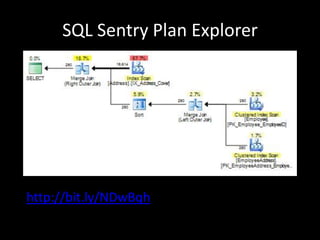
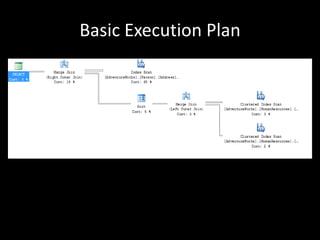
The document provides an overview of SQL Server execution plans, including the types, reading methods, and limitations associated with execution plans such as ad hoc query plans and parameter sniffing. It suggests various tools for further analysis, like SQL Sentry Plan Explorer and SQL Server Profiler, and outlines steps to mitigate issues with execution plans. Additional resources are shared for further learning on the topic.





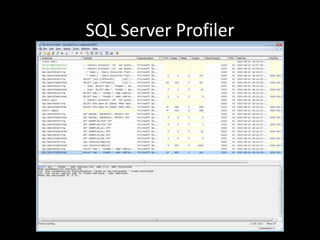
![List of Existing Plans
SELECT [cp].[refcounts]
,[cp].[usecounts]
,[cp].[objtype]
,[st].[dbid]
,[st].[objectid]
,[st].[text]
,[qp].[query_plan]
FROM sys.dm_exec_cached_plans cp
CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_sql_text(cp.plan_handle) st
CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_query_plan(cp.plan_handle)
qp;
* From SQL Server Execution Plans by Grant Fritchey – p. 23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beforeyouoptimize-120818184154-phpapp02/85/Before-you-optimize-Understanding-Execution-Plans-8-320.jpg)