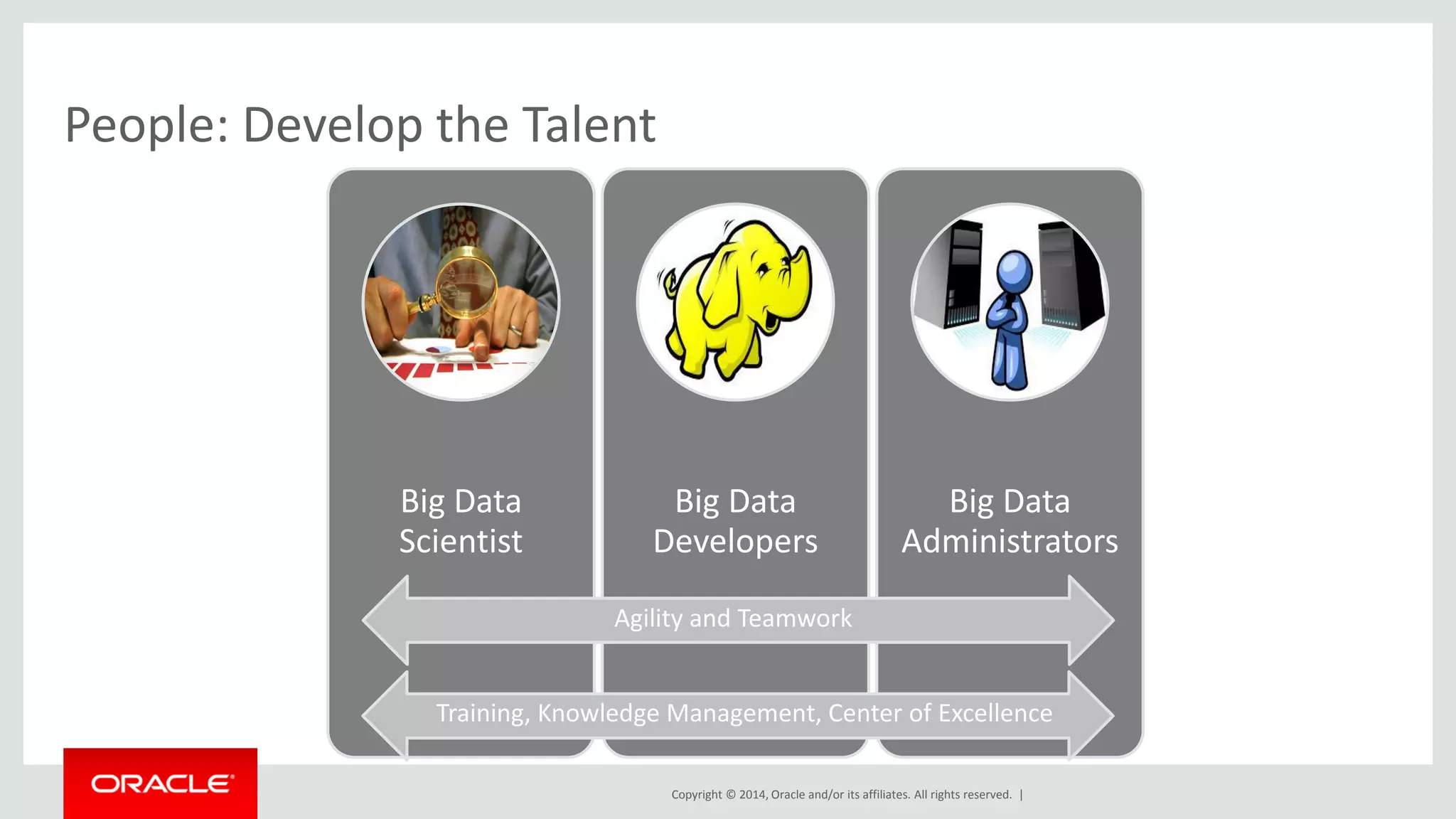
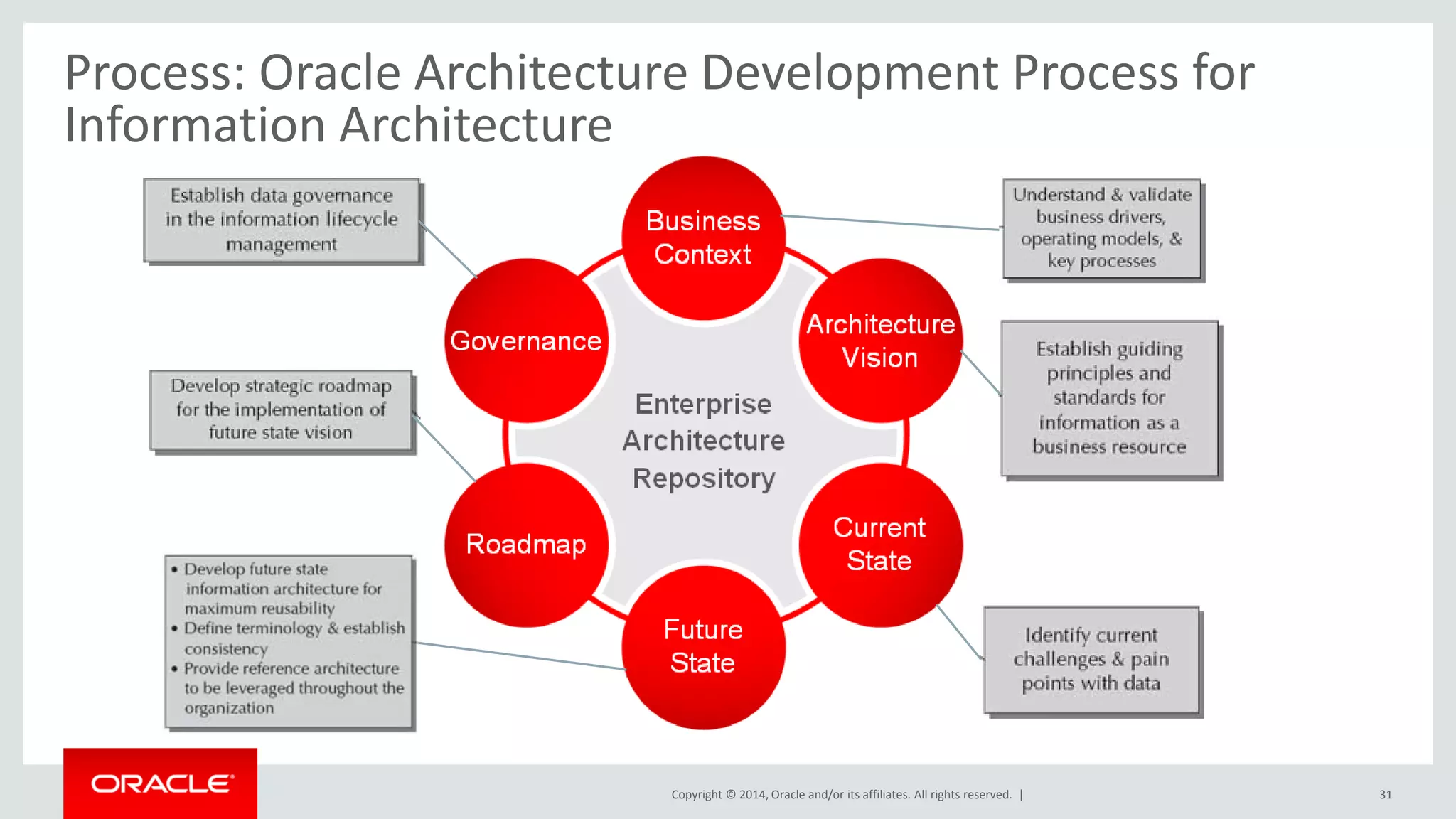
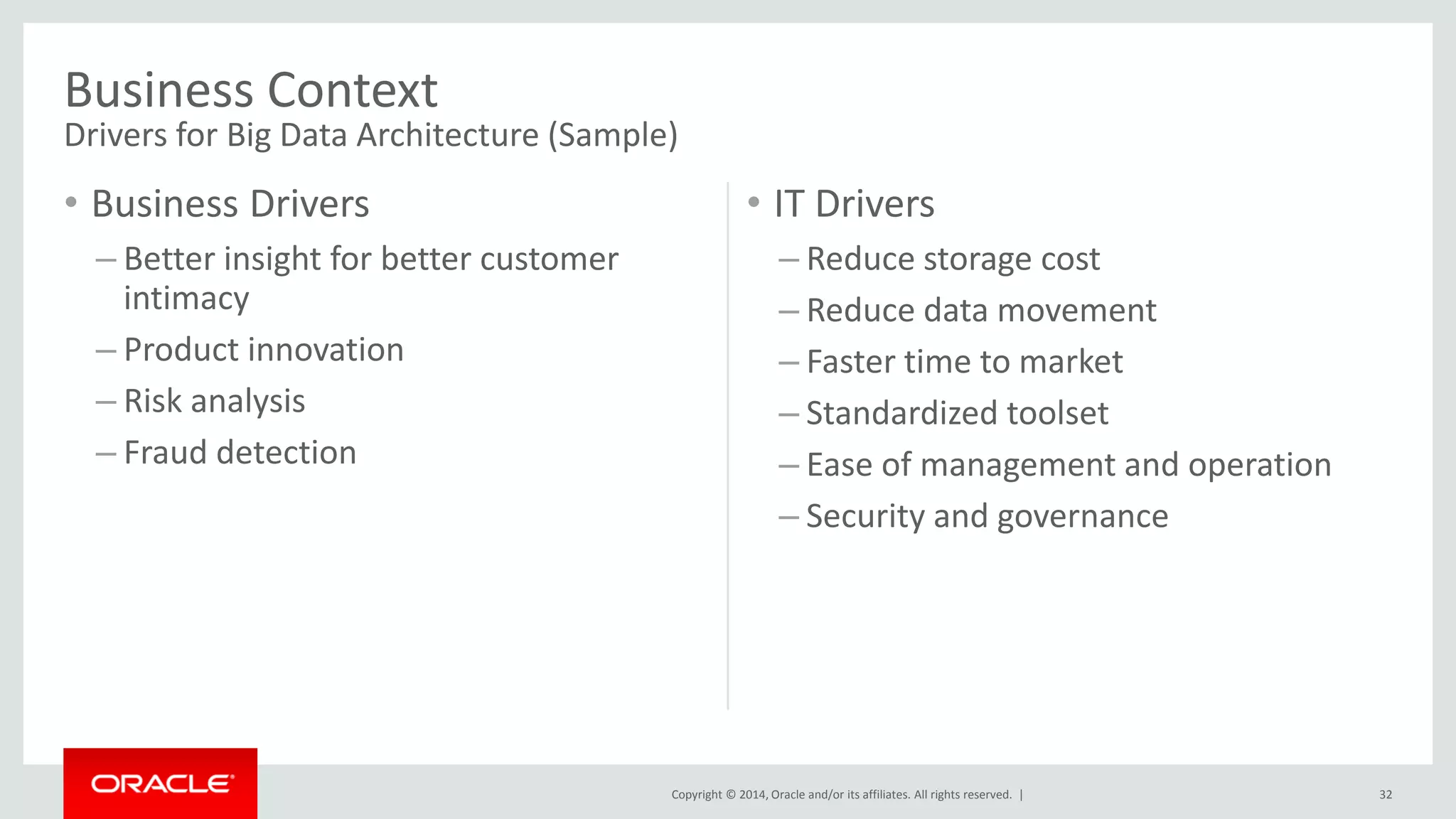
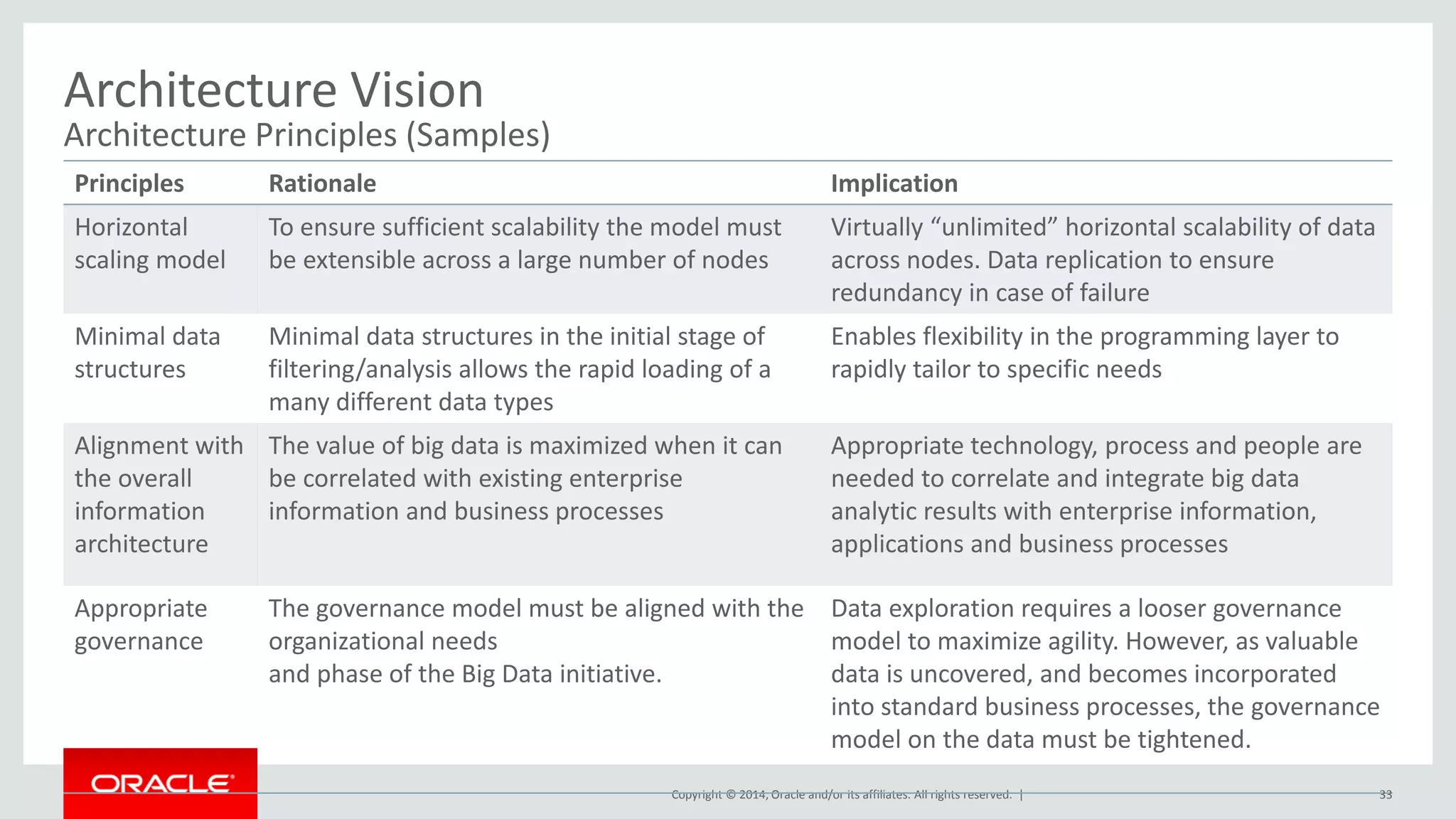
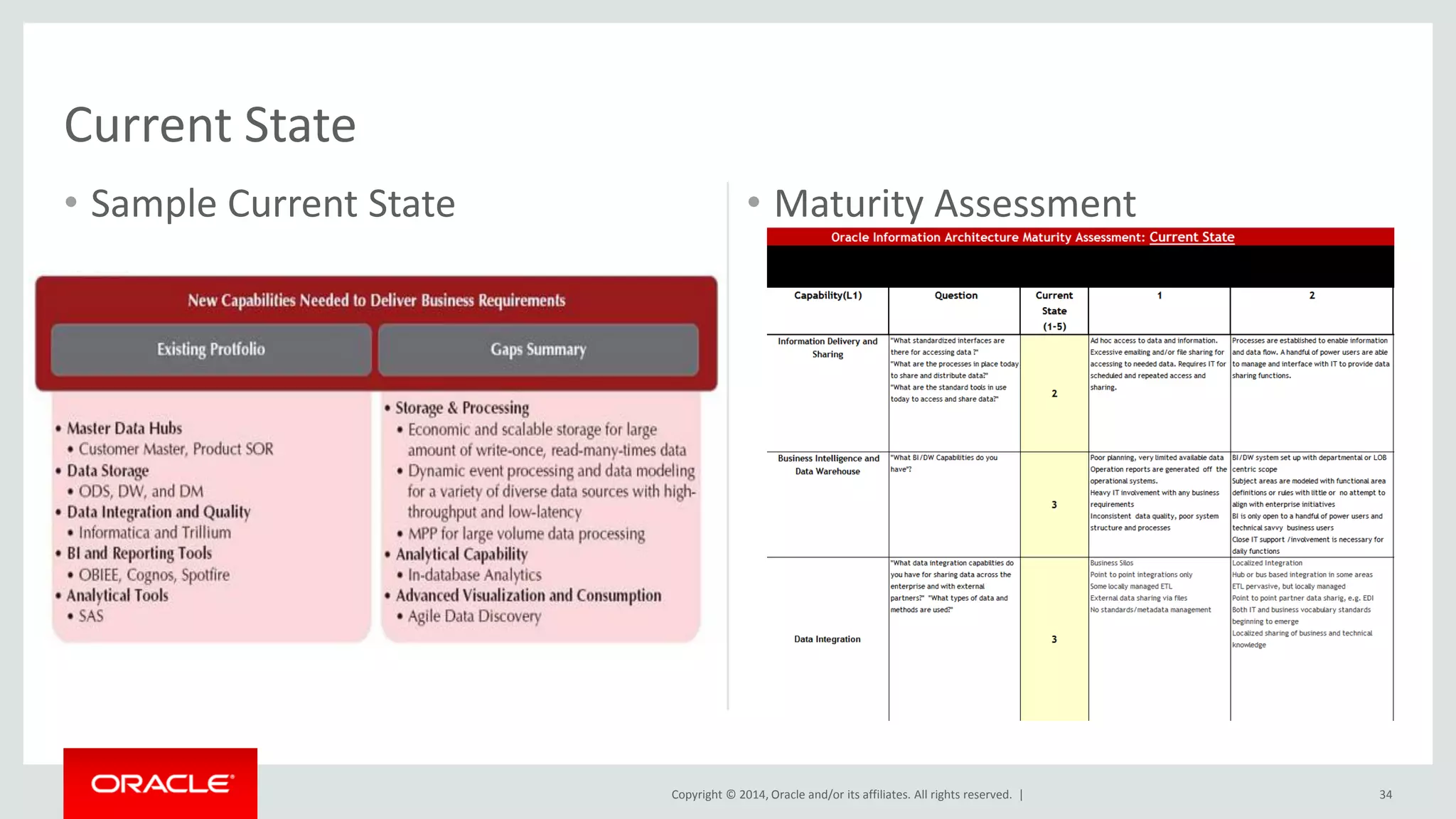
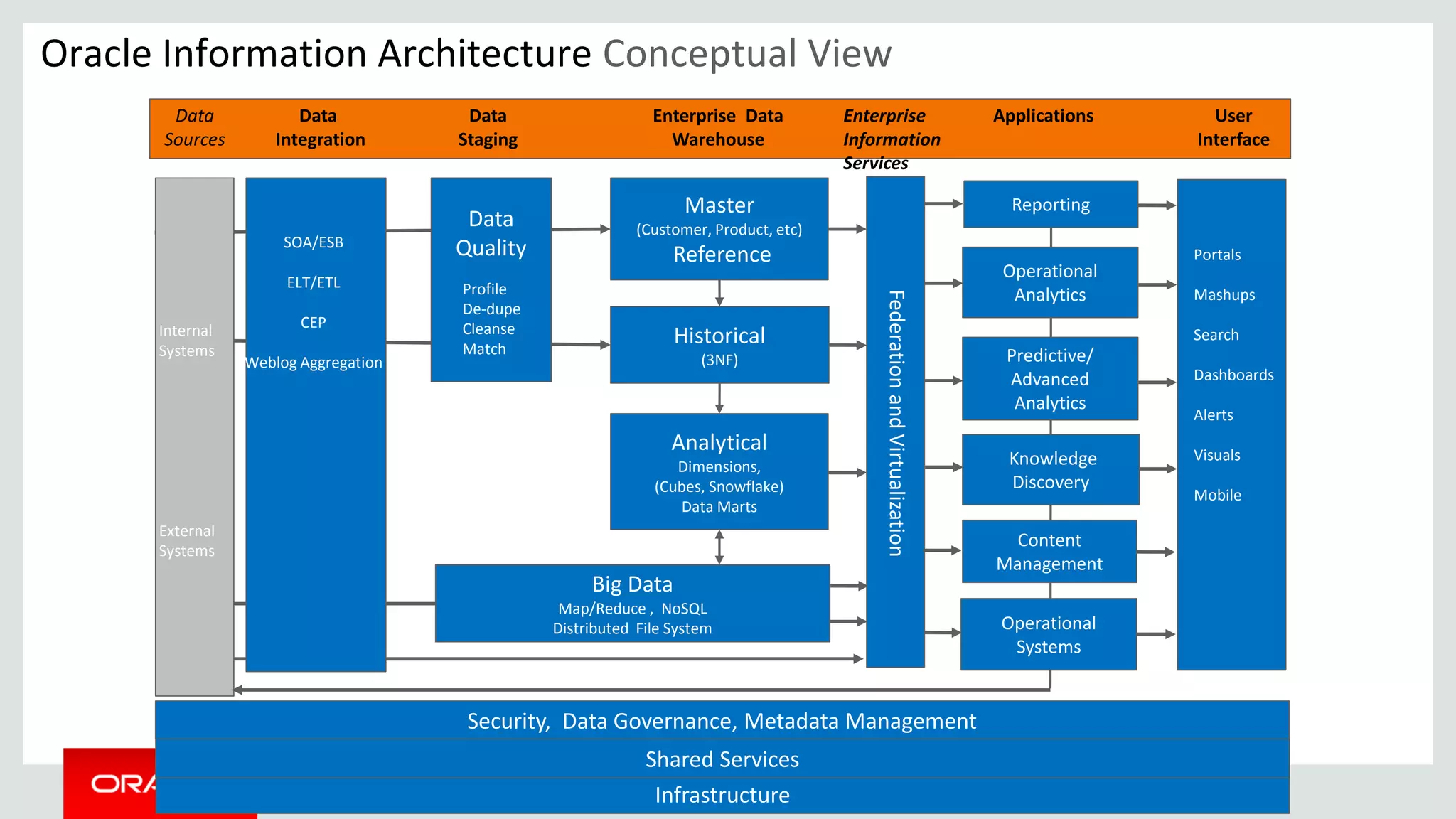
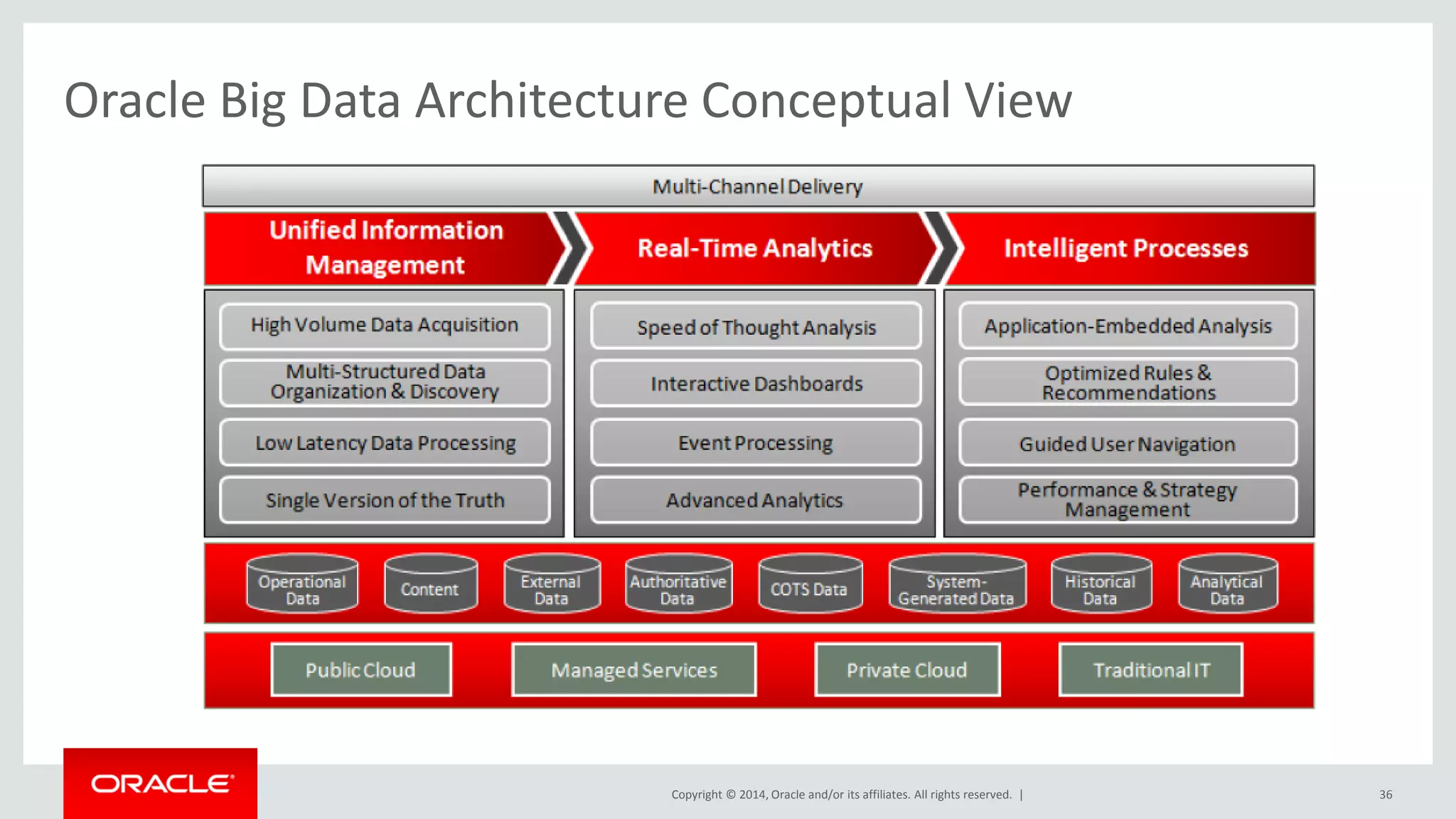
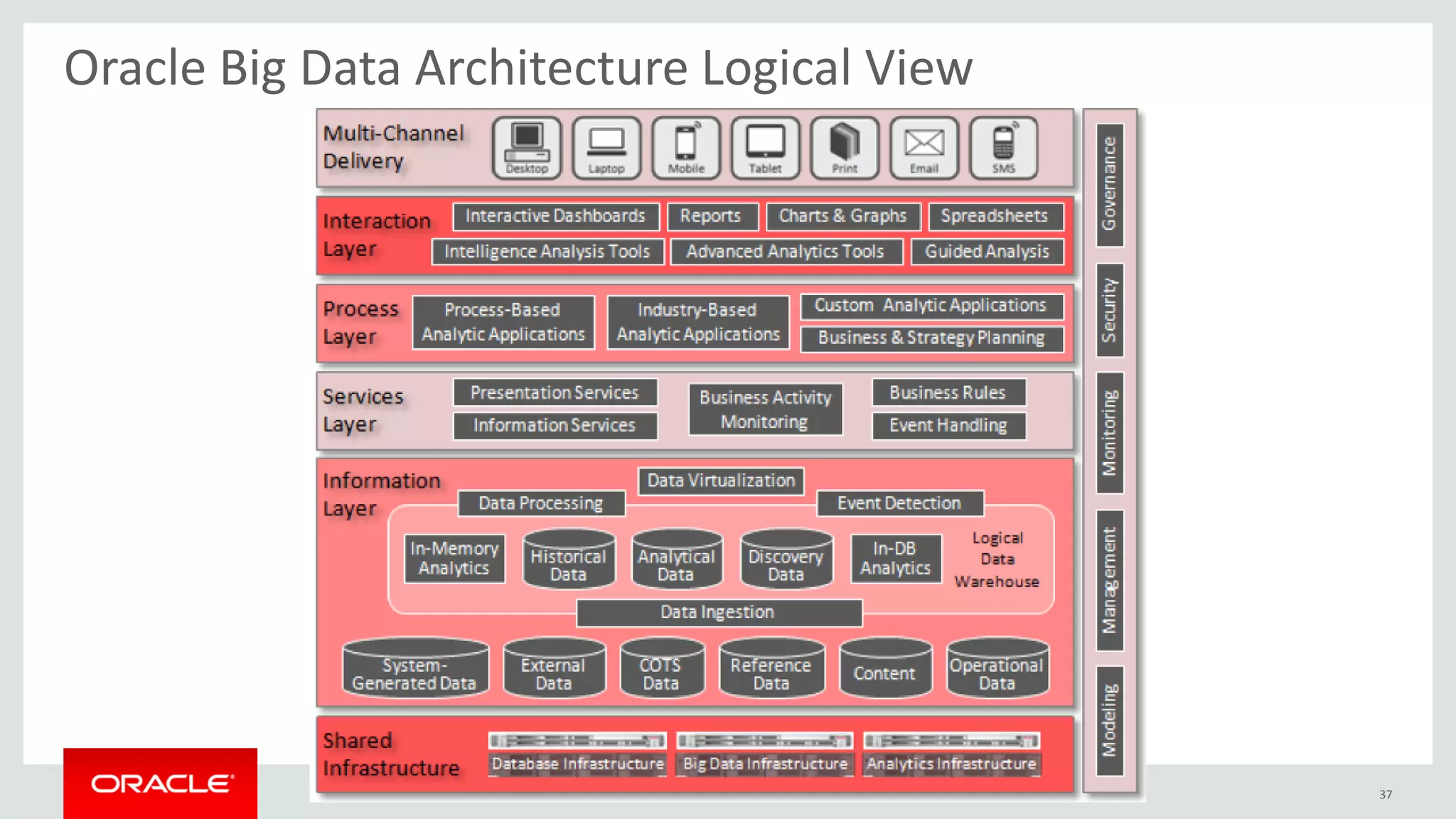
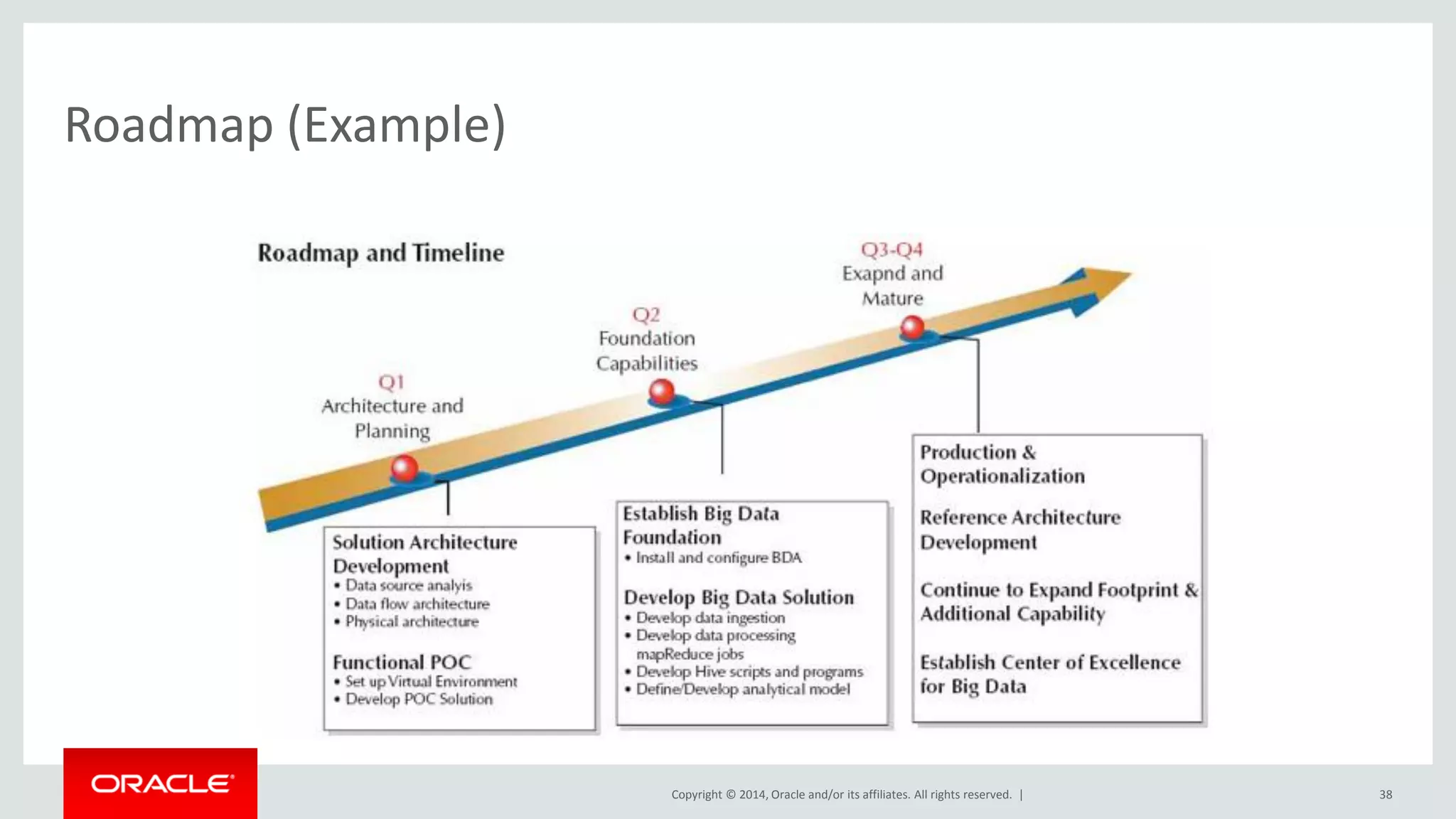
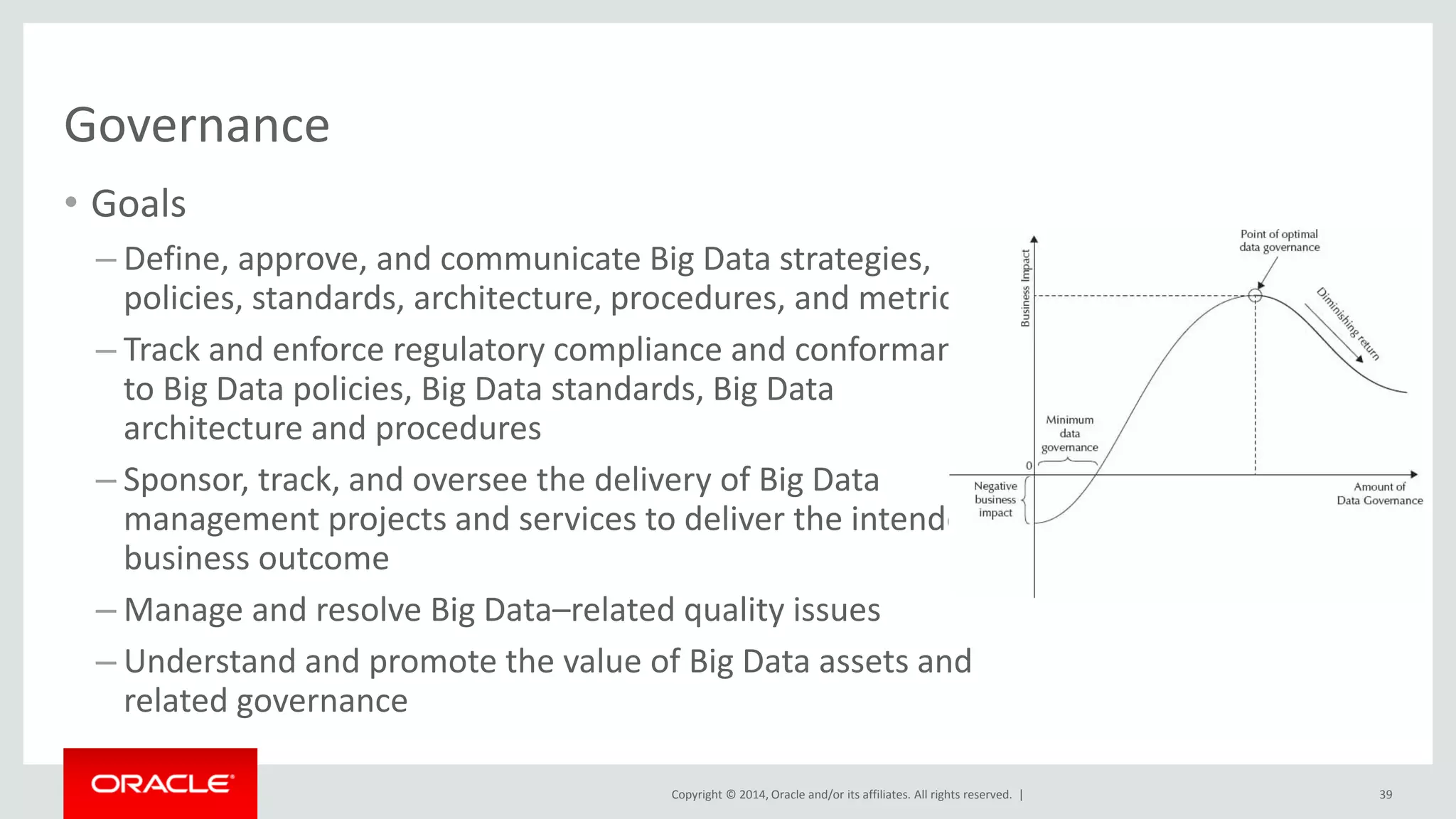
This document provides an overview and agenda for a presentation on big data landscape and implementation strategies. It defines big data, describes its key characteristics of volume, velocity and variety. It outlines the big data technology landscape including data acquisition, storage, organization and analysis tools. Finally it discusses an integrated big data architecture and considerations for implementation.