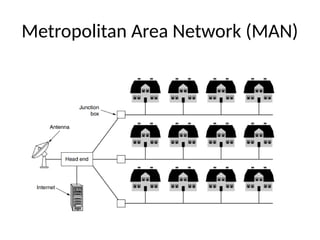
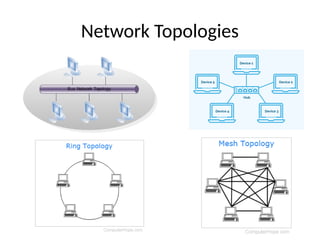
The document provides an overview of networking concepts, including types of networks such as PAN, LAN, MAN, and WAN, each with distinct characteristics and uses. It discusses key networking devices, network topologies, IP addressing, basic networking protocols, and security measures necessary for maintaining network integrity. Overall, it emphasizes the crucial role of networking in modern communication and technology.