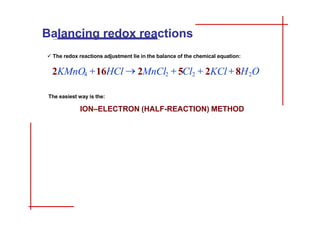
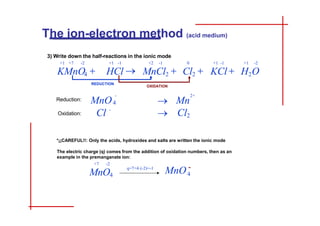
This document discusses the ion-electron method for balancing redox reactions in acid medium. It begins by explaining what redox reactions are and calculating oxidation numbers. It then shows how to identify the oxidation and reduction half-reactions, balance the ions and electrons, and combine the half-reactions into a whole reaction. Key steps include writing the half-reactions in ionic form, balancing elements other than H or O, adding H2O and H+ to balance O and H, and adding electrons to balance charge. The ionic equation is then converted to a molecular equation by adding spectator ions in equal amounts to both sides.