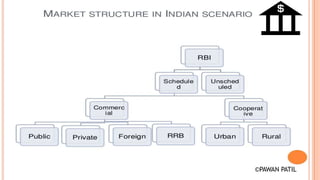
The document summarizes the history and development of the Indian banking sector. It notes that banking in India developed during the British era through the establishment of three banks by the British East India Company in the early 19th century. The Reserve Bank of India was established in 1935 and was followed by several other major public and private sector banks. As of 2019, the Indian banking system consists of 18 public sector banks, 22 private sector banks, and other types of banks. The document also outlines some key players in the public and private sector as well as recent government initiatives to support the banking sector.