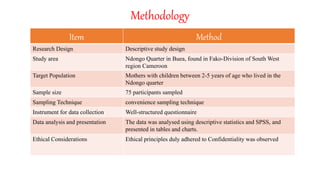
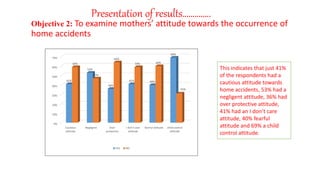
This document outlines a research project examining mothers' knowledge, attitudes, and prevention of home accidents among toddlers aged 2-5 years old in the Ndongo community of Buea, Cameroon. The study had three objectives: 1) determine mothers' knowledge of home accidents, 2) examine mothers' attitudes towards accidents, and 3) identify prevention measures used. A survey of 75 mothers found good knowledge of accident causes but negligent attitudes in some. Common prevention measures included supervision, safety precautions, and moving hazards. However, many mothers did not receive accident sensitization. The study recommends increased counseling from healthcare professionals to improve prevention strategies and attitudes towards reducing child accidents.