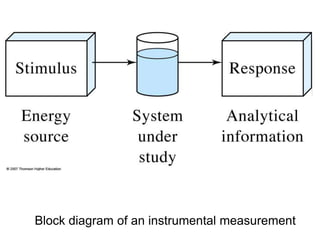
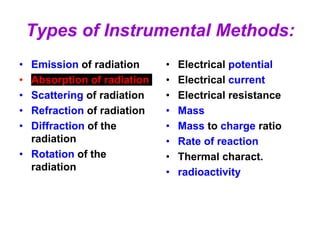
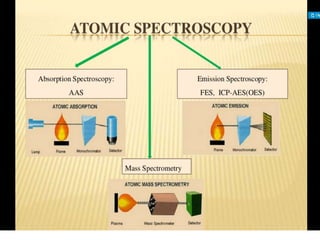
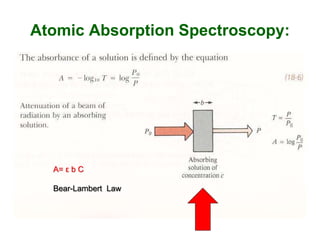
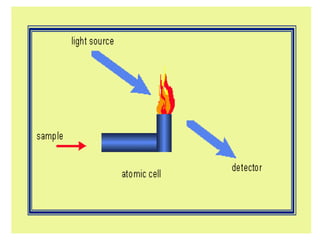
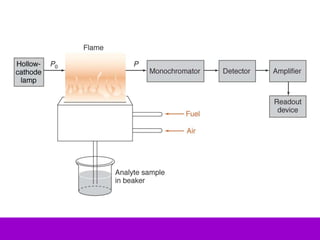
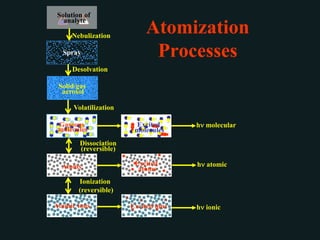
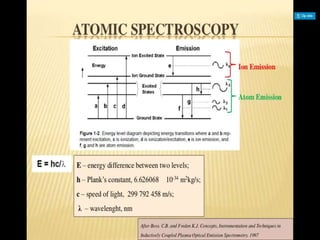
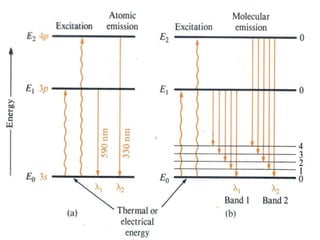
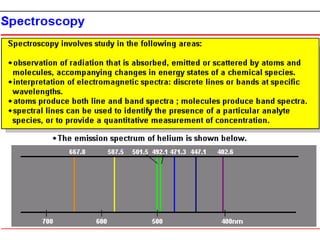
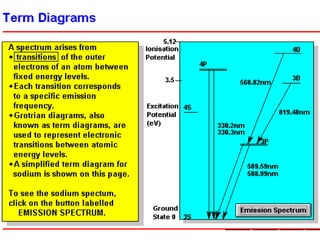
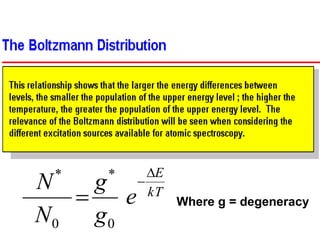
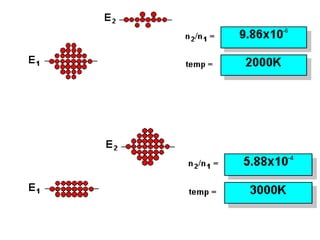
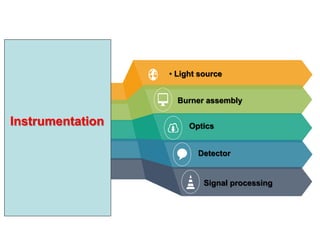
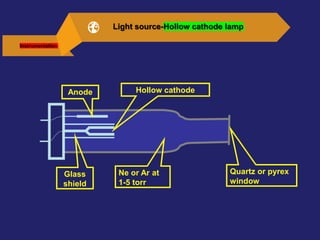
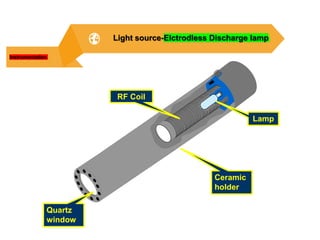
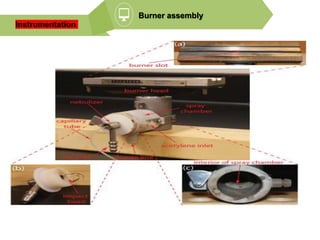
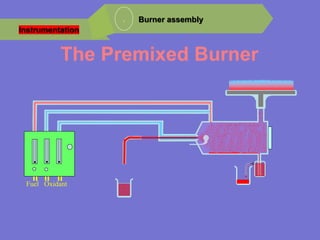
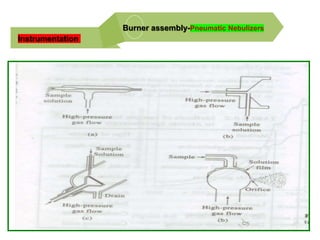
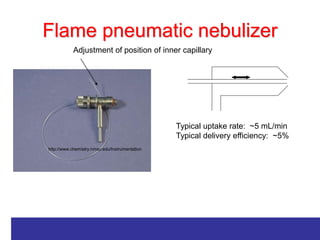
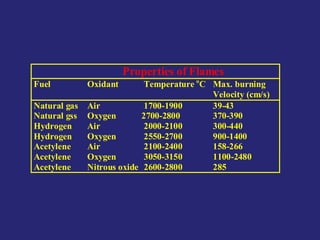
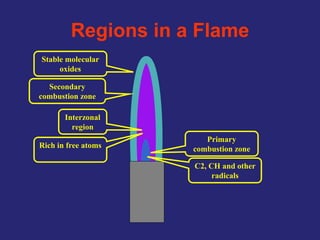
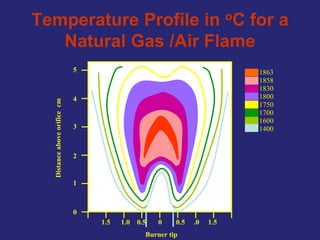
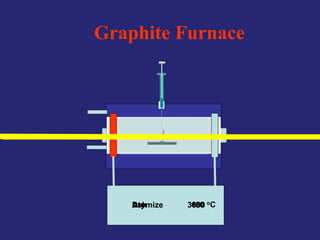
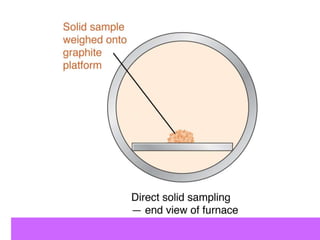
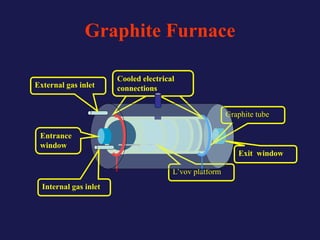
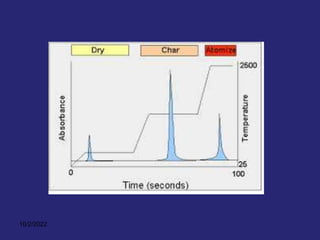
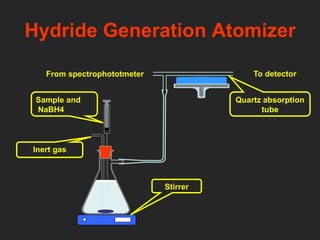
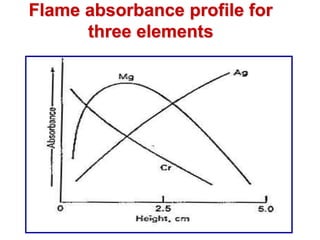
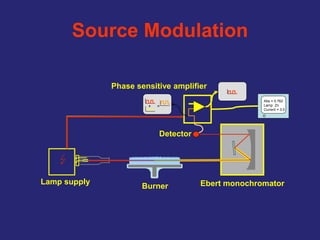
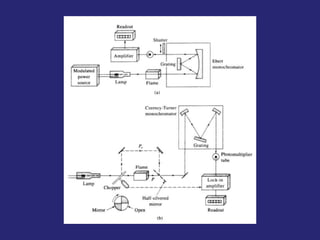
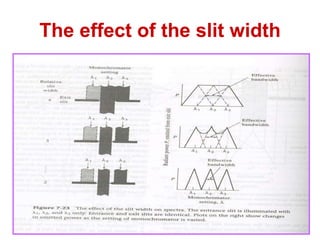
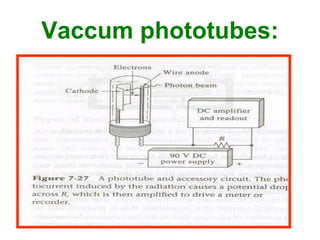
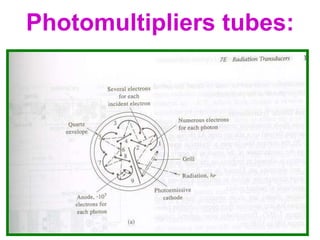
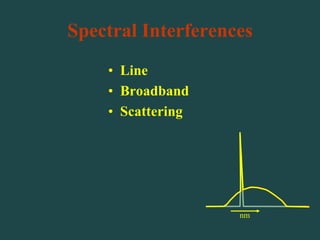
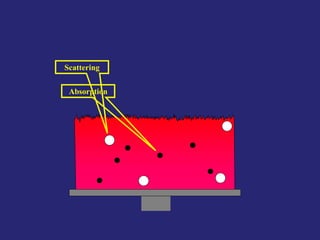
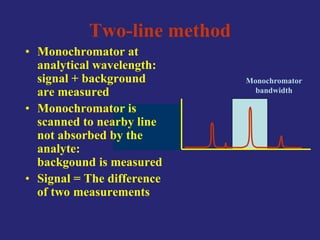
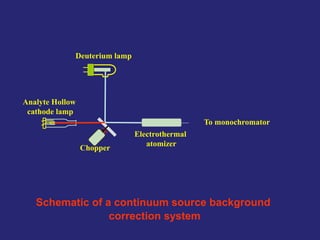
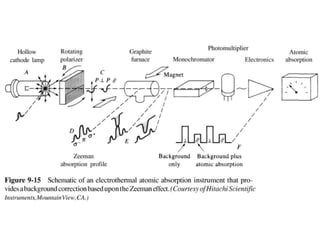
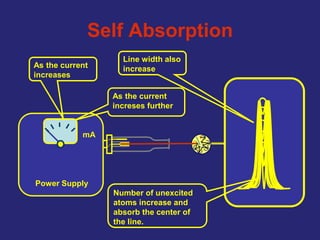
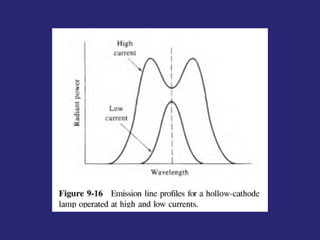
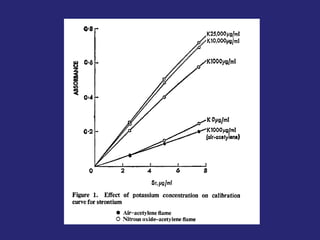
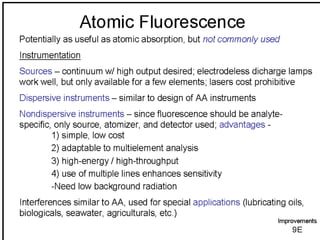
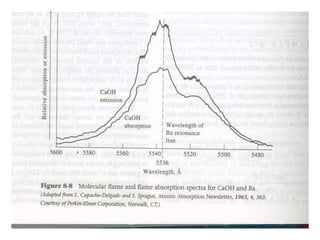
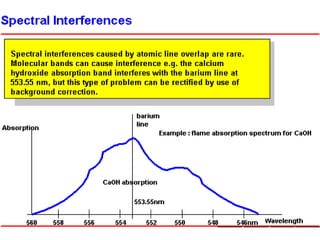
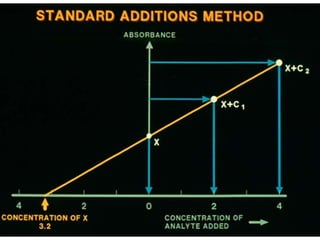
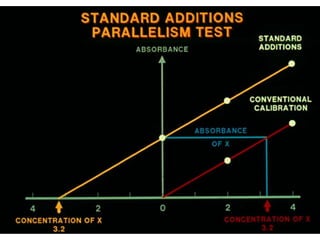
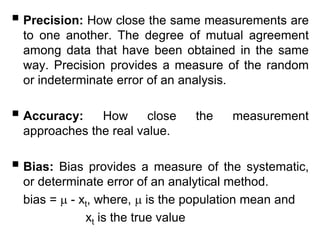
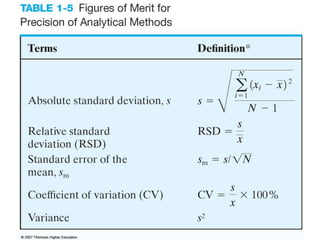
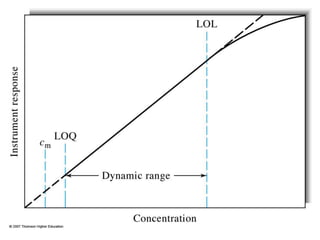
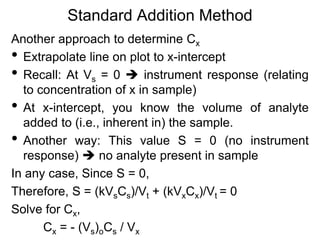
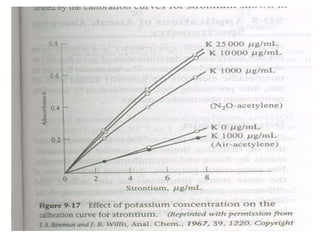
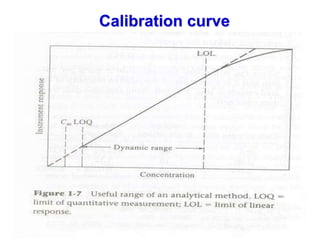
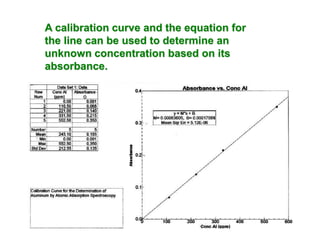
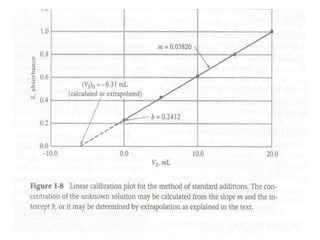
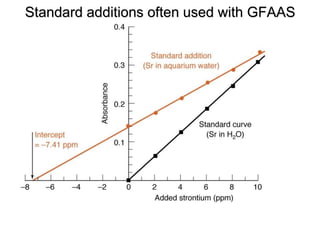
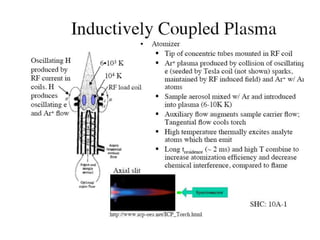
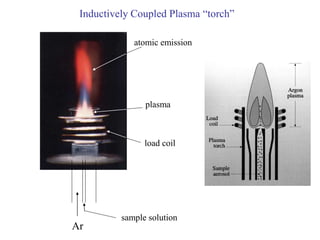
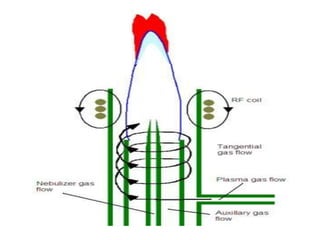
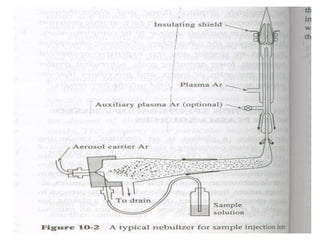
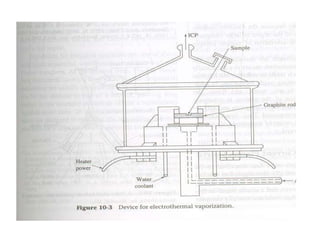
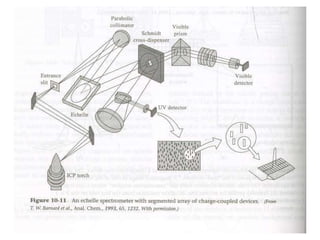
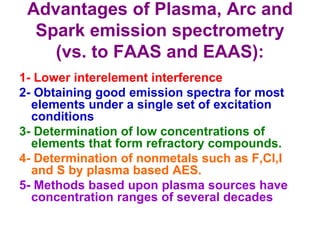
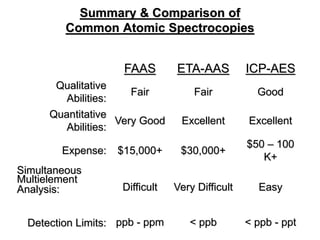
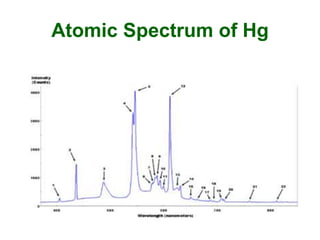
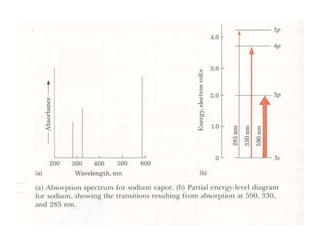
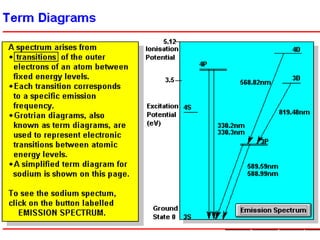
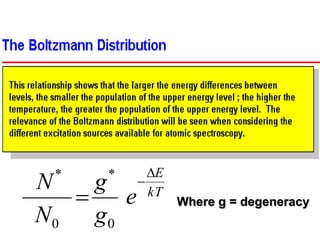
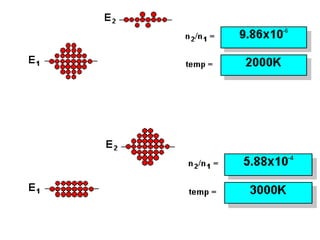
Analytical chemistry deals with qualitative and quantitative analysis of samples. Qualitative analysis identifies analytes while quantitative analysis determines exact amounts. Instrumental methods use instrumentation to make analytical measurements and are preferred over classical wet chemistry methods. Spectroscopy, chromatography, and electrochemistry are common instrumental techniques. Proper method selection considers accuracy needed, sample amount, concentration range, interferences, and cost. Interferences include spectral and chemical effects that must be addressed to obtain accurate results.