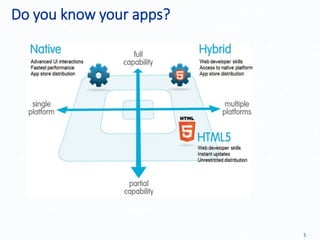
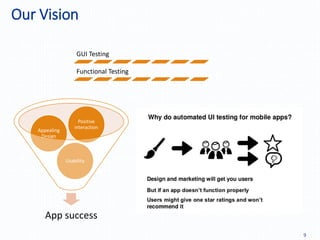
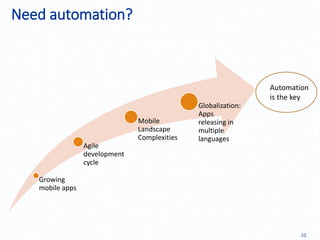
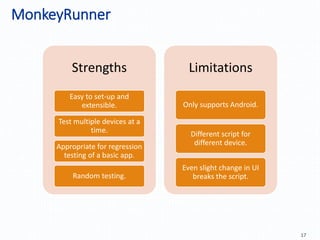
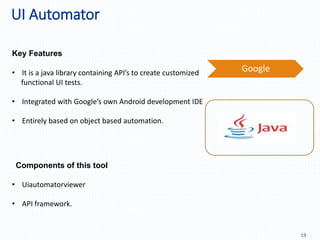
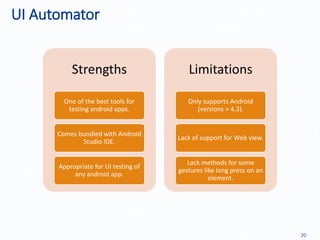
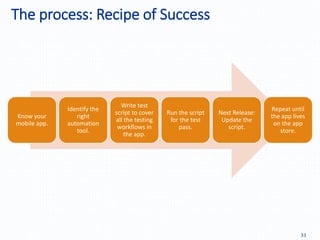
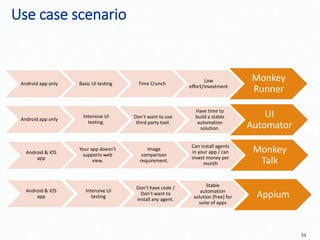
Automation testing of mobile apps is becoming increasingly important due to the growing number of apps and agile development cycles. The presentation compares automation testing solutions and tools for mobile apps. It evaluates MonkeyRunner, UI Automator, MonkeyTalk and Appium based on criteria like platform support, ease of use, and effectiveness. The best tool depends on factors like whether the app has web views, budget, and testing requirements. Following a defined process including identifying the right tool, writing test cases, and updating scripts for new releases can help ensure testing success.