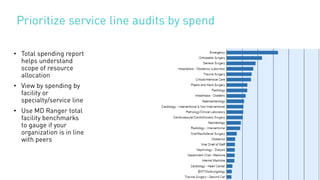
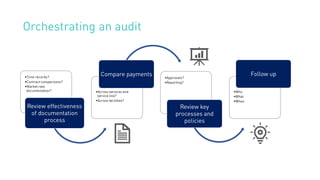
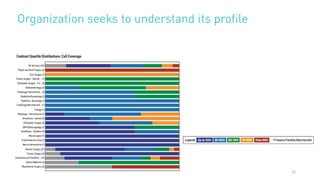
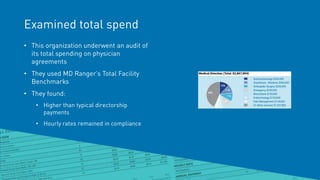
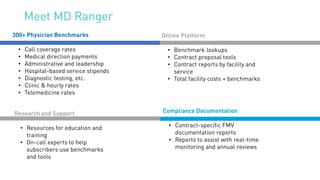
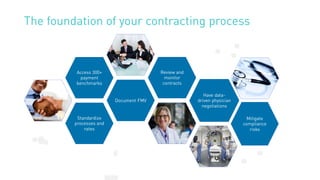
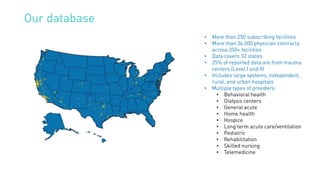
The document summarizes key points from an MD Ranger webinar on auditing physician contracts effectively. It discusses the importance of audits to ensure compliance with regulations and align contracts with organizational goals. It provides tips for planning audits such as checking processes, knowing resources, and prioritizing high spend service lines. An example is given where total spend analysis in MD Ranger uncovered higher than typical directorship payments. The document also introduces MD Ranger as a platform providing over 300 physician payment benchmarks and tools to standardize processes, document fair market value, review contracts, and mitigate compliance risks.