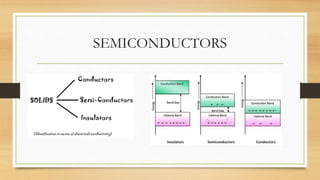
This document provides an overview of basic electronics. It discusses that electronics deals with the emission, flow and control of electrons. The basic electronic components for designing circuits are resistors, capacitors, inductors, diodes, LEDs, transistors, ICs, relays and batteries. The history of electronics began with the discovery of electrons by J.J. Thomson in 1897. Key developments include the vacuum tube era, the transistor era in 1947, and the integrated circuit era starting in 1958. Semiconductors are materials whose conductivity is between conductors and insulators and can be varied by temperature and doping.