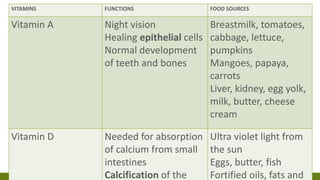
The document by Mr. Allan, an RN from Aga Khan University Hospital, outlines the fundamental aspects of nutrition and dietetics, emphasizing the importance of good nutrition in preventing health issues like obesity and diabetes. It details the two categories of nutrients: macronutrients, which include carbohydrates, proteins, fats, fibers, and water, and micronutrients like vitamins and minerals, highlighting their sources and roles in the body. Additionally, it presents a set of dietary principles and special diets aimed at promoting health and managing conditions such as diabetes and high cholesterol.