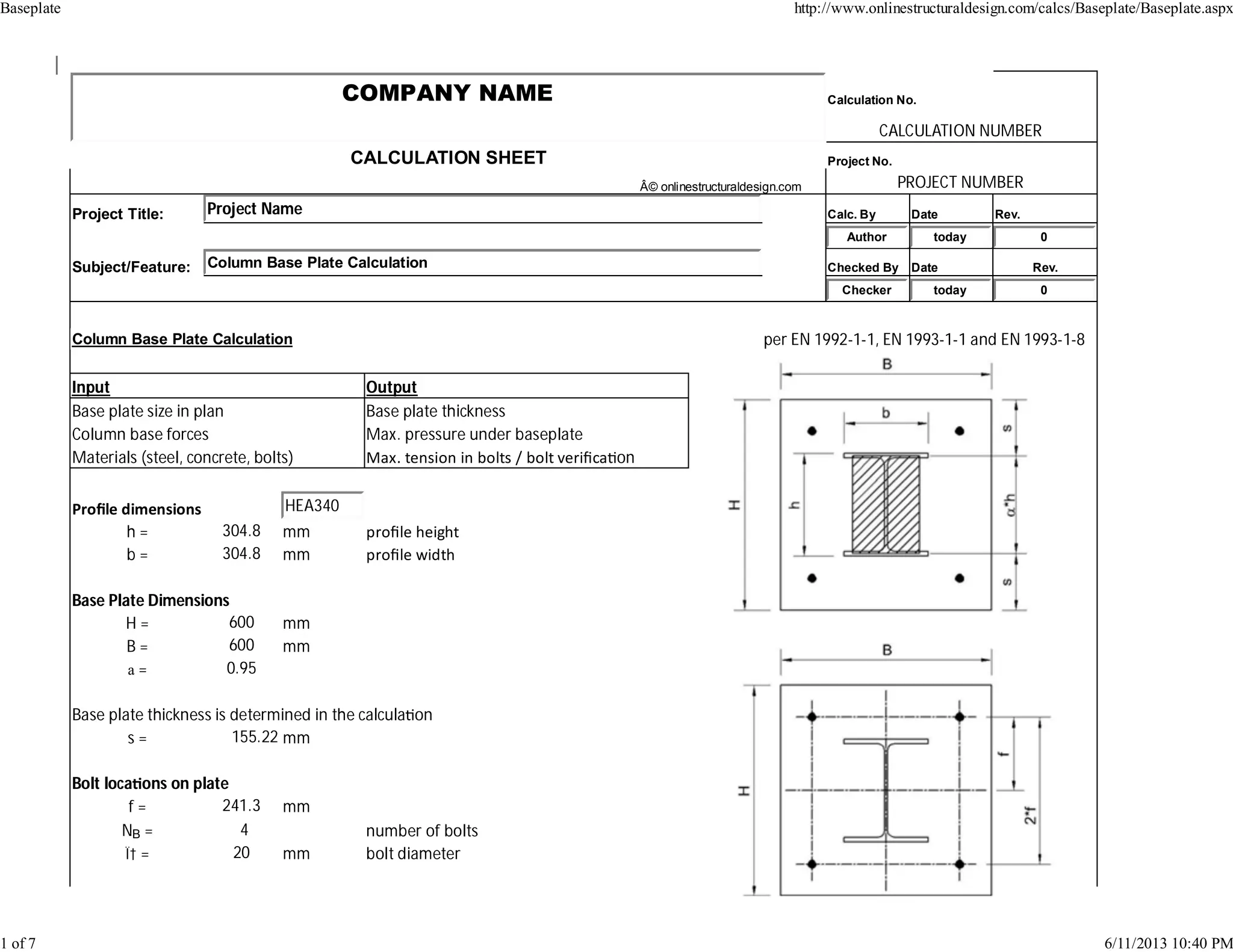
(1) The document provides calculations to determine the required base plate thickness for a column base connection according to Eurocode standards. It includes input parameters such as column forces, material properties, bolt sizes and locations.
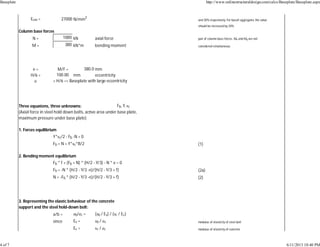
(2) Three equations are solved simultaneously to determine the maximum pressure under the base plate, tension in the hold down bolts, and active concrete area.
(3) The calculated pressure and bolt tension exceed design values, requiring a redesign of the base plate length/width or use of higher strength concrete.
(4) The minimum required base plate thickness is then calculated based on the design bending moment and material yield strength.


![nb = 2 number of steel hold down bolts
Ab = 2* π*φ2
/4 = 628.3 mm2
area of steel hold down bolts
sb = Fb / Ab
n = Es / Ec = 7.78 modular ra o of elas city, steel to concrete
References:
Design of Welded Structures - O. W. Blodge (James F. Lincoln Arc Welding Founda on)
EN 1992-1-1:2004 - Eurocode 2: Design of concrete structures - Part 1-1: General rules and rules for buildings
EN 1993-1-1:2005 - Eurocode 3: Design of steel structures - Part 1-1: General rules and rules for buildings
EN 1993-1-8:2005 - Eurocode 3: Design of steel structures - Part 1-8: Design of joints
COMPANY NAME Calculation No.
CALCULATION NUMBER
CALCULATION SHEET Project No.
© onlinestructuraldesign.com PROJECT NUMBER
Project Title: Project Name Calc. By Date Rev.
Author today 0
Subject Column Base Plate Calculation Ckd. By Date Rev.
Checker today 0
a/b = (N/Ab)/(sc*n) = N/(Ab*sc*n)
From similar triangles =>
a/b = (H/2-Y+f)/Y
=> N/(Ab*sc*n) = (H/2-Y+f)/Y =>
=> sc = Fb * Y / (Ab * n *(H/2 - Y + f)) (3)
From (1), (2) and (3)
-Fb * (H/2 - Y/3 -e)/(H/2 - Y/3 + b) + Fb = (Fb * Y2
* B) / [2 * Ab * n *(H/2 - Y + f)]
Solve for Y:
Y3
+ 3 * (e - H/2) * Y2
+ [(6 * n * Ab)/B] * (f + e) * Y - [(6 * n * Ab)/B] * (H/2 + f) * (f + e) = 0
Baseplate http://www.onlinestructuraldesign.com/calcs/Baseplate/Baseplate.aspx
5 of 7 6/11/2013 10:40 PM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/baseplate-130724110641-phpapp02/85/Baseplate-5-320.jpg)
![or
Y3
+ K1 * Y2
+ K2 * Y + K3 = 0
where
K1 = 3 * (e - H/2) = 240
K2 = [(6 * n * Ab)/B] * (f + e) = 30362
K3 = - K2 * (H/2 + f) = -16435192
Y = 166.5 mm
Fb = 278.92 kN (in 2 bolts ) per (2a) hold down bolts max. tension (in all bolts)
F1.bolt = Fb /2 = 139.46 kN hold down bolt max. tension - in 1 bolt
F1.bolt /(π*φ2
/4) = 443.92 N/mm2 > fyd-b redimension, bolt effec ve stress is larger than bolt design stress
192.0 N/mm2
sc = 25.35 MPa per (3)
sc > fcd fcd = 8.00 MPa effec ve max. pressure under baseplate is compared
redesign base plate length and/or width with the concrete design compressive strength
stress under base plate is larger than the concrete compressive capacity if the max. pressure is higher than the concrete
Design of the Base Plate Thickness
Cri cal sec on loca on
s = 155.22 mm
Stress at the cri cal sec on loca on
ssc = sc*(Y - s) / Y = 1.72 MPa
Design cri cal moment - at cri cal sec on
MEd.plate = [(σsc*s/2)*(s/3)+(σc*s/2)*(s*2/3)]*B 126.31 kN*m
MC,Rd = Mpl,rd = (Wpl * fy)/ γM0 (4)
per EN 1993-1-1
Sec on 6.2.5 (2) Formula 6.13
Design resistance for bending for bending about one
principal axis for class 1 or 2 cross sec ons
Plas c sec on modulus of rectangular sec ons
Baseplate http://www.onlinestructuraldesign.com/calcs/Baseplate/Baseplate.aspx
6 of 7 6/11/2013 10:40 PM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/baseplate-130724110641-phpapp02/85/Baseplate-6-320.jpg)
![Wpl = B*tpl
2
/4 (5)
(tpl = base plate thickness)
from (4) and (5) => [fy * (B*tpl
2
)/4]/ γM0≥ MEd.plate
=> tpl≥ √[4 * MEd.plate * γM0 / (B * fy)]
=> tpl≥ 62.58 mm (with fy = 215 N/mm2
)
References:
Design of Welded Structures - O. W. Blodge (James F. Lincoln Arc Welding Founda on)
EN 1992-1-1:2004 - Eurocode 2: Design of concrete structures - Part 1-1: General rules and rules for buildings
EN 1993-1-1:2005 - Eurocode 3: Design of steel structures - Part 1-1: General rules and rules for buildings
EN 1993-1-8:2005 - Eurocode 3: Design of steel structures - Part 1-8: Design of joints
Baseplate http://www.onlinestructuraldesign.com/calcs/Baseplate/Baseplate.aspx
7 of 7 6/11/2013 10:40 PM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/baseplate-130724110641-phpapp02/85/Baseplate-7-320.jpg)