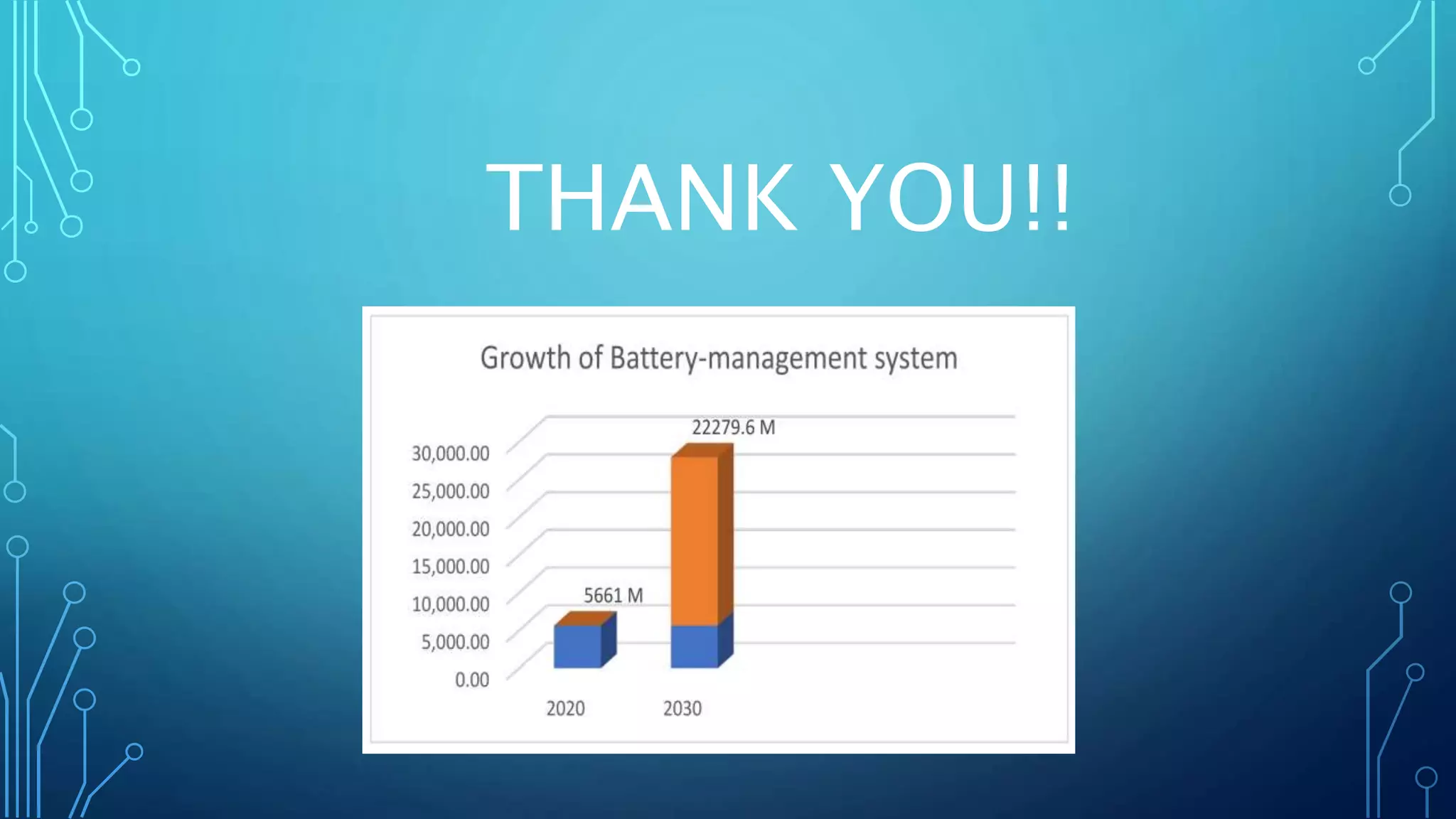
This document discusses battery health detection testing in battery swapping systems. It describes how battery swapping systems work and their advantages over traditional charging. It also explains that battery health detection tests are important to ensure only high-quality batteries are used. Common tests discussed include capacity, voltage, resistance, cycle life, age, and thermography tests. The cycle life test and capacity test are described in more detail. The cycle life test measures the number of charge-discharge cycles before capacity drops, while the capacity test measures the battery's current charge level. Non-invasive optical testing is also summarized as a method to evaluate batteries without disrupting their operation.