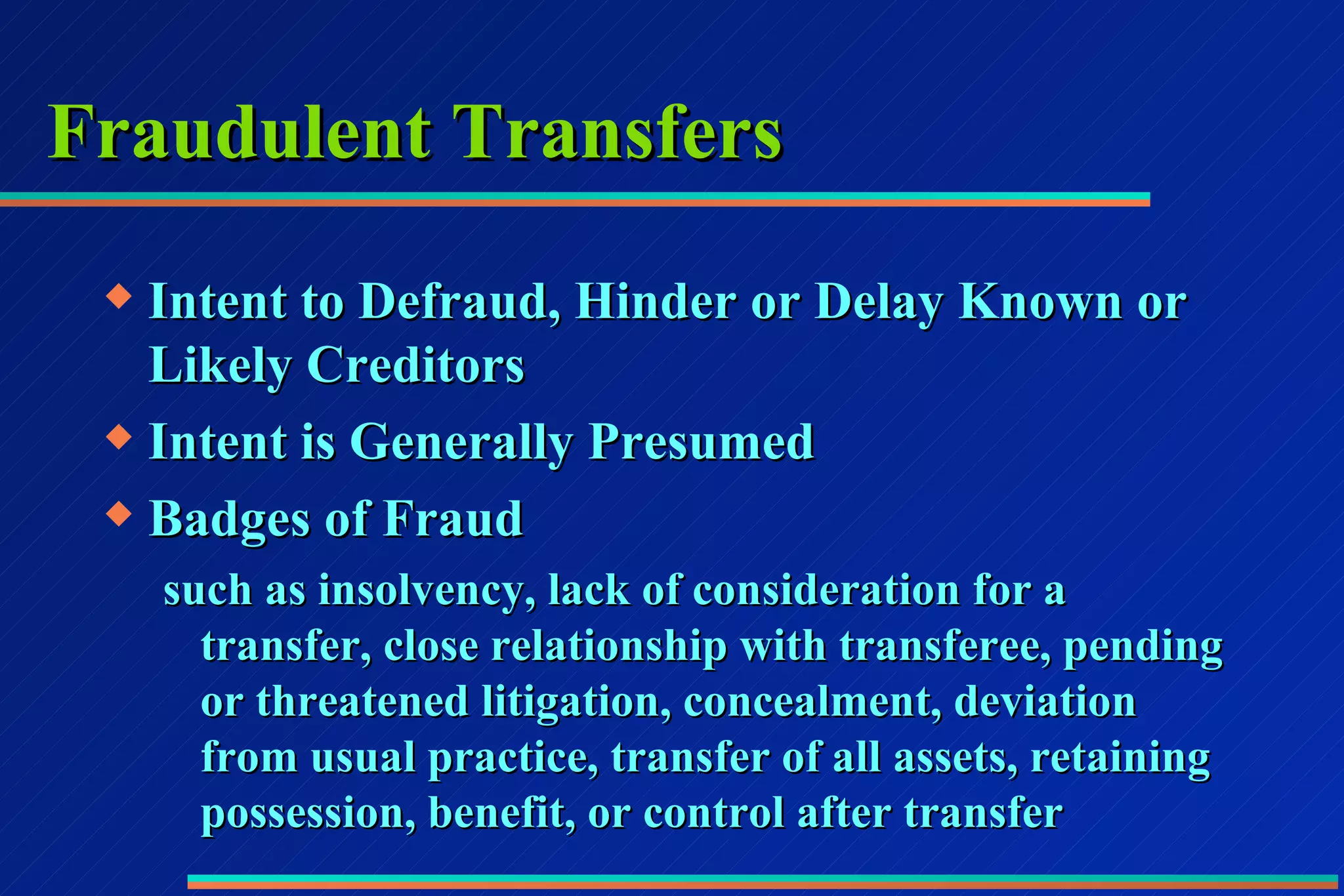
This document discusses various estate planning and asset protection strategies, including:
1) Using corporations or LLCs to obtain liability protection while maintaining control over assets.
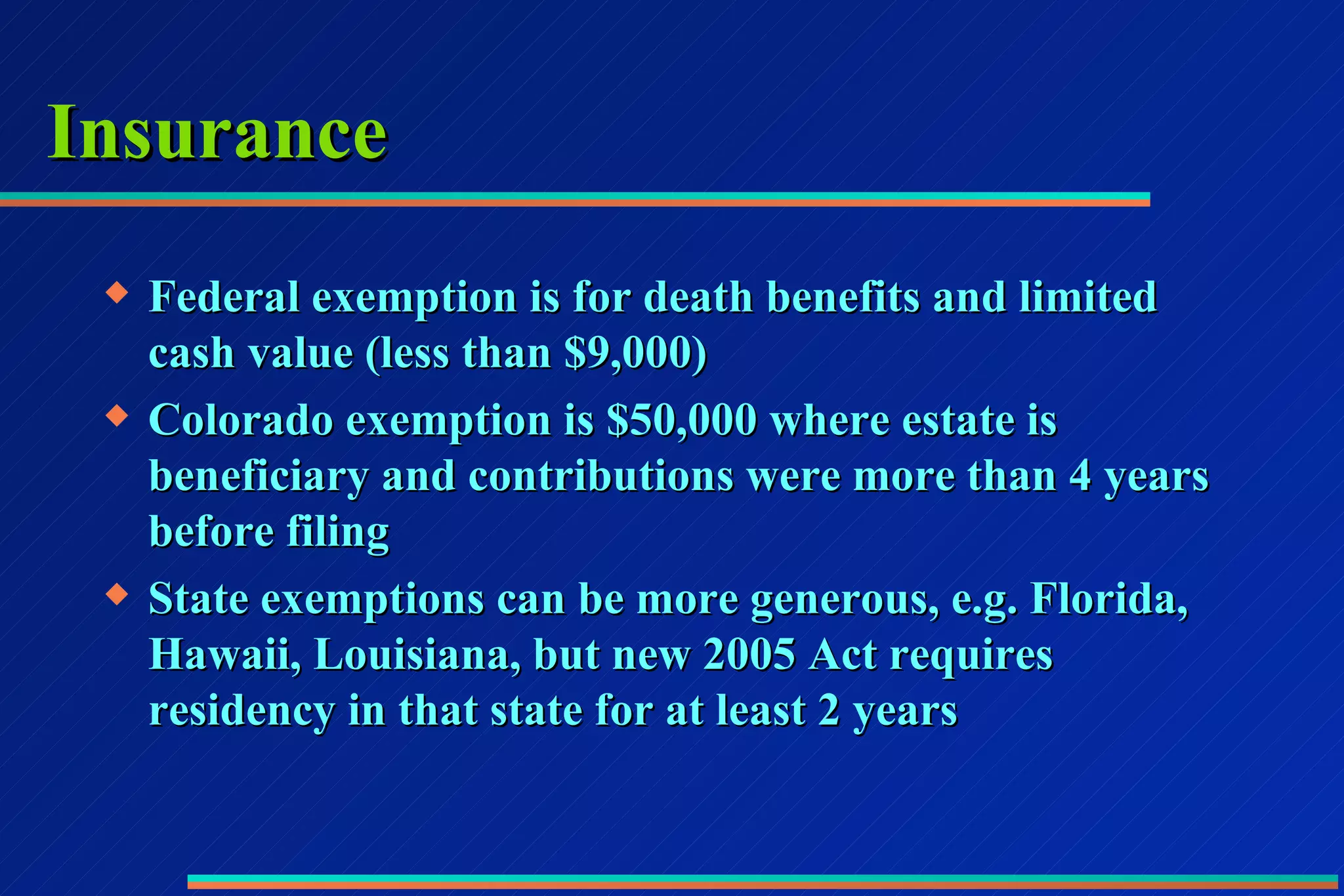
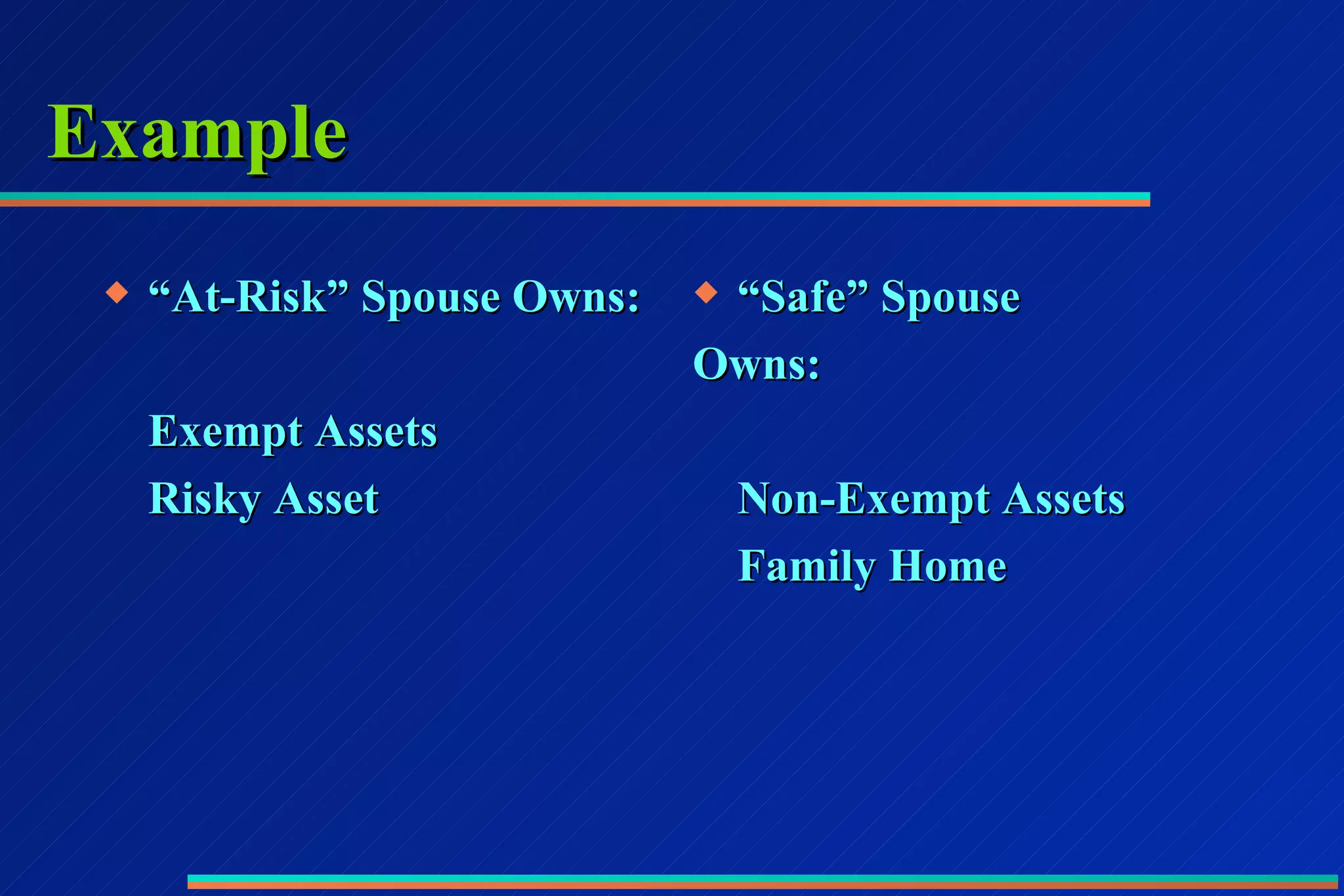
2) Protecting exempt assets like homes and retirement accounts which have protections under state law.
3) Establishing revocable living trusts to avoid probate and allow control over assets if incapacitated.
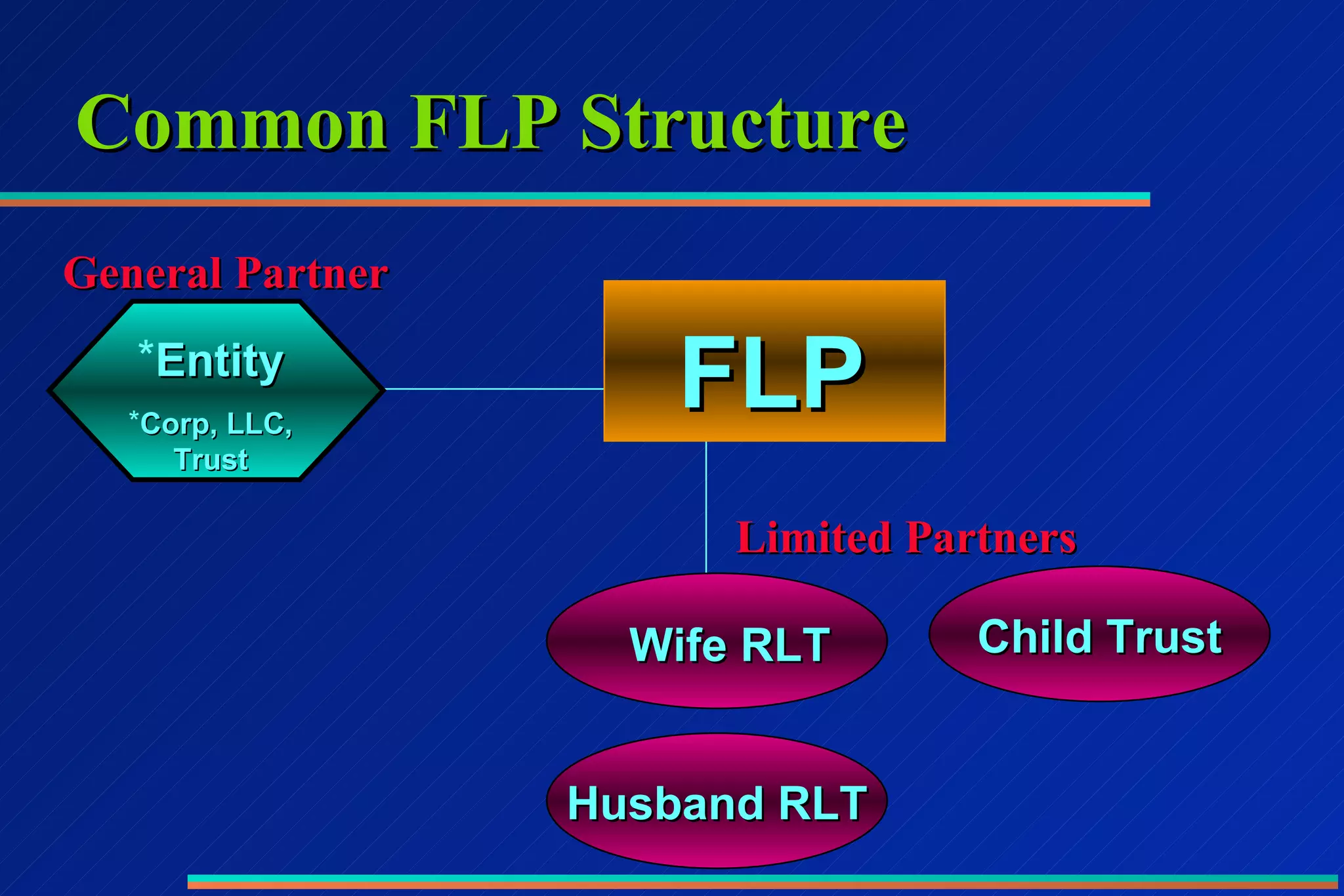
4) Using property agreements, family limited partnerships (FLPs), and irrevocable trusts to partition assets between family members and take advantage of discounts and creditor protections.
5) Considering domestic and offshore asset protection trusts to further shield assets from lawsuits under favorable jurisdictions. Proper planning requires a customized approach.