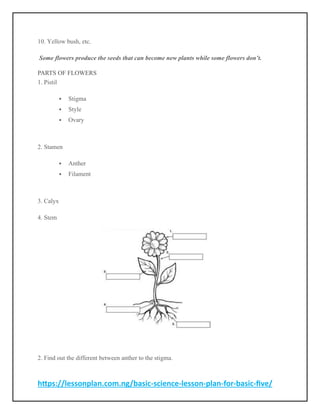
The document outlines a basic science lesson plan for Basic Five students, covering topics such as environmental quality, soil erosion, pollution, and waste disposal. Each week includes specific learning objectives, resources, and activities aimed at helping students understand and engage with the material. Key themes include identifying pollution types, understanding environmental impacts, and learning waste management practices.