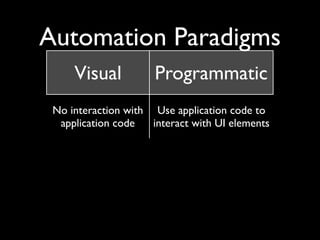
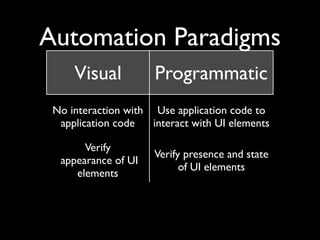
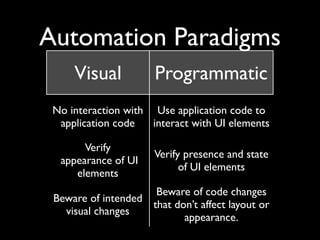
This document provides an overview of automated testing tools for mobile user interfaces. It discusses two main paradigms for automation: visual testing, which verifies the appearance of UI elements without interacting with application code, and programmatic testing, which uses application code to interact with and verify UI elements. The document cautions that both approaches need to account for intended visual changes and code changes that don't affect layout or appearance. It also addresses questions around testing on physical devices and considerations like device integration, platform support, and compatibility with continuous integration processes.