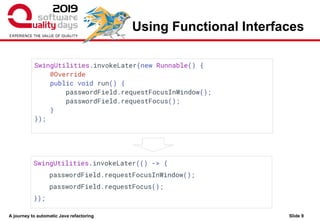
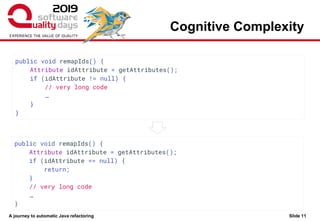
The document discusses the journey towards automatic Java refactoring, emphasizing the importance of refactoring for improving code quality, maintainability, and performance. It highlights typical problems in existing code, the human approach to refactoring, and the role of automated tools like Jsparrow, addressing technical debt and enhancing developer efficiency. The presentation concludes with the benefits and challenges of implementing automatic refactoring tools within the development process.