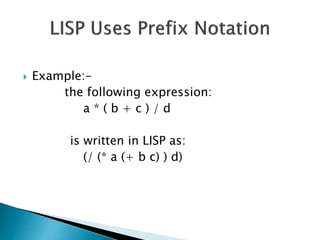
This document discusses the Lisp programming language. It provides an introduction to Lisp, describes some of its key features like rich arithmetic, generic functions, and macros. It explains that Lisp is well-suited for artificial intelligence programs. The document also gives some examples of Lisp code and applications that use Lisp like Yahoo Store, AutoCAD, and Emacs.