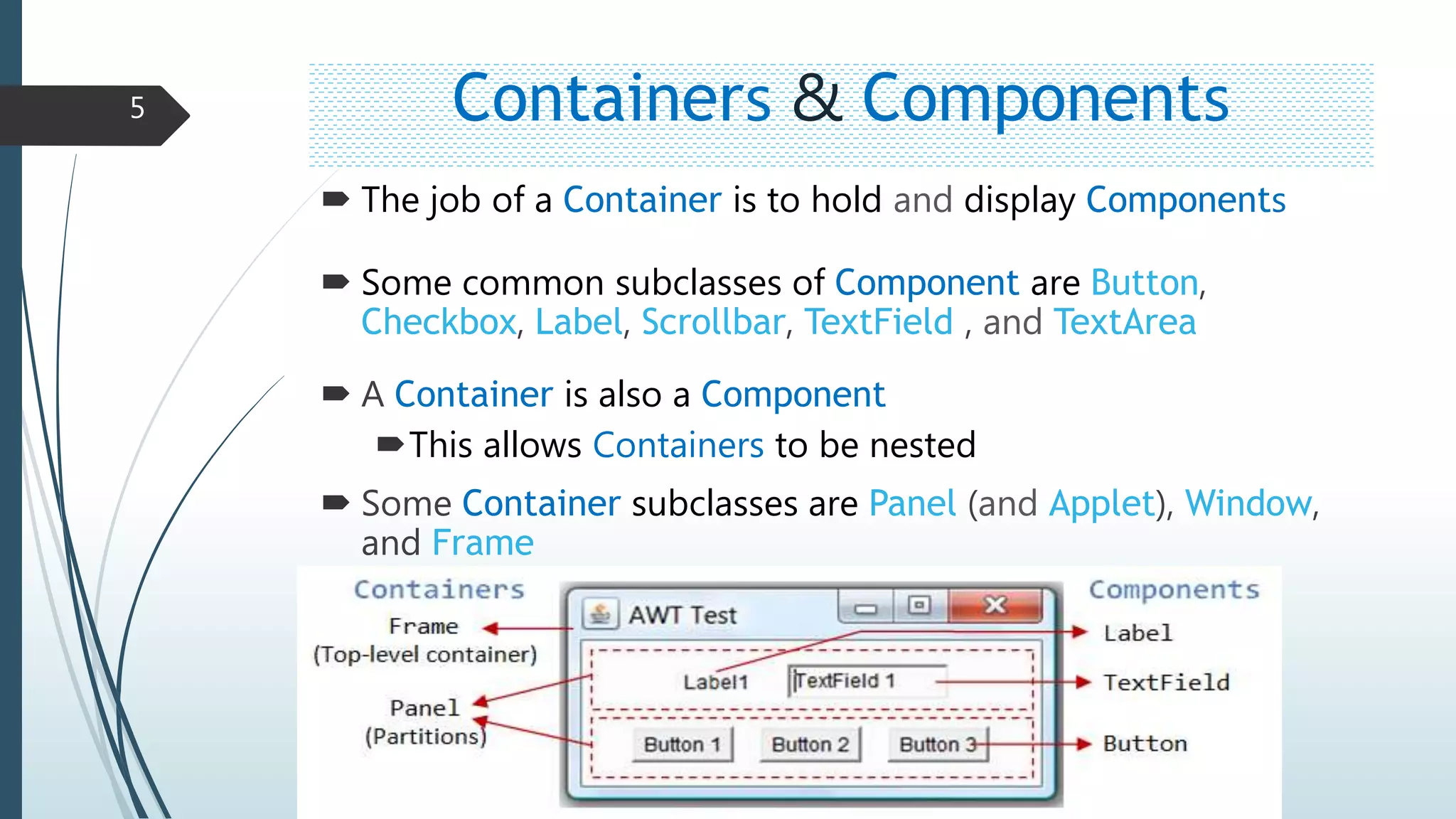
The AWT package provides basic graphics tools for Java applications. It contains classes like Container, Component, Button, Label, etc. that allow creating and managing GUI elements. Containers can hold and display Components. Components are user interface elements like buttons and text fields. Containers are also Components, allowing nesting. The example code creates a Frame container with a Panel child container holding a Label, TextField, and Button component.





![Example…..
import java.awt.*;
public class Test extends Frame {
public void test() {
Frame frame=new Frame("My Frame");
Button button=new Button("Button");
Label label=new Label("Simple Test");
TextField textfield=new TextField(20);
Panel panel=new Panel();
panel.add(label);
panel.add(textfield);
panel.add(button);
frame.add(panel);
frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
frame.setSize(400,300);
frame.setVisible(true); }
public static void main(String args[]) {
Test t=new Test();
t.test();
}
}
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05-171213182337/75/AWT-Packages-Containers-and-Components-8-2048.jpg)