This document outlines best practices for structuring public-private partnership (PPP) and concession contracts. Key points include:
1. Using output-based contracts focused on performance rather than investment obligations to incentivize efficiency.
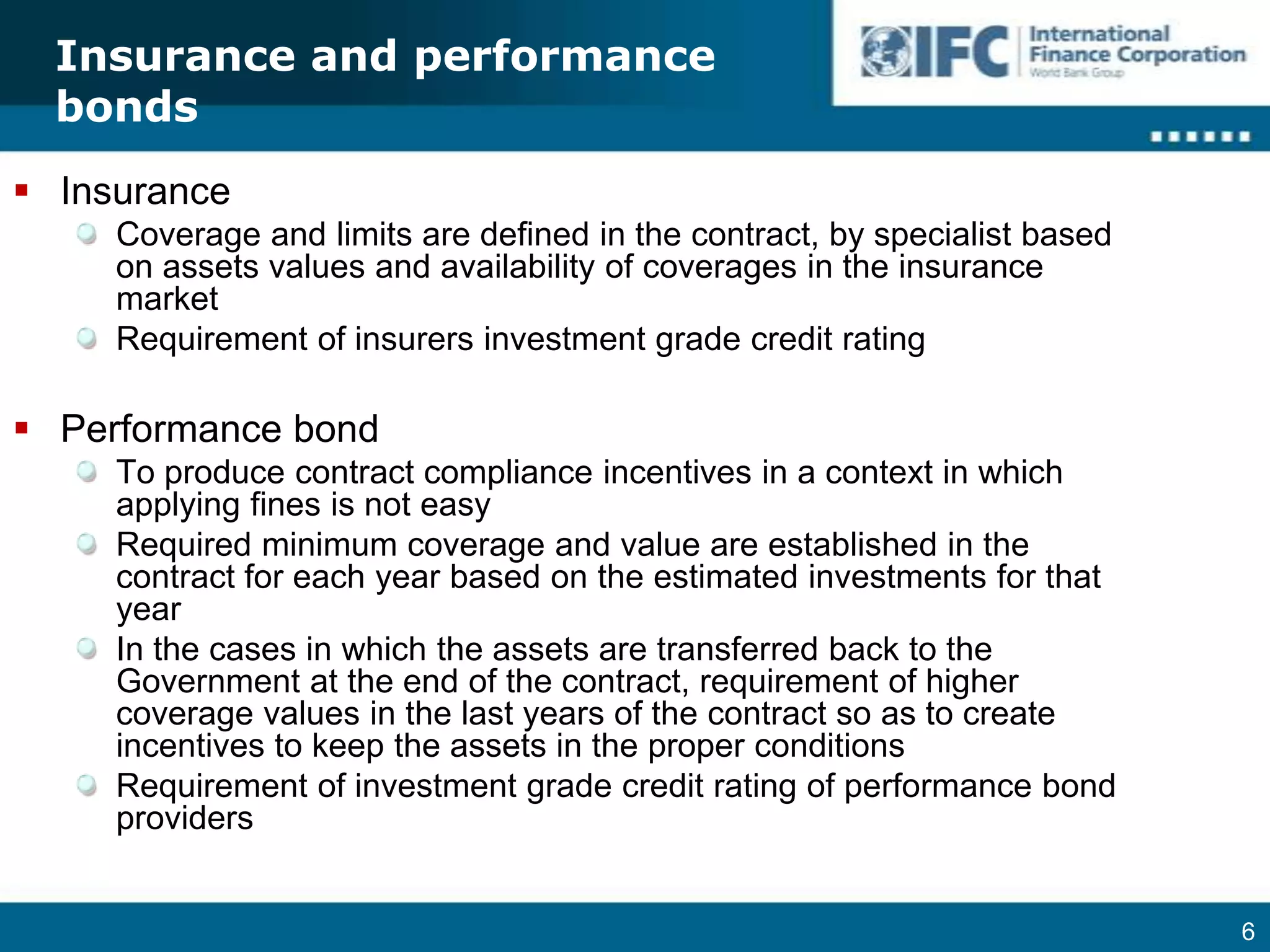
2. Requiring adequate insurance, performance bonds, and credit ratings to ensure compliance.
3. Protecting financiers and monitoring concessionaire finances through revenue assignment, financial disclosure, and notification of non-compliance.
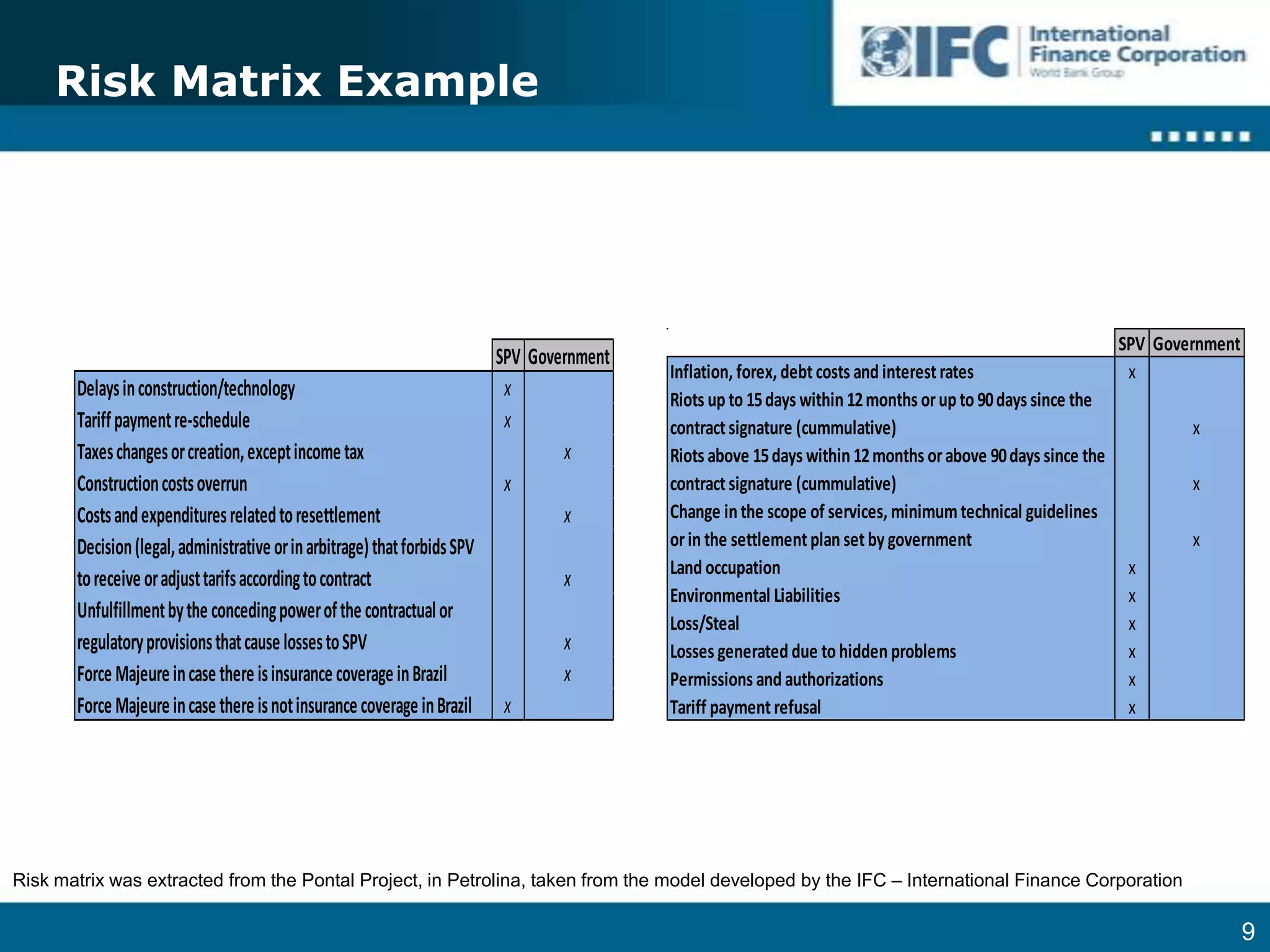
4. Establishing clear risk matrices and sharing arrangements based on ability to control risks and potential for externalization.
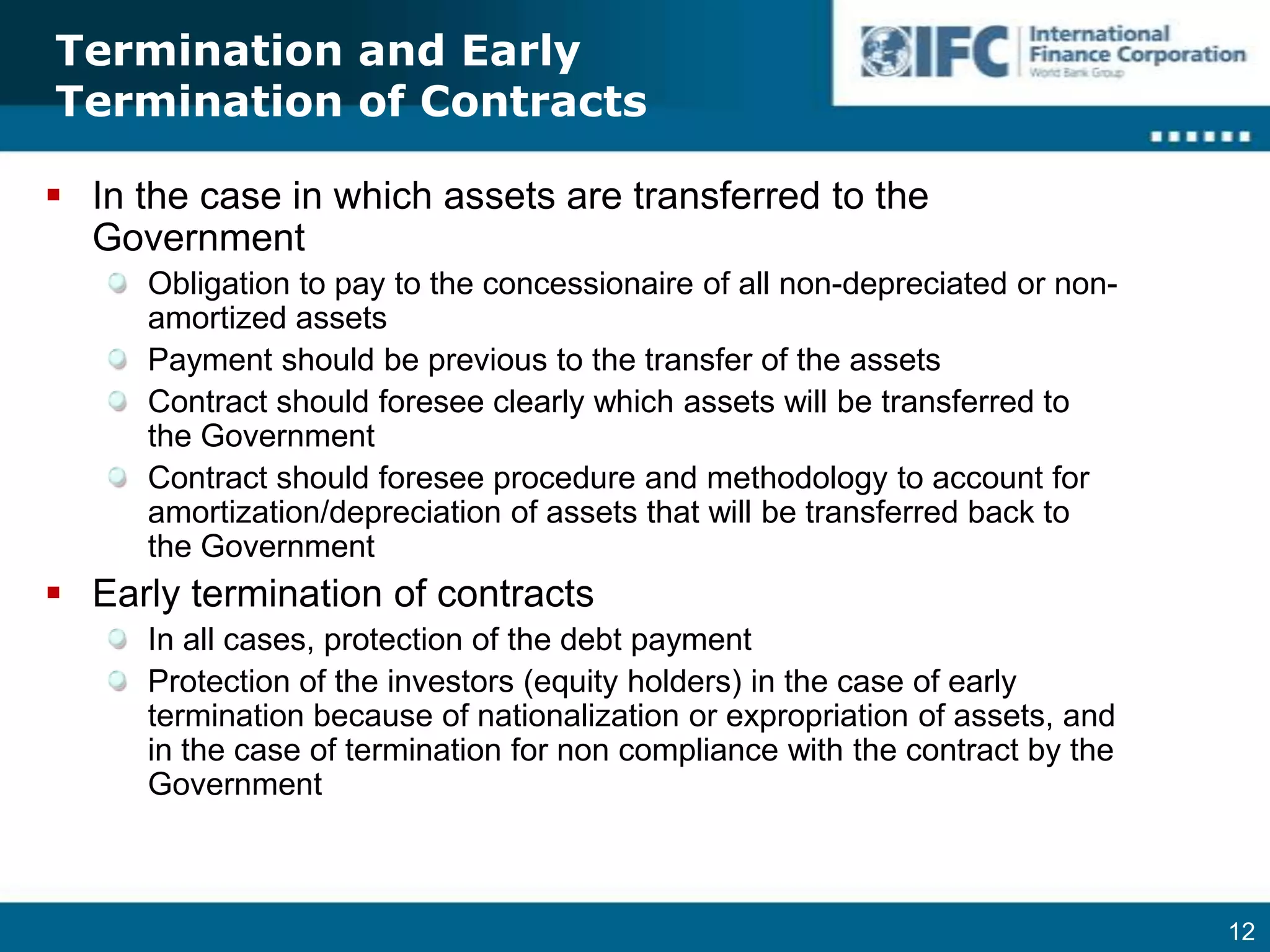
5. Including provisions for default management, mediation, termination, and credit enhancement of government payments.