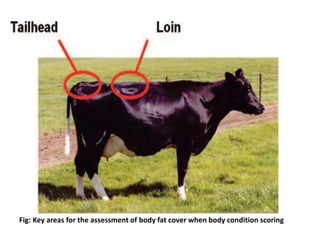
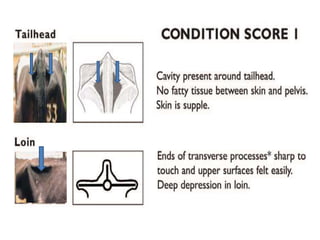
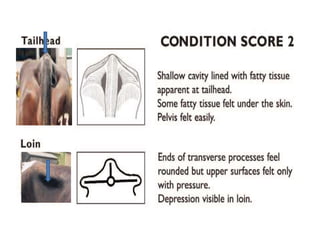
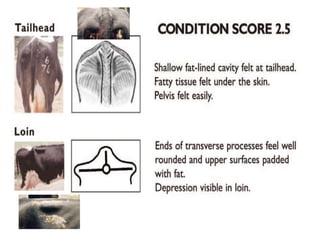
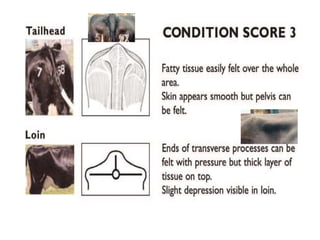
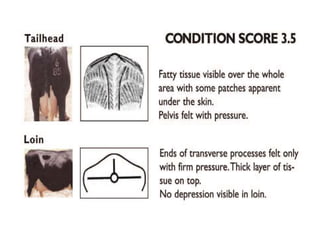
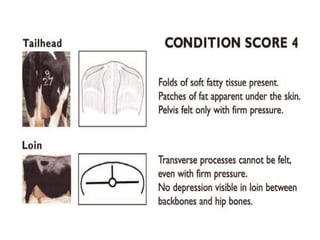
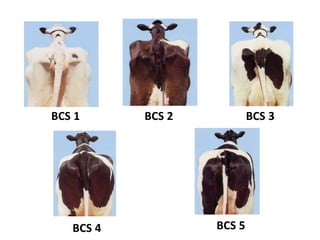
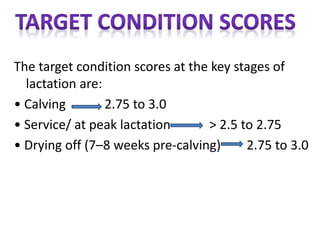
Body condition scoring involves visually assessing and handling cows to determine their fat reserves based on a 1-5 point scale. It is conducted at key stages of lactation, including before drying off and calving, to ensure cows are in the ideal condition and fertility is not compromised. Regular scoring allows adjustments to feeding to maintain targets of 2.75-3 at calving and >2.5-2.75 at peak lactation, linking cow condition to milk production and reproductive health.