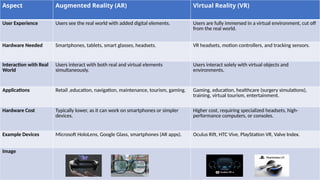
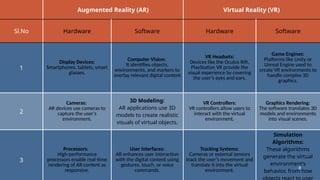
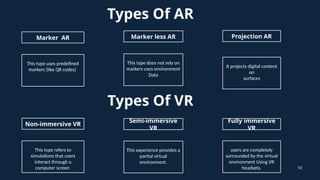
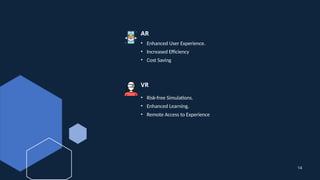
The document discusses augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), outlining their definitions, core components, types, applications, and benefits. AR overlays digital content onto the real world, enhancing user interaction, while VR immerses users in a simulated environment, allowing for complete engagement. Both technologies have various applications across industries such as gaming, education, healthcare, and retail, each with different hardware and software requirements.