The document summarizes new Russian laws regarding the processing and storage of personal data of Russian citizens. Key points include:
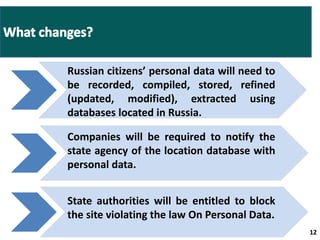
- From January 1, 2015, all personal data of Russian citizens must be stored on databases located in Russia, with some exceptions.
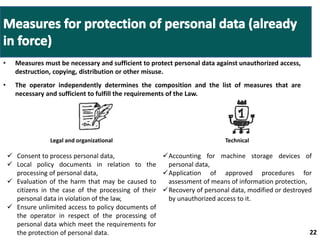
- The law broadly defines personal data in a manner similar to the EU's definition. Personal data includes any information that can directly or indirectly identify an individual.
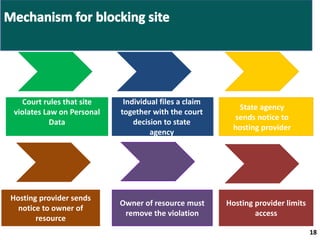
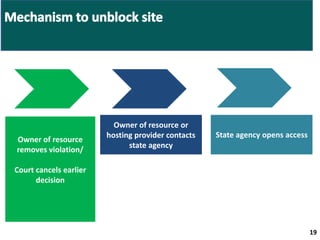
- Companies will need to notify authorities of the location of databases storing personal data and could face fines or blocking of websites for non-compliance.
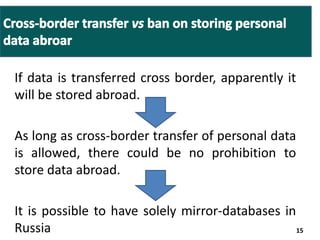
- There is debate around whether some personal data can still be stored abroad if it is also stored in Russia, or if all personal data of Russian citizens