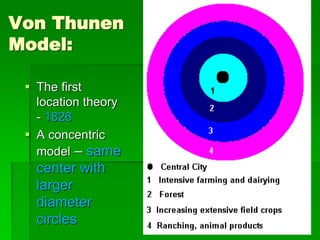
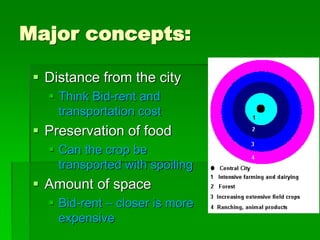
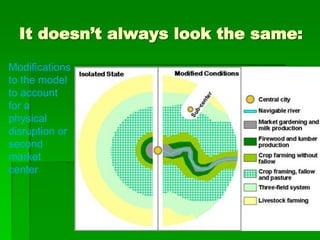
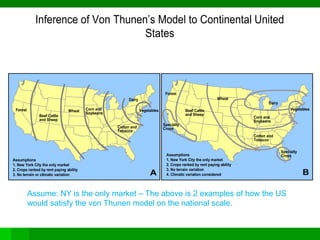
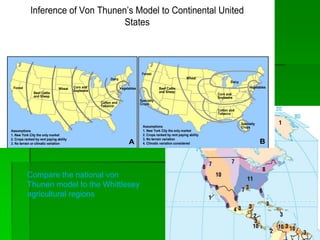
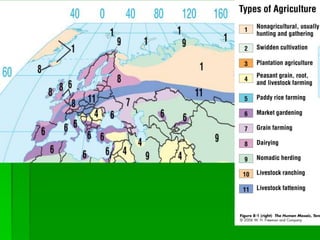
Von Thunen's model of agricultural land use proposes that the type of agriculture at a given distance from the central market will depend on transportation costs and how perishable the crop is. Higher value crops that are perishable or expensive to transport, like dairy and vegetables, will be grown closest to the market. Lower value crops that can withstand longer transport times, like grains and ranching, will be farther from the market. The model makes simplifying assumptions about uniform land quality and a single central market to demonstrate this concept. It has been applied to predict agricultural patterns on national scales but modifications are needed to account for additional factors like terrain, climate, and multiple urban markets.