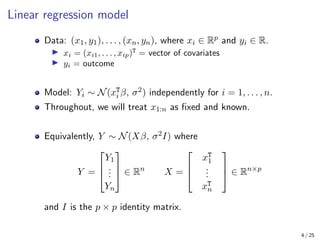
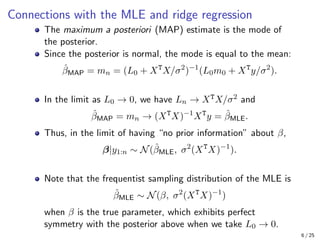
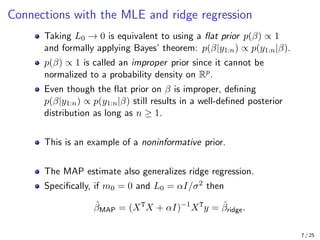
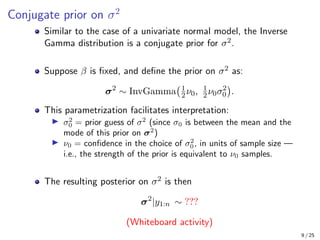
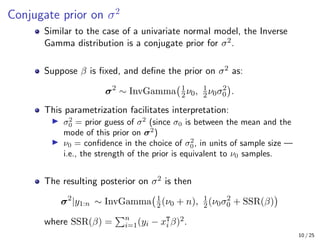
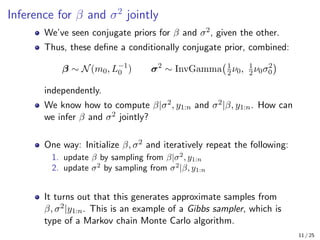
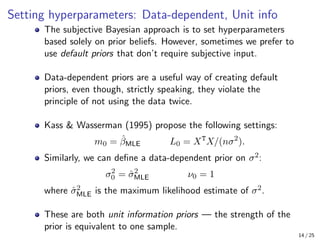
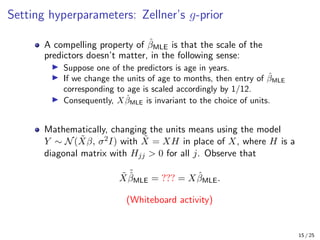
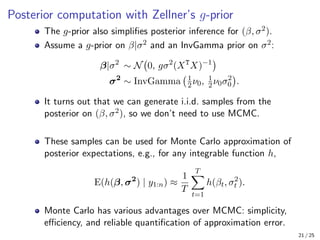
The document provides an in-depth overview of Bayesian linear regression, discussing the model, prior and posterior distributions, and various settings of hyperparameters including unit information and Zellner’s g-prior. It highlights the connections between Bayesian methods and frequentist approaches like maximum likelihood estimation and ridge regression, as well as the use of conjugate priors for efficient inference. Moreover, it introduces the Gibbs sampler for joint inference and outlines the advantages of Monte Carlo methods over MCMC for posterior computation.