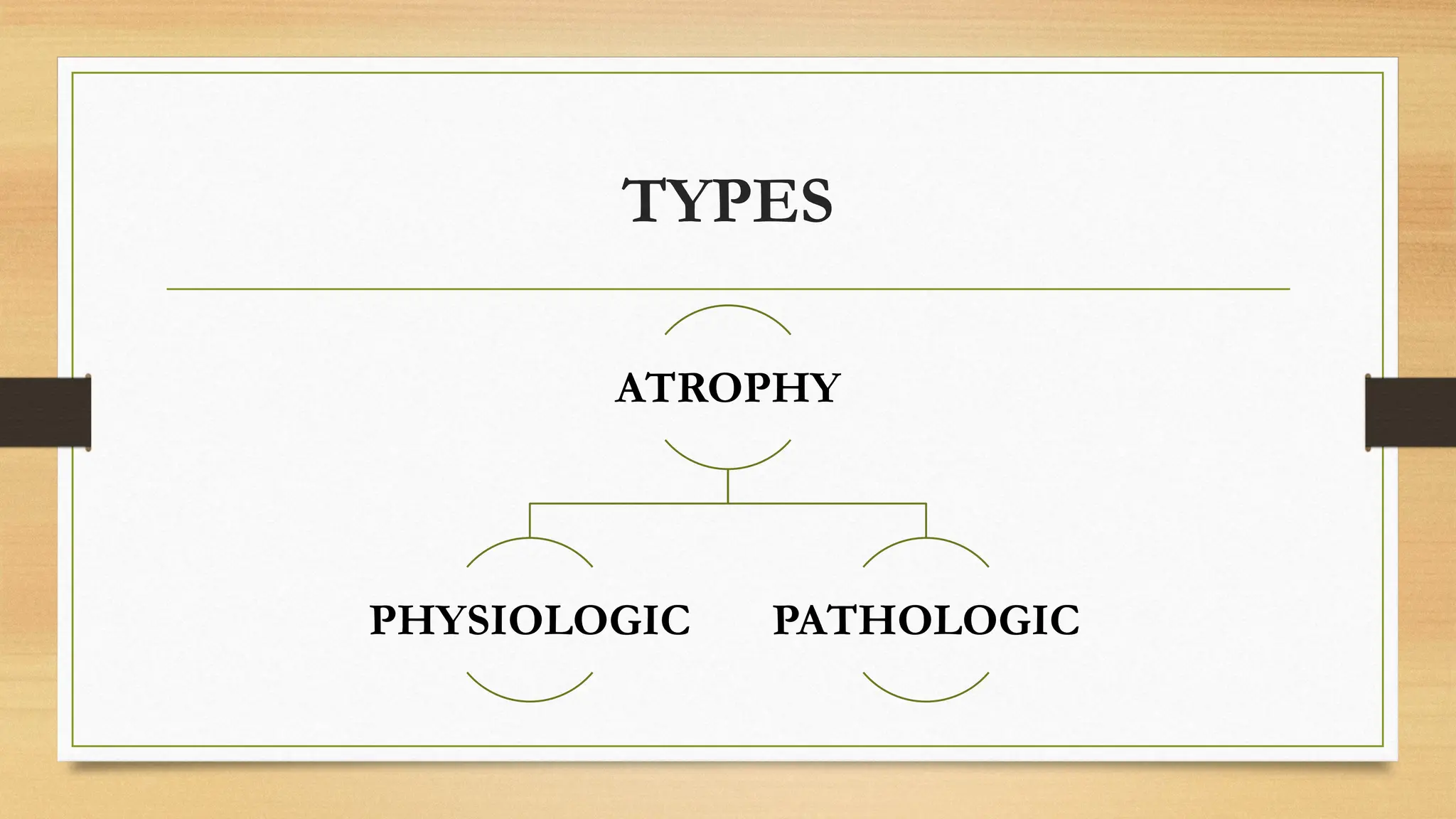
Atrophy is defined as the shrinkage of cell size due to loss of cell substance, which can affect entire tissues or organs without causing cell death. It can be classified as physiologic, such as uterine shrinkage post-childbirth, or pathologic, caused by factors including decreased workload and inadequate nutrition. The underlying mechanisms of atrophy involve decreased protein synthesis, increased protein degradation via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, and autophagy, which allows cells to survive by consuming their own organelles.