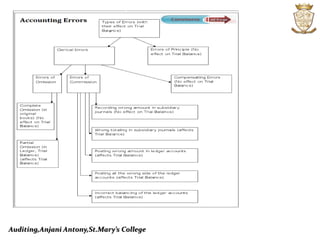
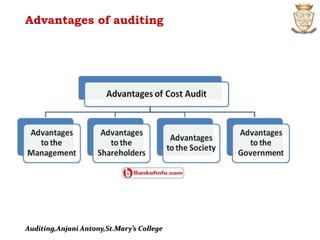
This document discusses the introduction, objectives, and advantages of auditing. It covers the history of auditing from double-entry bookkeeping to modern practices. The objectives of auditing are to verify the accuracy of financial statements and detect errors and fraud. Auditing ensures the primary objective of reporting accurate financial information to management and compliance with laws. It also aims to detect and prevent errors, frauds, and false representations in financial records through systematic examination of books and accounts.