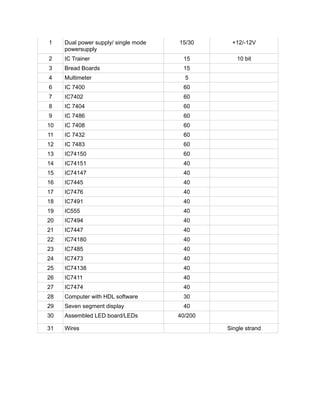
This document outlines the objectives and topics covered in a course on signals and systems. The course aims to study continuous and discrete signals and systems. Key topics covered include classification of continuous and discrete time signals, analysis of continuous and discrete time signals using Fourier transforms and z-transforms, and analysis of linear time-invariant continuous and discrete time systems. The document also lists two textbooks and references for the course.