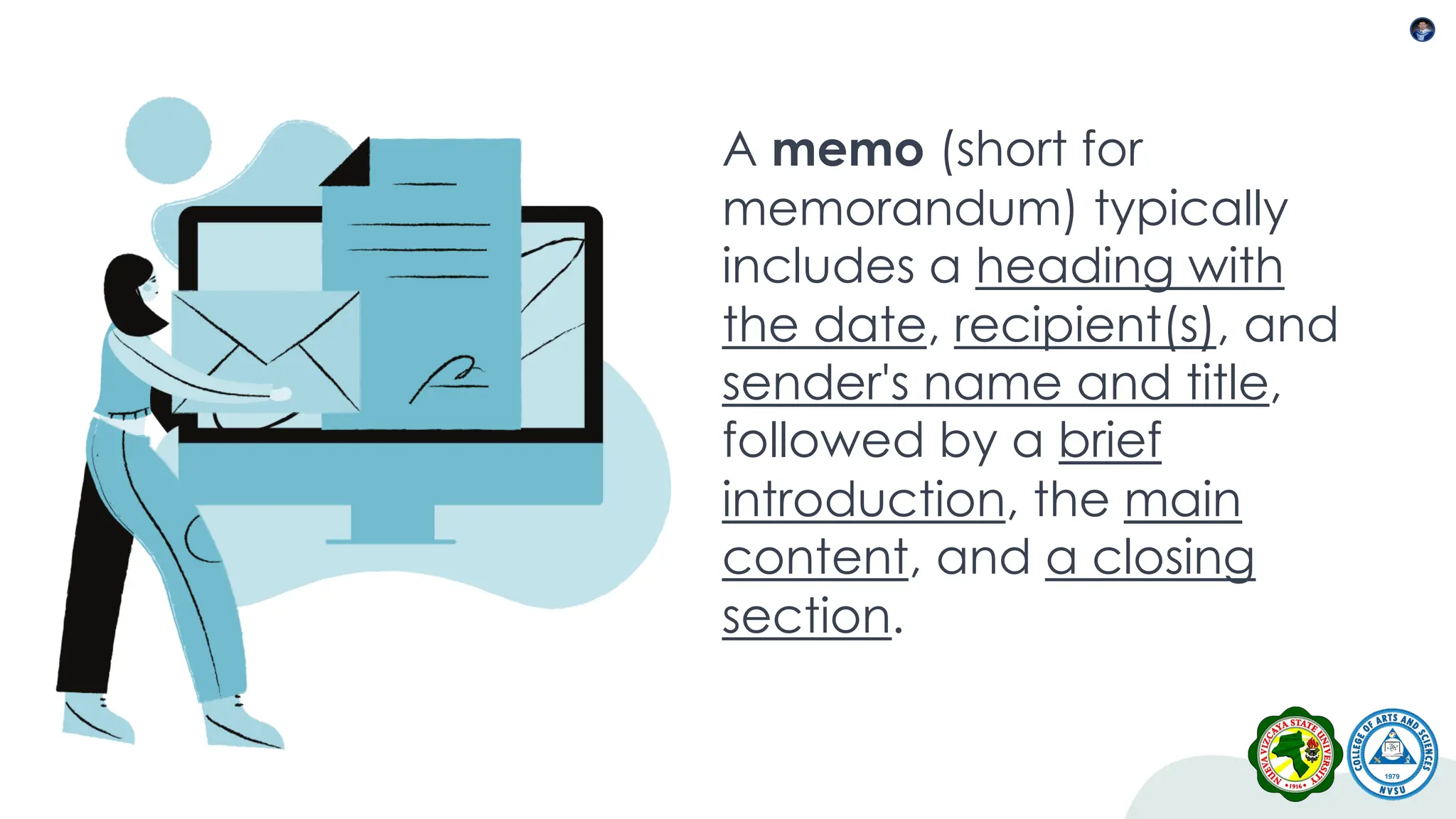
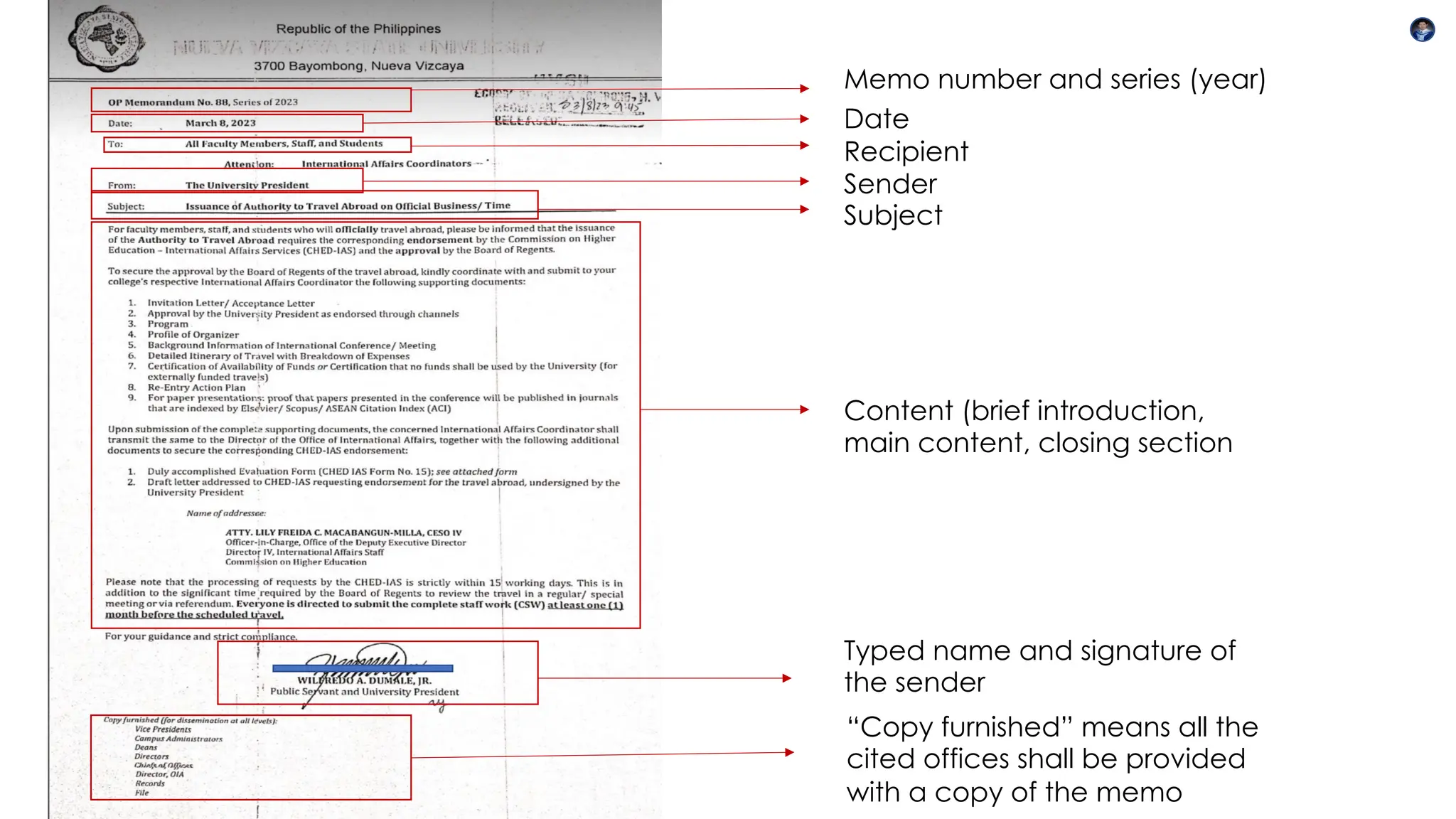
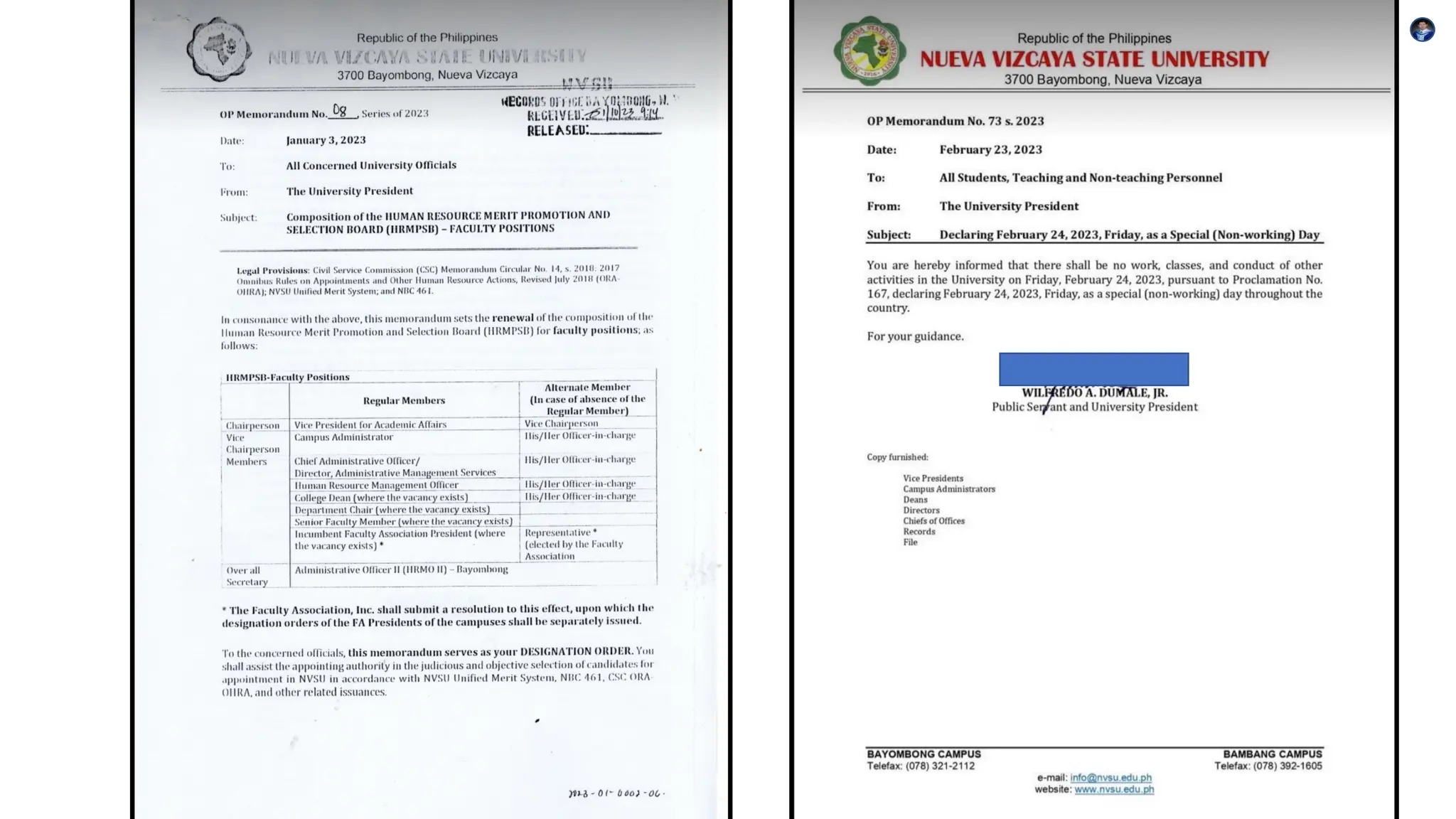
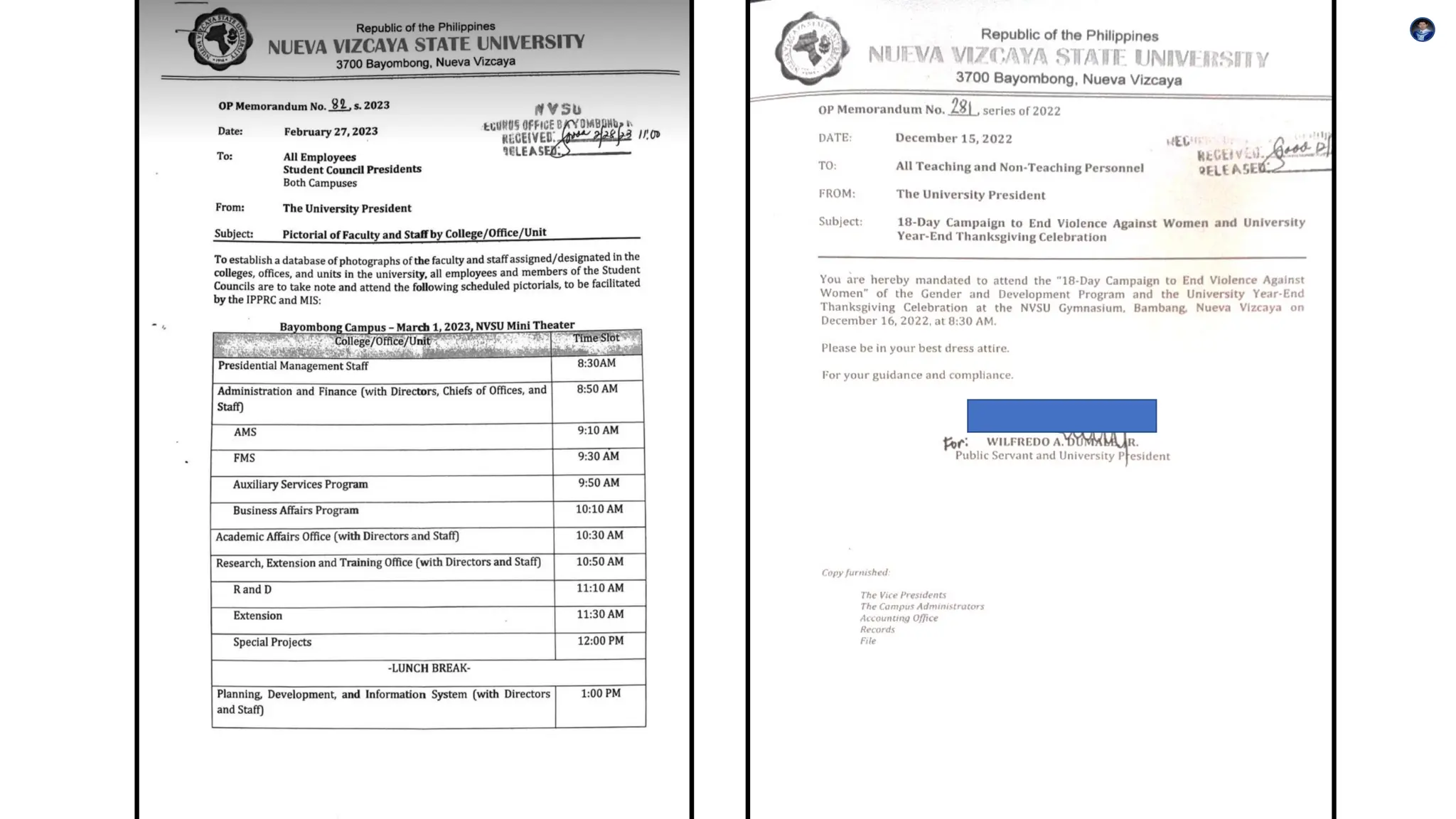
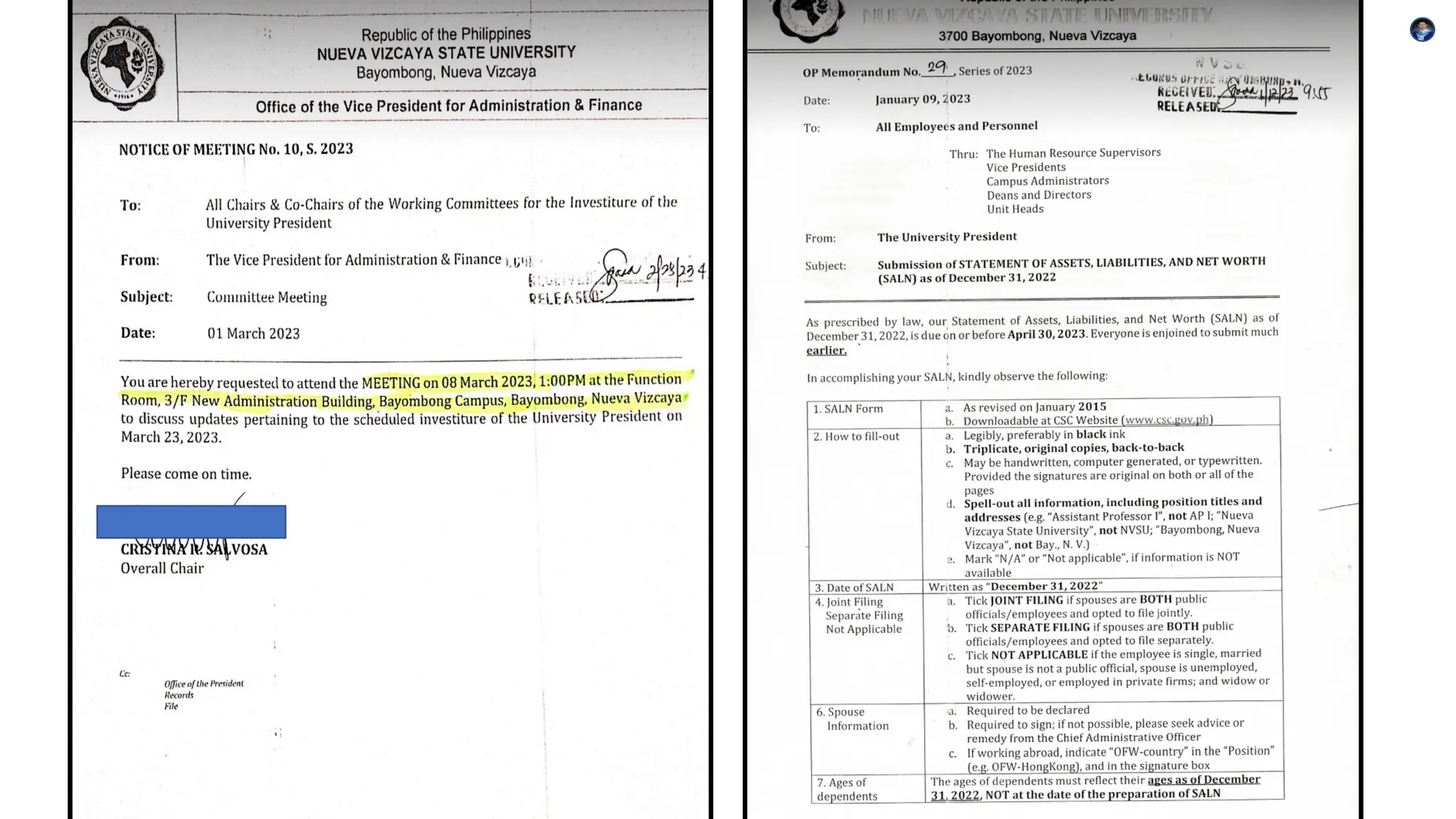
This document outlines the key components, functions, and types of memos, including informational, policy, directive, progress report, and request memos. It emphasizes the importance of tone, audience awareness, clarity, brevity, formatting, and proofreading when writing a memo. Memos serve as an effective means of internal communication within organizations, conveying essential information and instructions.