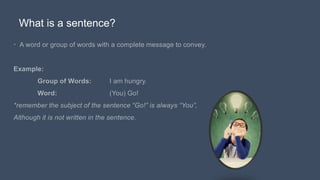
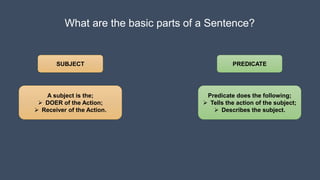
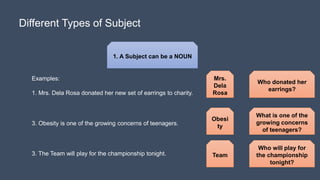
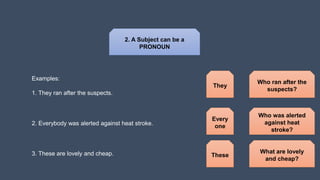
Here is a 5 sentence story using my own experiences:
My family and I went to the beach on Saturday. The waves were large and crashing onto the shore. I decided to go bodyboarding in the surf but found it difficult to catch any waves. After many failed attempts, I finally managed to ride a wave all the way to shore. It was so much fun that I wanted to go bodyboarding again the next time we visit the beach.