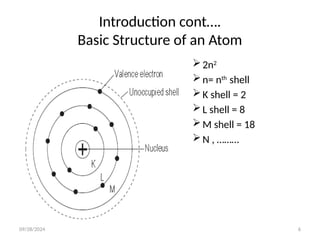
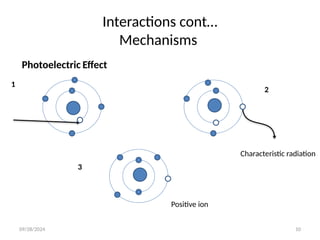
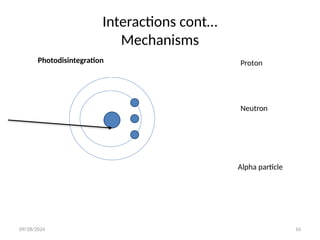
The document discusses the fundamental interactions of X-rays with matter, including transmission, absorption, and scatter, and highlights mechanisms such as the photoelectric effect and Compton effect, which are crucial in diagnostic radiology. It explains the atomic structure relevant to X-ray interactions and provides terminologies like half-value layer and attenuation. The conclusion emphasizes that X-ray photons can be transmitted, absorbed, or scattered, with photoelectric effect and Compton scattering being the most significant for diagnostic imaging.