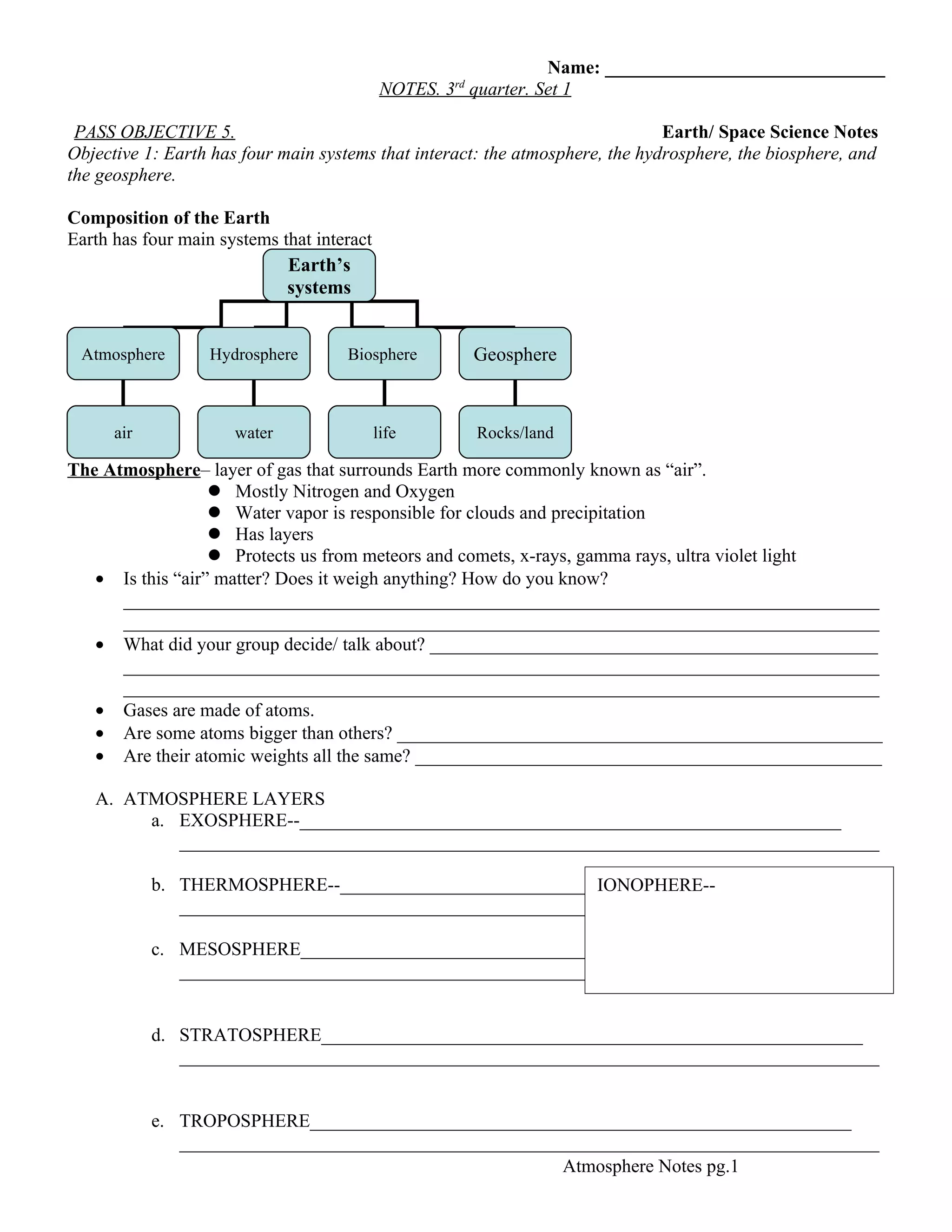
This document contains notes about Earth's four main systems - the atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and geosphere. It focuses on describing the layers and composition of the atmosphere. The notes define the troposphere and discuss factors that influence weather like temperature, air pressure, humidity, and dewpoint. Other atmospheric layers are also mentioned but not described.