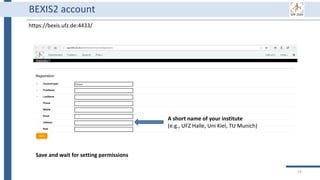
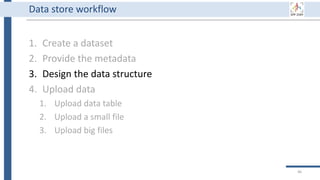
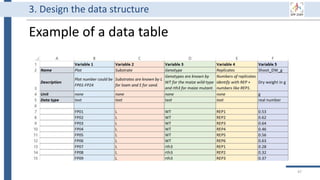
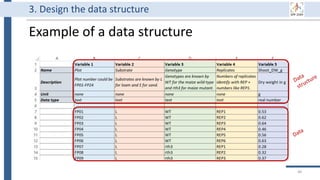
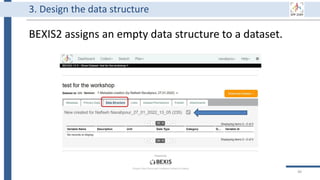
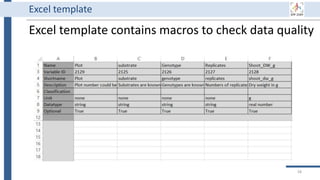
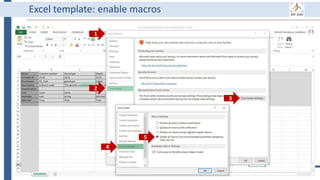
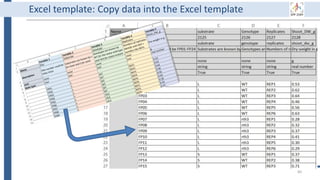
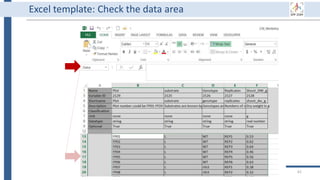
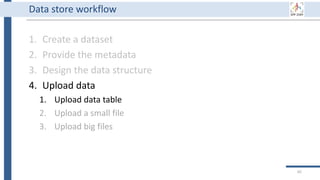
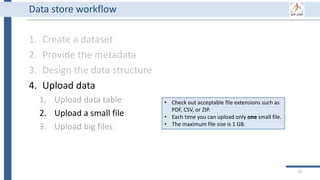
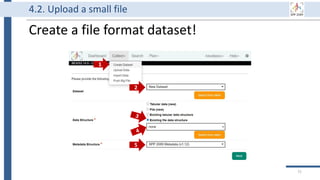
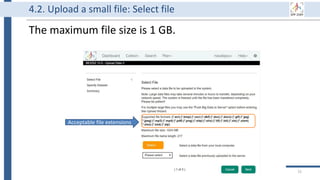
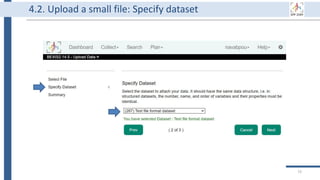
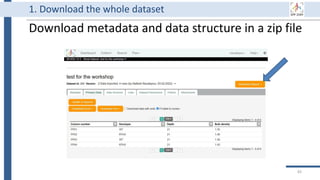
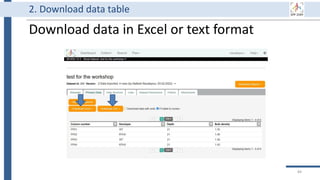
This document outlines an agenda for a data management training session. The full-day session will cover basics in the morning, advanced topics after lunch, and end with a question and answer period and required homework. Attendees will learn about account creation and login procedures for various research platforms, file labeling standards, and data management best practices including uploading, downloading, sharing and archiving data throughout its lifecycle. The document provides details on specific topics to be covered as well as templates and guidelines for research activities like field and column experiments.




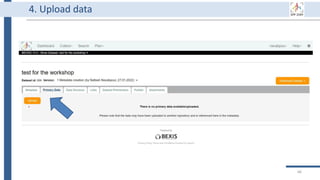
![Universal labelling code
• Labelling of soil column experiments
[projectnumber_SCE#_C#];
• Soil colum expriment = SCE01,…
• Column in the experiment = C01
• example: P21_SCE01_C01
• Labelling of sampling campaigns in soil plot experiment
[projectnumber_SPE_sampling date_FP#_type of sample#];
• Field plot = FP01, FP02..
• Depth 0-20 cm = D00_20
• Sampling of several points within each plot = a, b, c
• example: P21_SPE_20181105_FP01_UC#
• You may extend the name by providing further details if required
(i.e. bulk/rhizosphere/rhizoplane)…
• If you extend the details, communicate that to your cooperation partners
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workshop2022-part1-220323200811/85/BEXIS2-Workshop-Part1-23-320.jpg)




![30
It is data collected or produced in the course of scientific research activities and
used as evidence in the research process, or commonly accepted in the research
community as necessary to validate research findings and results (European open
science cloud [1]).
Research data might include measurement data, laboratory values, audiovisual
information, texts, survey data, objects from collections, or samples that were
created, developed or evaluated during scientific work. Methodical forms of
testing such as questionnaires, software and simulations may also produce
important results for scientific research and should therefore also be categorized
as research data (DFG Guidelines on the Handling of Research Data [2]).
Research data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workshop2022-part1-220323200811/85/BEXIS2-Workshop-Part1-30-320.jpg)
![32
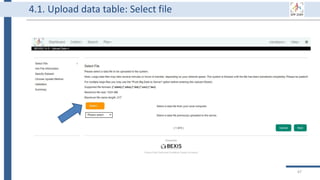
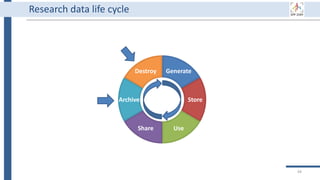
Why using a data management platform (DMP)
1. DMP supports data throughout its life cycle.
2. All components of the research process must be available to ensure
transparency, reproducibility, and reusability [3].
3. A DMP gathers research data in one place and keeps it usable for a
long time.
4. A DMP has to deal with security and privacy concerns due to
collecting private data.
5. Using a data management system is a DFG requirement, and it is
mentioned in the SPP 2089 bylaws.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workshop2022-part1-220323200811/85/BEXIS2-Workshop-Part1-32-320.jpg)
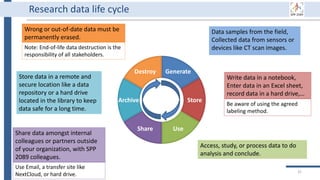
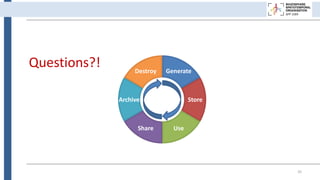
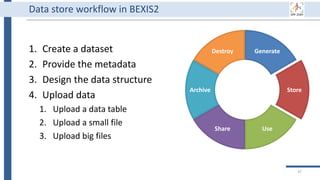
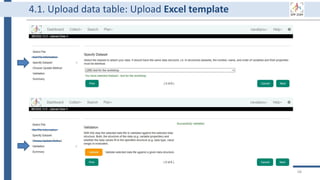
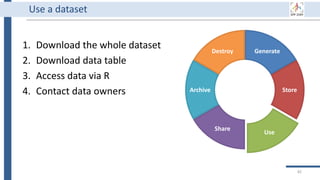
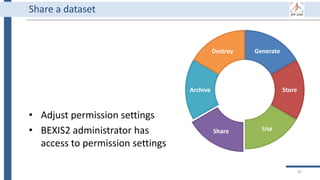
![Generate
Store
Use
Share
Archive
Destroy
34
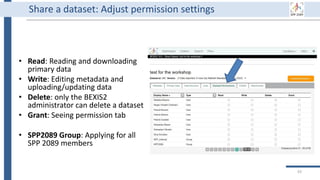
BEXIS2 administrator can remove
incorrect or useless data forever.
Of course, it requires special
permission from the data owner.
BEXIS2 is a free and open source
software supporting researchers in
managing their data throughout
the data life cycle from data storing
to sharing research data [4].
BEXIS2 keeps track of the
evolution of a dataset and returns
to any previous version if needed.
Start to store data in BEXIS2
at this point of your work.
Data security is a major
concern for BEXIS2. It specify
fine grained data permissions
on who can view, access, or
update a dataset.
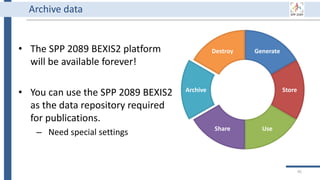
Why using BEXIS2?
BEXIS2 can be used for long-
term data archiving even as
the publication requirement.
In the near future, you can
get DOI for each dataset.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workshop2022-part1-220323200811/85/BEXIS2-Workshop-Part1-34-320.jpg)

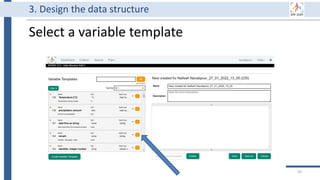
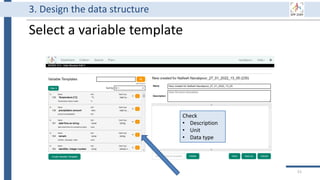
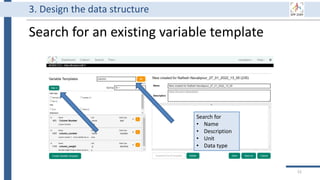
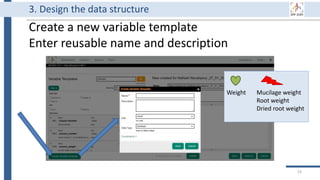
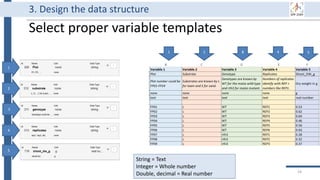
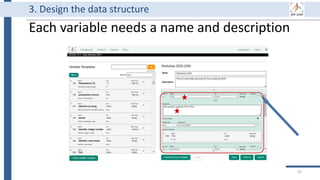
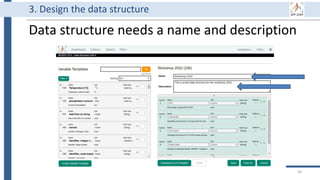
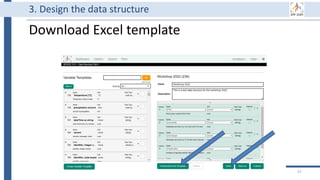


![99
[1] EOSC glossary: https://eosc-portal.eu/glossary
[2] DFG Guidelines on the Handling of Research Data:
https://www.dfg.de/download/pdf/foerderung/grundlagen_dfg_foerderung/forschungsdaten/g
uidelines_research_data.pdf
[3] Wilkinson, M. D. et al. (2016). https://www.nature.com/articles/sdata201618
[4] BEXIS Research Data Management: https://fusion.cs.uni-jena.de/bpp/
References](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/workshop2022-part1-220323200811/85/BEXIS2-Workshop-Part1-99-320.jpg)